Abstract
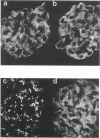
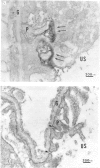
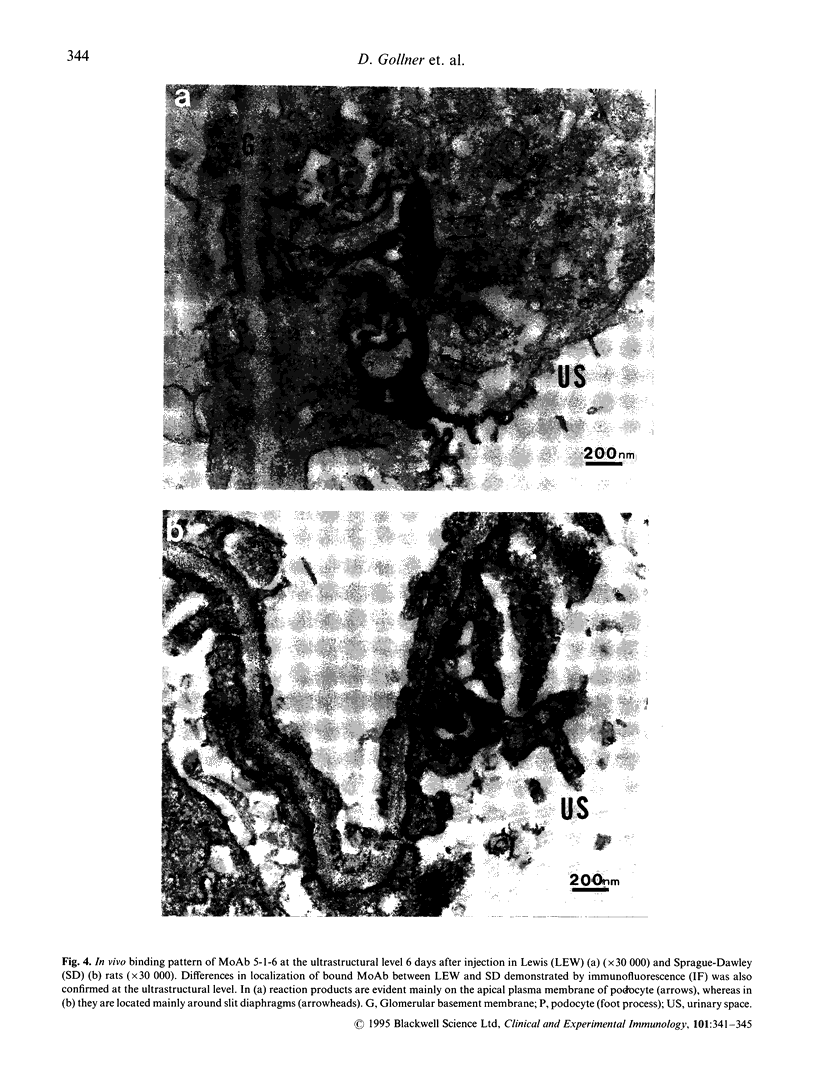
Susceptibility to the development of MoAb 5-1-6-induced proteinuria was investigated in four different rat strains, i.e. Brown-Norway (BN), Lewis (LEW), Sprague-Dawley (SD) and Wistar. An intravenous injection of 5 mg of MoAb 5-1-6 to female 7-week-old rats of a given strain induced massive proteinuria in BN, LEW and Wistar rats. However, SD rats developed almost no proteinuria. A similar tendency was observed in the second experiment, in which the injected dose of MoAb was adjusted according to the body weight of each rat (3 mg/100 g body weight). Immunofluorescence (IF) and immunoelectron microscopy (IEM) revealed no differences between the binding patterns of the MoAbs to normal rat kidneys derived from each strain. Quantitative study using 125I-labelled MoAb showed that there was no significant difference in the amount of antibody bound to the kidney 1 h and 5 days after injection between two rat strains, LEW and SD. Localization of 5-1-6 in vivo and its kinetics were investigated. In IF a linear-like pattern along capillary walls was observed 2 h after injection in both LEW and SD strains. This linear-like pattern was shifted to a granular pattern in proteinuric LEW rats 6 days after injection, whereas it remained linear-like in non-proteinuric SD rats. IEM confirmed this difference in the localization of injected MoAb 6 days after injection to LEW and SD rats also at the ultrastructural level. We conclude that there is a clear-cut strain difference in the development of proteinuria induced by MoAb 5-1-6. SD rats were less susceptible to MoAb-induced glomerular injury than BN, LEW and Wistar rats. Although the exact reason for strain variation in susceptibility to MoAb-induced proteinuria remains to be clarified, the movement of bound MoAb, presumably together with corresponding antigenic molecule along the glomerular epithelial cell surface followed by endocytosis into the epithelial cell, seems to be closely related to the induction of proteinuria.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kawachi H., Matsui K., Orikasa M., Morioka T., Oite T., Shimizu F. Quantitative studies of monoclonal antibody 5-1-6-induced proteinuric state in rats. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Feb;87(2):215–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb02977.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narisawa M., Kawachi H., Oite T., Shimizu F. Divalency of the monoclonal antibody 5-1-6 is required for induction of proteinuria in rats. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Jun;92(3):522–526. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb03431.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okasora T., Nagase M., Kawachi H., Matsui K., Orikasa M., Morioka T., Yamazaki I., Oite T., Shimizu F. Altered localization of antigen recognized by proteinuria-inducing monoclonal antibody in experimental nephrosis. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1991;60(1):41–46. doi: 10.1007/BF02899526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orikasa M., Matsui K., Oite T., Shimizu F. Massive proteinuria induced in rats by a single intravenous injection of a monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):807–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takashima N., Kawachi H., Oite T., Nishi S., Arakawa M., Shimizu F. Effect of chlorpromazine on kinetics of injected monoclonal antibody in MoAb-induced glomerular injury. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Jan;91(1):135–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb03368.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]