Abstract
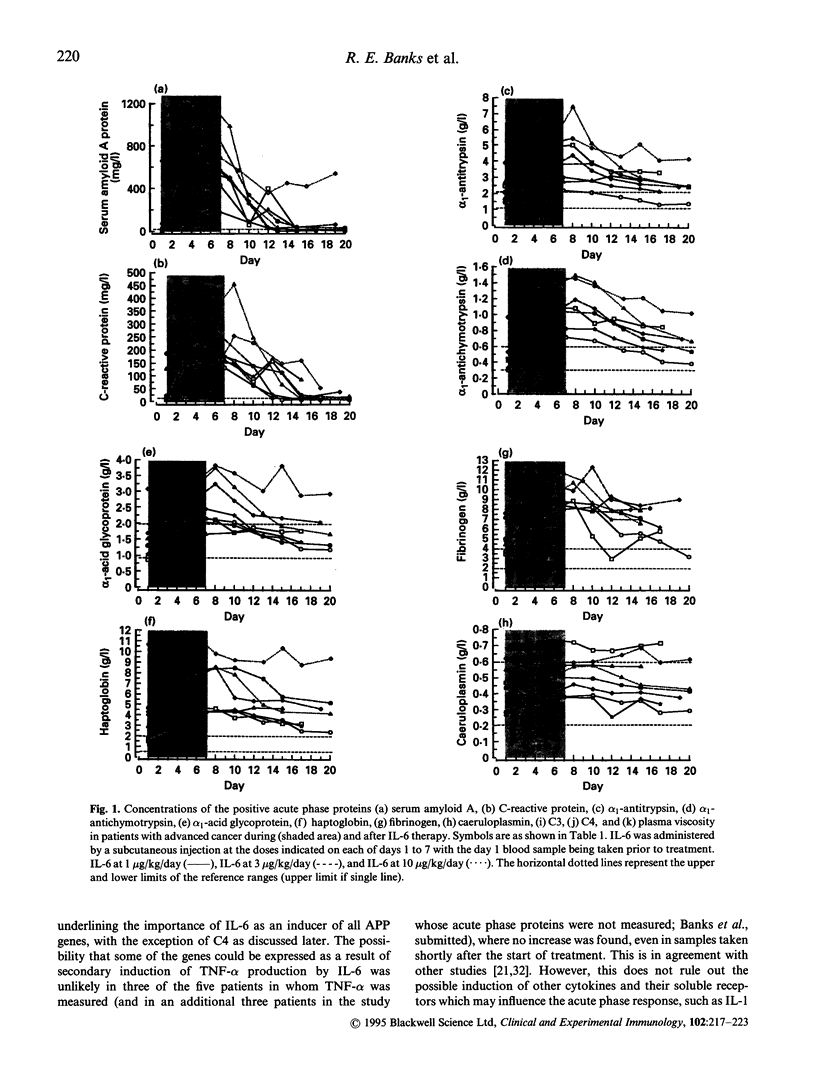
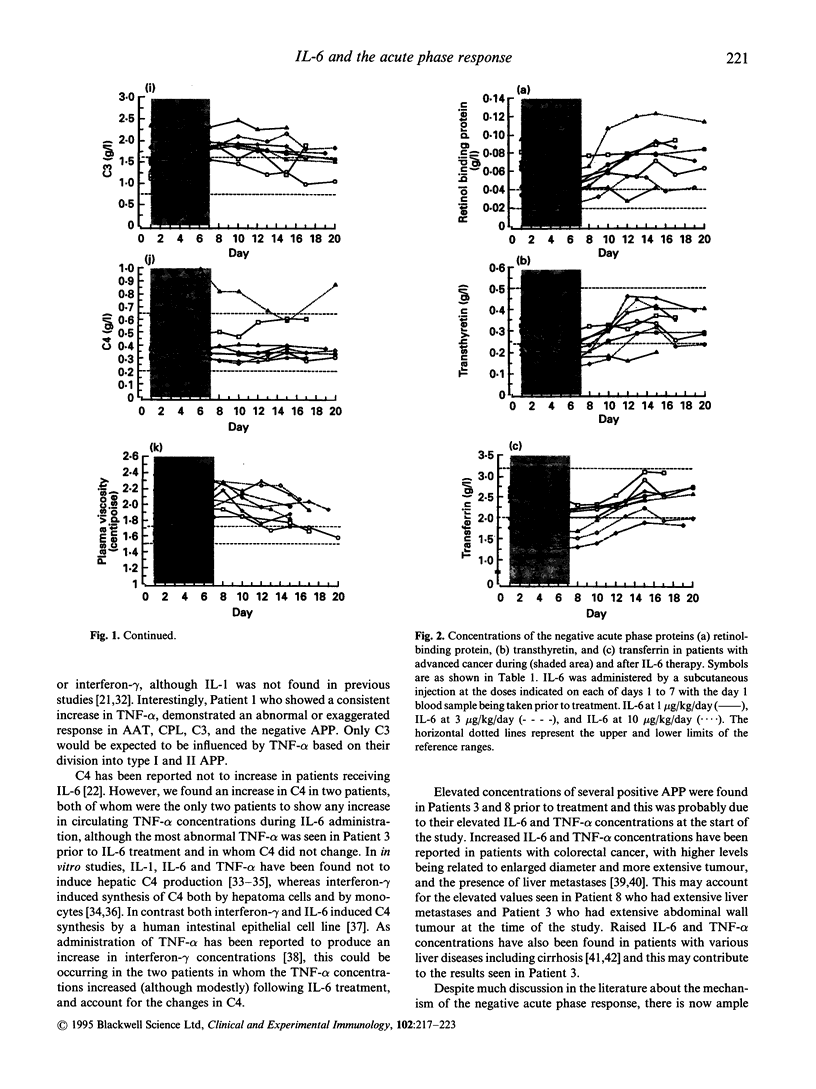
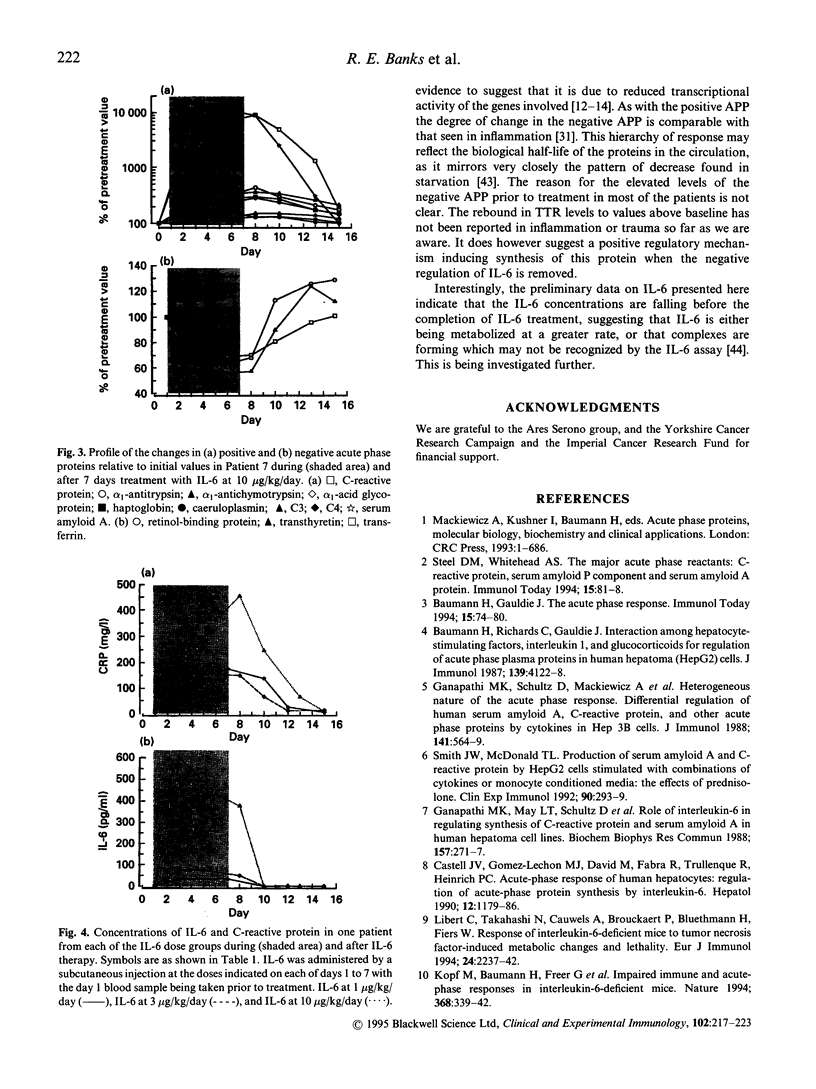
IL-6, tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and IL-1 are thought to be the key mediators of the acute phase response although much of the evidence is based on in vitro studies. It is not clear to what extent each of the acute phase proteins are regulated in vivo by each of these cytokines. The aim of this study was to examine the effects of IL-6 treatment in eight patients with cancer on the concentrations of an extensive range of positive and negative acute phase proteins. It was part of a larger investigation to assess the value of IL-6 in the management of chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia. IL-6 was administered by a daily subcutaneous injection for 7 days at a dose level of 1, 3, or 10 micrograms/kg/day. Increases in the positive acute phase proteins, serum amyloid A, C-reactive protein, alpha 1-acid glycoprotein, alpha 1-antichymotrypsin, haptoglobin, alpha 1-antitrypsin, fibrinogen, complement component C3, and caeruloplasmin, were observed, with the greatest incremental changes and fastest responses being seen for C-reactive protein and serum amyloid A protein. The negative acute phase proteins transferrin, transthyretin and retinol binding protein all fell to a nadir within 48-96 h after the first IL-6 injection. Increases in complement component C4 were only found in two patients, which may be related to the increase in circulating TNF-alpha concentrations found only in these patients. This study has therefore shown that IL-6 is capable of causing changes in the majority of acute phase proteins in vivo. Although secondary induction of TNF-alpha was not observed in the majority of patients examined, it is still possible however that other cytokines involved in regulation of the acute phase response, such as IL-1, may have been induced and contributed to the overall response.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andoh A., Fujiyama Y., Bamba T., Hosoda S. Differential cytokine regulation of complement C3, C4, and factor B synthesis in human intestinal epithelial cell line, Caco-2. J Immunol. 1993 Oct 15;151(8):4239–4247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronsen K. F., Ekelund G., Kindmark C. O., Laurell C. B. Sequential changes of plasma proteins after surgical trauma. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:127–136. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aulitzky W. E., Tilg H., Gastl G., Mull R., Flener R., Vogel W., Herold M., Berger M., Judmaier G., Huber C. Recombinant tumour necrosis factor alpha administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly for treatment of advanced malignant disease: a phase I trial. Eur J Cancer. 1991;27(4):462–467. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(91)90387-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartalena L., Farsetti A., Flink I. L., Robbins J. Effects of interleukin-6 on the expression of thyroid hormone-binding protein genes in cultured human hepatoblastoma-derived (Hep G2) cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Jun;6(6):935–942. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.6.1323058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Gauldie J. The acute phase response. Immunol Today. 1994 Feb;15(2):74–80. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90137-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Richards C., Gauldie J. Interaction among hepatocyte-stimulating factors, interleukin 1, and glucocorticoids for regulation of acute phase plasma proteins in human hepatoma (HepG2) cells. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4122–4128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. A., Buck M., Feitelberg S. P., Chojkier M. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibits albumin gene expression in a murine model of cachexia. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jan;85(1):248–255. doi: 10.1172/JCI114419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos S. P., Baumann H. Insulin is a prominent modulator of the cytokine-stimulated expression of acute-phase plasma protein genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1789–1797. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castell J. V., Gómez-Lechón M. J., David M., Fabra R., Trullenque R., Heinrich P. C. Acute-phase response of human hepatocytes: regulation of acute-phase protein synthesis by interleukin-6. Hepatology. 1990 Nov;12(5):1179–1186. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke B. M., Stuart J. Automated measurement of plasma viscosity by capillary viscometer. J Clin Pathol. 1988 Nov;41(11):1213–1216. doi: 10.1136/jcp.41.11.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falus A., Rokita H., Walcz E., Brozik M., Hidvégi T., Merétey K. Hormonal regulation of complement biosynthesis in human cell lines--II. Upregulation of the biosynthesis of complement components C3, factor B and C1 inhibitor by interleukin-6 and interleukin-1 in human hepatoma cell line. Mol Immunol. 1990 Feb;27(2):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(90)90115-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fattori E., Cappelletti M., Costa P., Sellitto C., Cantoni L., Carelli M., Faggioni R., Fantuzzi G., Ghezzi P., Poli V. Defective inflammatory response in interleukin 6-deficient mice. J Exp Med. 1994 Oct 1;180(4):1243–1250. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.4.1243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganapathi M. K., May L. T., Schultz D., Brabenec A., Weinstein J., Sehgal P. B., Kushner I. Role of interleukin-6 in regulating synthesis of C-reactive protein and serum amyloid A in human hepatoma cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 30;157(1):271–277. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganapathi M. K., Schultz D., Mackiewicz A., Samols D., Hu S. I., Brabenec A., Macintyre S. S., Kushner I. Heterogeneous nature of the acute phase response. Differential regulation of human serum amyloid A, C-reactive protein, and other acute phase proteins by cytokines in Hep 3B cells. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):564–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godenir N. L., Jeenah M. S., Coetzee G. A., Van der Westhuyzen D. R., Strachan A. F., De Beer F. C. Standardisation of the quantitation of serum amyloid A protein (SAA) in human serum. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Nov 7;83(2):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90243-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz Y., Guterman M., Lahat E. Regulation of synthesis of complement proteins in HEp2 cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1993 May;67(2):117–123. doi: 10.1006/clin.1993.1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopf M., Baumann H., Freer G., Freudenberg M., Lamers M., Kishimoto T., Zinkernagel R., Bluethmann H., Köhler G. Impaired immune and acute-phase responses in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Nature. 1994 Mar 24;368(6469):339–342. doi: 10.1038/368339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulics J., Colten H. R., Perlmutter D. H. Counterregulatory effects of interferon-gamma and endotoxin on expression of the human C4 genes. J Clin Invest. 1990 Mar;85(3):943–949. doi: 10.1172/JCI114523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libert C., Takahashi N., Cauwels A., Brouckaert P., Bluethmann H., Fiers W. Response of interleukin-6-deficient mice to tumor necrosis factor-induced metabolic changes and lethality. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Sep;24(9):2237–2242. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackiewicz A., Ganapathi M. K., Schultz D., Kushner I. Monokines regulate glycosylation of acute-phase proteins. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):253–258. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May L. T., Viguet H., Kenney J. S., Ida N., Allison A. C., Sehgal P. B. High levels of "complexed" interleukin-6 in human blood. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19698–19704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestries J. C., Kruithof E. K., Gascon M. P., Herodin F., Agay D., Ythier A. In vivo modulation of coagulation and fibrinolysis by recombinant glycosylated human interleukin-6 in baboons. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1994 May-Jun;5(3):275–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrone G., Cortese R., Sorrentino V. Post-transcriptional control of negative acute phase genes by transforming growth factor beta. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3767–3771. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08553.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordan R. P., Potter M. A macrophage-derived factor required by plasmacytomas for survival and proliferation in vitro. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):566–569. doi: 10.1126/science.3726549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numata A., Minagawa T., Asano M., Nakane A., Katoh H., Tanabe T. Functional evaluation of tumor-infiltrating mononuclear cells. Detection of endogenous interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human colorectal adenocarcinomas. Cancer. 1991 Nov 1;68(9):1937–1943. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19911101)68:9<1937::aid-cncr2820680916>3.0.co;2-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter D. H., Dinarello C. A., Punsal P. I., Colten H. R. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor regulates hepatic acute-phase gene expression. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1349–1354. doi: 10.1172/JCI112721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramadori G., Sipe J. D., Dinarello C. A., Mizel S. B., Colten H. R. Pretranslational modulation of acute phase hepatic protein synthesis by murine recombinant interleukin 1 (IL-1) and purified human IL-1. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):930–942. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynes J. G., McAdam K. P. Purification of serum amyloid A and other high density apolipoproteins by hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;173(1):116–124. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90168-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryffel B., Car B. D., Woerly G., Weber M., DiPadova F., Kammüller M., Klug S., Neubert R., Neubert D. Long-term interleukin-6 administration stimulates sustained thrombopoiesis and acute-phase protein synthesis in a small primate--the marmoset. Blood. 1994 Apr 15;83(8):2093–2102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid C., Young R., McDermott R., Fitzsimmons L., Scarffe J. H., Stern P. L. Immune function of patients receiving recombinant human interleukin-6 (IL-6) in a phase I clinical study: induction of C-reactive protein and IgE and inhibition of natural killer and lymphokine-activated killer cell activity. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1994 Feb;38(2):119–126. doi: 10.1007/BF01526207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheron N., Bird G., Goka J., Alexander G., Williams R. Elevated plasma interleukin-6 and increased severity and mortality in alcoholic hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jun;84(3):449–453. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiels B. R., Northemann W., Gehring M. R., Fey G. H. Modified nuclear processing of alpha 1-acid glycoprotein RNA during inflammation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12826–12831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., McDonald T. L. Production of serum amyloid A and C-reactive protein by HepG2 cells stimulated with combinations of cytokines or monocyte conditioned media: the effects of prednisolone. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Nov;90(2):293–299. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb07945.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel D. M., Rogers J. T., DeBeer M. C., DeBeer F. C., Whitehead A. S. Biosynthesis of human acute-phase serum amyloid A protein (A-SAA) in vitro: the roles of mRNA accumulation, poly(A) tail shortening and translational efficiency. Biochem J. 1993 May 1;291(Pt 3):701–707. doi: 10.1042/bj2910701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel D. M., Whitehead A. S. The major acute phase reactants: C-reactive protein, serum amyloid P component and serum amyloid A protein. Immunol Today. 1994 Feb;15(2):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90138-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D., Harrison S. P., Evans S. W., Whicher J. T. Insulin modulation of acute-phase protein production in a human hepatoma cell line. Cytokine. 1991 Nov;3(6):619–626. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(91)90489-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilg H., Trehu E., Atkins M. B., Dinarello C. A., Mier J. W. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) as an anti-inflammatory cytokine: induction of circulating IL-1 receptor antagonist and soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor p55. Blood. 1994 Jan 1;83(1):113–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilg H., Wilmer A., Vogel W., Herold M., Nölchen B., Judmaier G., Huber C. Serum levels of cytokines in chronic liver diseases. Gastroenterology. 1992 Jul;103(1):264–274. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91122-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Shimada E., Urakawa T. Serum levels of cytokines in patients with colorectal cancer: possible involvement of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 in hematogenous metastasis. J Gastroenterol. 1994 Aug;29(4):423–429. doi: 10.1007/BF02361238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J., Gunn H., Yang J., Parkinson D., Topalian S., Schwartzentruber D., Ettinghausen S., Levitt D., Rosenberg S. A. A phase I trial of intravenous interleukin-6 in patients with advanced cancer. J Immunother Emphasis Tumor Immunol. 1994 May;15(4):292–302. doi: 10.1097/00002371-199405000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J., Yang J. C., Topalian S. L., Parkinson D. R., Schwartzentruber D. S., Ettinghausen S. E., Gunn H., Mixon A., Kim H., Cole D. Phase I trial of subcutaneous interleukin-6 in patients with advanced malignancies. J Clin Oncol. 1993 Mar;11(3):499–506. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1993.11.3.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gameren M. M., Willemse P. H., Mulder N. H., Limburg P. C., Groen H. J., Vellenga E., de Vries E. G. Effects of recombinant human interleukin-6 in cancer patients: a phase I-II study. Blood. 1994 Sep 1;84(5):1434–1441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



