Abstract
The underlying immunopathogenic mechanism of CVID has been suspected to involve a chronic viral infection or an autoimmune condition. However, formal proof of viral infection is lacking. Measurement of MxA-protein in leucocyte lysates is a sensitive test for evaluating the activation of the host's interferon system. Both viral infections and autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) strongly induce MxA-protein in peripheral leucocytes. We therefore examined 15 patients with longlasting hypogammaglobulinaemia for MxA-protein induction in vivo: 13 patients suffered from CVID, one from hyper-IgM syndrome, and one patient had chronic B lymphocytic leukaemia associated with immunoglobulin deficiency and chronic papilloma virus infection (condylomata accuminata). Only the latter patient exhibited a strong MxA-protein expression; two CVID patients were borderline positive, and the remaining 12 patients including the hyper-IgM syndrome were MxA-protein-negative. There was no relationship between MxA expression and low CD4/CD8 ratios or increased CD8/CD57+ T cell counts, although both conditions are often observed in CVID as well as in chronic viral infections. When exposed in vitro to interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha), peripheral blood leucocytes of four MxA-negative patients were capable of producing normal amounts of MxA-protein. Taken together, these results argue against a viral or autoimmune pathogenesis of CVID.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumert E., Wolff-Vorbeck G., Schlesier M., Peter H. H. Immunophenotypical alterations in a subset of patients with common variable immunodeficiency (CVID). Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Oct;90(1):25–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb05826.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
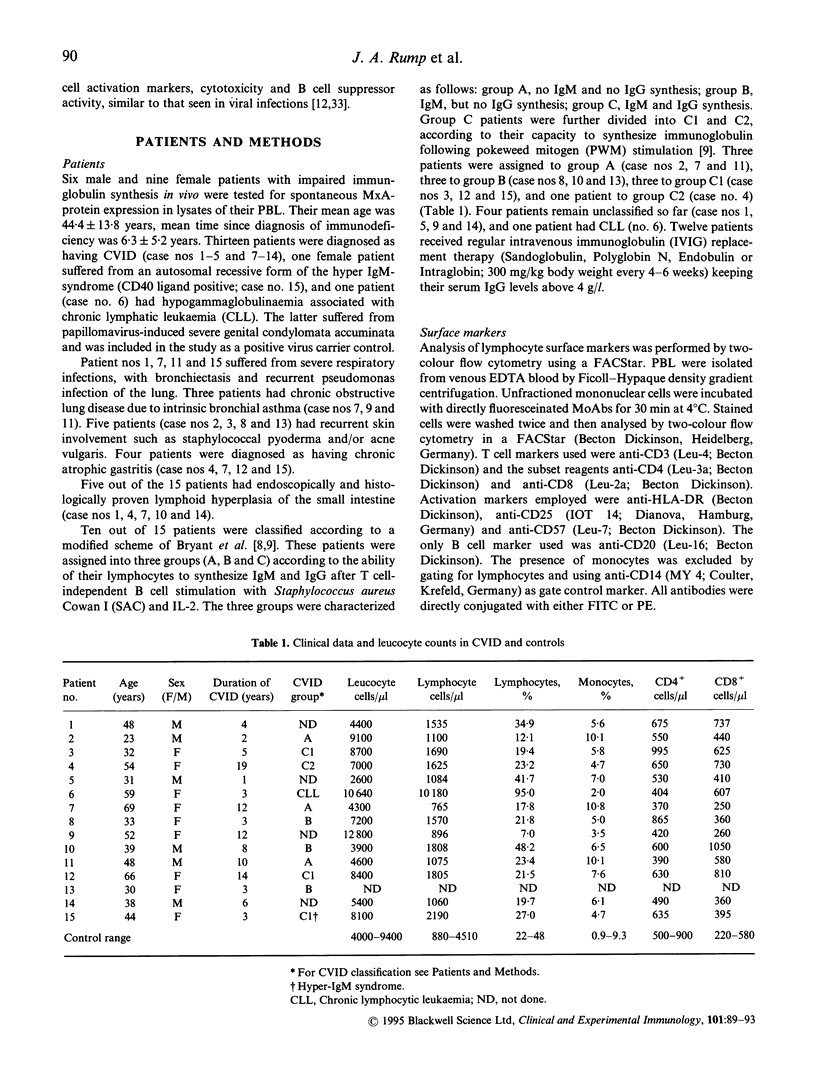
- Bryant A., Calver N. C., Toubi E., Webster A. D., Farrant J. Classification of patients with common variable immunodeficiency by B cell secretion of IgM and IgG in response to anti-IgM and interleukin-2. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 Aug;56(2):239–248. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(90)90145-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham-Rundles C. Clinical and immunologic analyses of 103 patients with common variable immunodeficiency. J Clin Immunol. 1989 Jan;9(1):22–33. doi: 10.1007/BF00917124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham-Rundles C., Lieberman P., Hellman G., Chaganti R. S. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma in common variable immunodeficiency. Am J Hematol. 1991 Jun;37(2):69–74. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830370202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döcke W. D., Simon H. U., Fietze E., Prösch S., Diener C., Reinke P., Stein H., Volk H. D. Cytomegalovirus infection and common variable immunodeficiency. Lancet. 1991 Dec 21;338(8782-8783):1597–1597. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92422-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
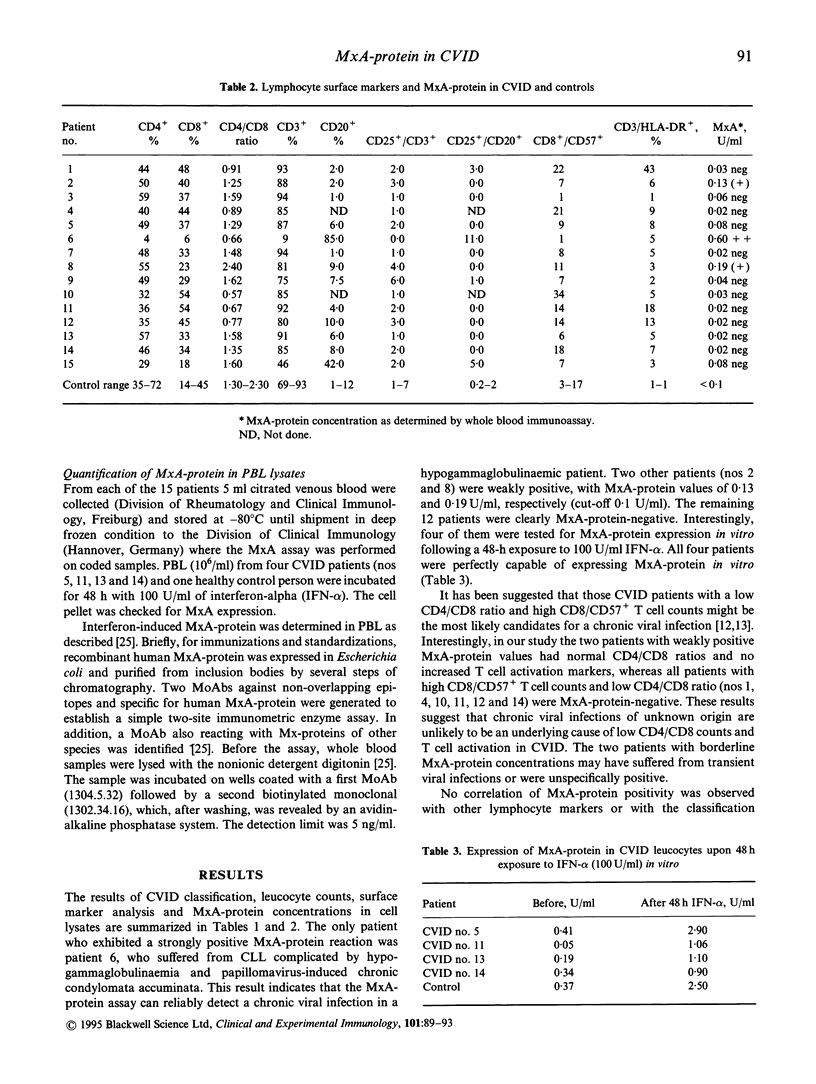
- Eisenstein E. M., Jaffe J. S., Strober W. Reduced interleukin-2 (IL-2) production in common variable immunodeficiency is due to a primary abnormality of CD4+ T cell differentiation. J Clin Immunol. 1993 Jul;13(4):247–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00919383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrington M., Grosmaire L. S., Nonoyama S., Fischer S. H., Hollenbaugh D., Ledbetter J. A., Noelle R. J., Aruffo A., Ochs H. D. CD40 ligand expression is defective in a subset of patients with common variable immunodeficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):1099–1103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer M. B., Hauber I., Vogel E., Wolf H. M., Mannhalter J. W., Eibl M. M. Defective interleukin-2 and interferon-gamma gene expression in response to antigen in a subgroup of patients with common variable immunodeficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1993 Aug;92(2):340–352. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(93)90178-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst E. W., Armbruster M., Rump J. A., Buscher H. P., Peter H. H. Intestinal B cell defects in common variable immunodeficiency. Clin Exp Immunol. 1994 Feb;95(2):215–221. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1994.tb06513.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe J. S., Strober W., Sneller M. C. Functional abnormalities of CD8+ T cells define a unique subset of patients with common variable immunodeficiency. Blood. 1993 Jul 1;82(1):192–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebranchu Y., Thibault G., Degenne D., Bardos P. Abnormalities in CD4+ T lymphocyte subsets in patients with common variable immunodeficiency. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Oct;61(1):83–92. doi: 10.1016/s0090-1229(06)80009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilssen D. E., Halstensen T. S., Frøland S. S., Fausa O., Brandtzaeg P. Distribution and phenotypes of duodenal intraepithelial gamma/delta T cells in patients with various types of primary B-cell deficiency. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1993 Sep;68(3):301–310. doi: 10.1006/clin.1993.1131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilssen D. E., Söderström R., Brandtzaeg P., Kett K., Helgeland L., Karlsson G., Söderström T., Hanson L. A. Isotype distribution of mucosal IgG-producing cells in patients with various IgG subclass deficiencies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jan;83(1):17–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05581.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastorelli G., Roncarolo M. G., Touraine J. L., Peronne G., Tovo P. A., de Vries J. E. Peripheral blood lymphocytes of patients with common variable immunodeficiency (CVI) produce reduced levels of interleukin-4, interleukin-2 and interferon-gamma, but proliferate normally upon activation by mitogens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Dec;78(3):334–340. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovic J., Haller O., Staeheli P. Human and mouse Mx proteins inhibit different steps of the influenza virus multiplication cycle. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2564–2569. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2564-2569.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovic J., Zürcher T., Haller O., Staeheli P. Resistance to influenza virus and vesicular stomatitis virus conferred by expression of human MxA protein. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3370–3375. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3370-3375.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roers A., Hochkeppel H. K., Horisberger M. A., Hovanessian A., Haller O. MxA gene expression after live virus vaccination: a sensitive marker for endogenous type I interferon. J Infect Dis. 1994 Apr;169(4):807–813. doi: 10.1093/infdis/169.4.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rump J. A., Jahreis A., Schlesier M., Dräger R., Melchers I., Peter H. H. Possible role of IL-2 deficiency for hypogammaglobulinaemia in patients with common variable immunodeficiency. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Aug;89(2):204–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06933.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sa'Adu A., Thomson B. J., Bountiff L., Webster A. D. Lymphotropic viruses in 'common variable' immunodeficiency--PCR analysis of lymphocyte DNA for HIV-1 and HHV-6. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Jan;91(1):50–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb03352.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon A., Fäh J., Haller O., Staeheli P. Interferon-regulated Mx genes are not responsive to interleukin-1, tumor necrosis factor, and other cytokines. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):968–971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.968-971.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spickett G. P., Farrant J. The role of lymphokines in common variable hypogammaglobulinemia. Immunol Today. 1989 Jun;10(6):192–194. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90323-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spickett G. P., Millrain M., Beattie R., North M., Griffiths J., Patterson S., Webster A. D. Role of retroviruses in acquired hypogammaglobulinaemia. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Nov;74(2):177–181. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Schmitz A., Jakschies D., Von Wussow P., Horisberger M. A. A whole blood immunoassay for the interferon-inducible human Mx protein. J Interferon Res. 1992 Apr;12(2):67–74. doi: 10.1089/jir.1992.12.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Broder S., Krakauer R., MacDermott R. P., Durm M., Goldman C., Meade B. The role of suppressor cells in the pathogenesis of common variable hypogammaglobulinemia and the immunodeficiency associated with myeloma. Fed Proc. 1976 Jul;35(9):2067–2072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster A. D., Dalgleish A. G., Malkovsky M., Beattie R., Patterson S., Asherson G. L., North M., Weiss R. A. Isolation of retroviruses from two patients with "common variable" hypogammaglobulinaemia. Lancet. 1986 Mar 15;1(8481):581–583. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92809-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bismarck U., Peest D., Dräger R., Serbin A., Schlesier M., Peter H. H. Terminale B-Zellreifung und Immunoglobulinsynthese in vitro bei primären und sekundären Immundefekten. Immun Infekt. 1984 Apr;12(2):75–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Wussow P., Jakschies D., Block B., Tschechne B., Schedel I., Horisberger M. A., Hochkeppel H. K., Deicher H. The interferon-induced Mx-homologous protein in people with symptomatic HIV-1 infection. AIDS. 1990 Feb;4(2):119–124. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199002000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Wussow P., Jakschies D., Hochkeppel H. K., Fibich C., Penner L., Deicher H. The human intracellular Mx-homologous protein is specifically induced by type I interferons. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Sep;20(9):2015–2019. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Wussow P., Jakschies D., Hochkeppel H., Horisberger M., Hartung K., Deicher H. MX homologous protein in mononuclear cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Jul;32(7):914–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


