Abstract
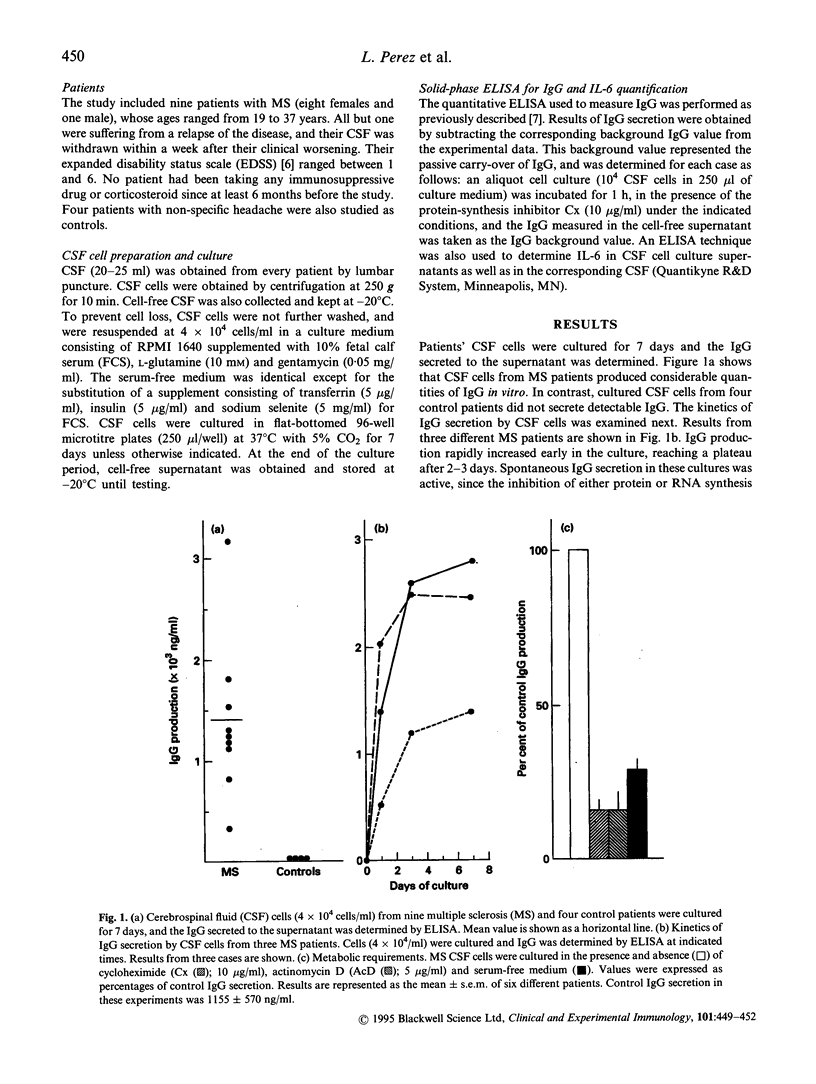
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from multiple sclerosis (MS) patients contains B cells capable of spontaneous IgG secretion in vitro. This study analyses the function and regulation of these cells. CSF cells obtained from nine MS patients actively produced IgG during 2-3 days in culture, and the activity decreased when CSF cells were cultured in serum-free medium. CSF cells from four controls did not secrete detectable IgG in vitro. Further experiments revealed that IL-6 played a role on MS CSF IgG-secreting cells, as can be deduced from the following findings: (i) the addition of exogenous IL-6, but not of other cytokines, to serum-free cultures restored missing CSF cell IgG secretion (ii) the inclusion of anti-IL-6, but not of control, blocking MoAb reduced IgG secretion by CSF cells in fetal calf serum (FCS)-containing cultures; and (iii) CSF cells were capable of active IL-6 production in the presence of FCS. These results suggest that endogenous IL-6 production by MS CSF cells seems to be responsible for inducing CSF IgG-secreting B cells to reach terminal differentiation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brieva J. A., Martin R. A., Martinez-Maza O., Kagan J., Merrill J., Saxon A., Van Damme J., Stevens R. H. Interleukin 6 is essential for antibody secretion by human in vivo antigen-induced lymphoblastoid B cells. Cell Immunol. 1990 Oct 15;130(2):303–310. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90273-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brieva J. A., Roldán E., Rodríguez C., Navas G. Human tonsil, blood and bone marrow in vivo-induced B cells capable of spontaneous and high-rate immunoglobulin secretion in vitro: differences in the requirements for factors and for adherent and bone marrow stromal cells, as well as distinctive adhesion molecule expression. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Feb;24(2):362–366. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ffrench-Constant C. Pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Lancet. 1994 Jan 29;343(8892):271–275. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksson A., Kam-Hansen S., Forsberg P., Grandien M. Cerebrospinal fluid lymphocytes from patients with multiple sclerosis do not increase immunoglobulin or measles antibody production after stimulation with pokeweed mitogen. J Neuroimmunol. 1986 Mar;11(1):15–30. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(86)90071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Akira S., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Biological and clinical aspects of interleukin 6. Immunol Today. 1990 Dec;11(12):443–449. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzke J. F. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology. 1983 Nov;33(11):1444–1452. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.11.1444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson T., Baig S., Höjeberg B., Link H. Antimyelin basic protein and antimyelin antibody-producing cells in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1990 Feb;27(2):132–136. doi: 10.1002/ana.410270207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez C., Roldán E., Navas G., Brieva J. A. Essential role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the differentiation of human tonsil in vivo induced B cells capable of spontaneous and high-rate immunoglobulin secretion. Eur J Immunol. 1993 May;23(5):1160–1164. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roldán E., Rodriguez C., Navas G., Parra C., Brieva J. A. Cytokine network regulating terminal maturation of human bone marrow B cells capable of spontaneous and high rate Ig secretion in vitro. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 1;149(7):2367–2371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


