Abstract
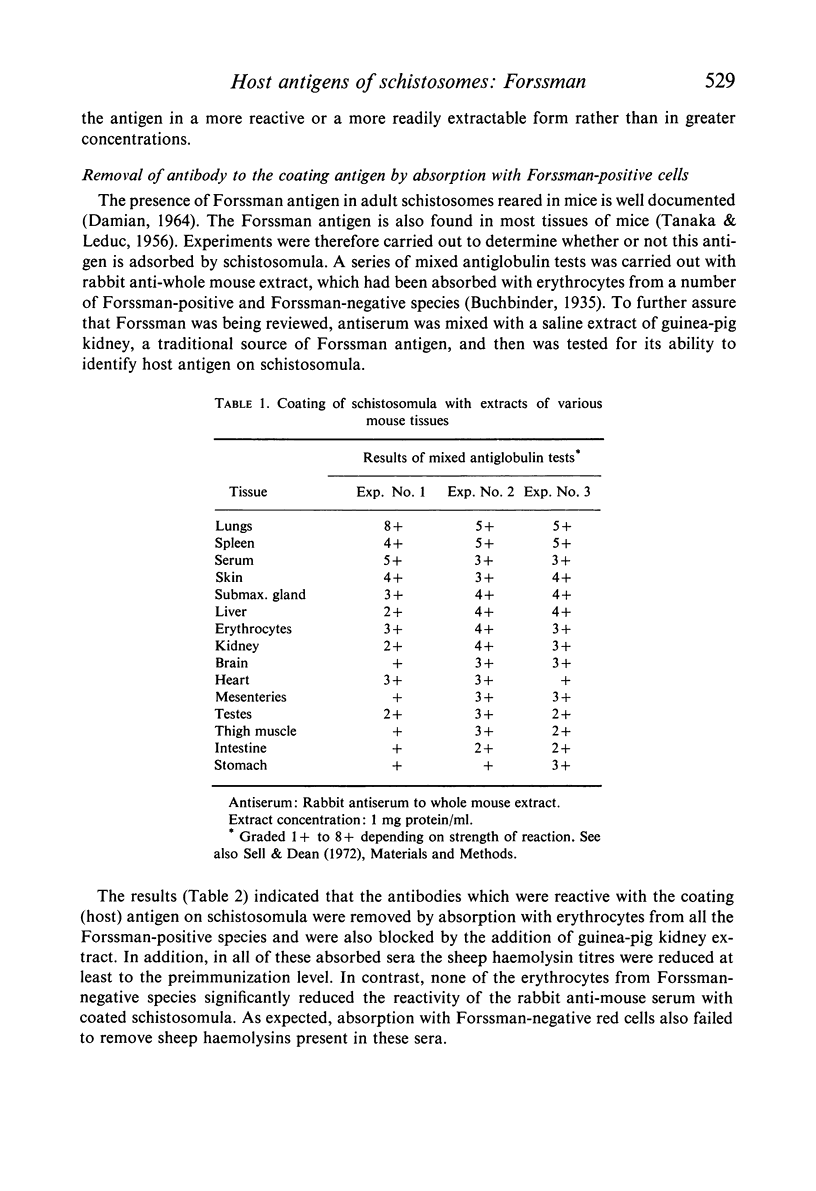
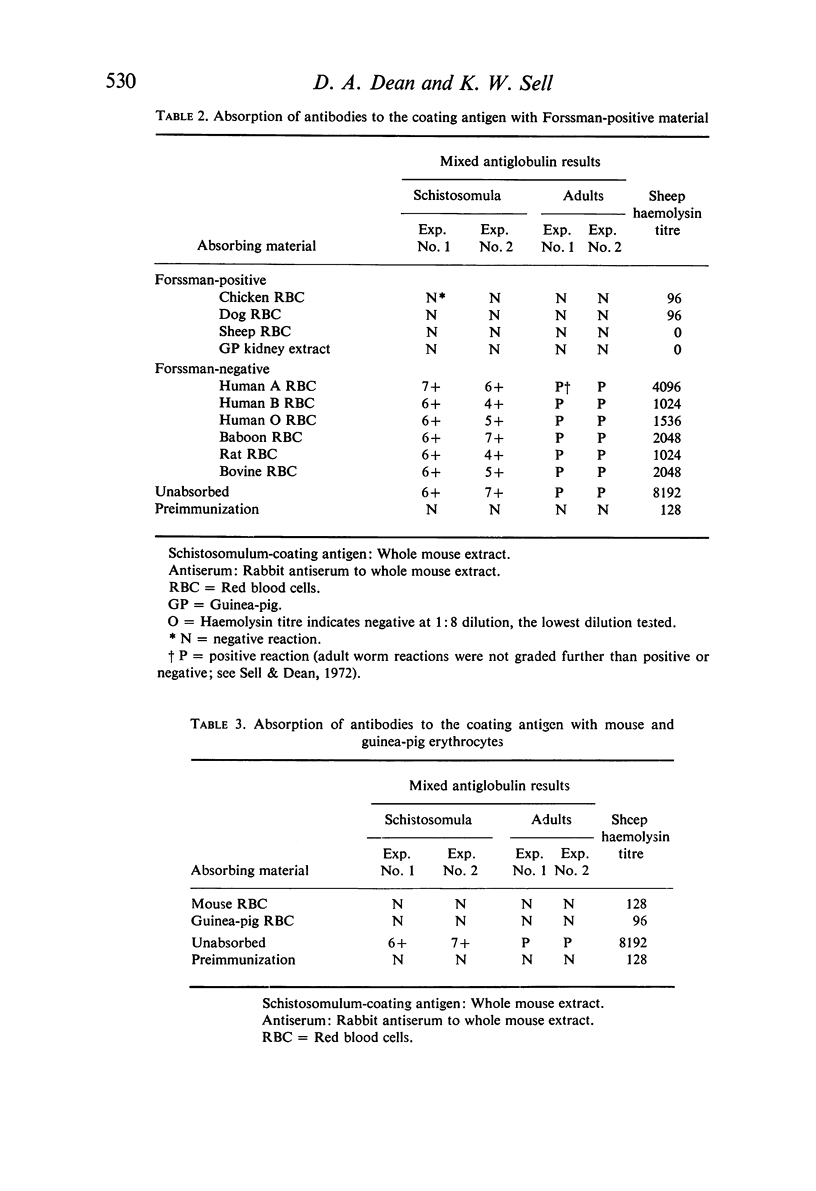
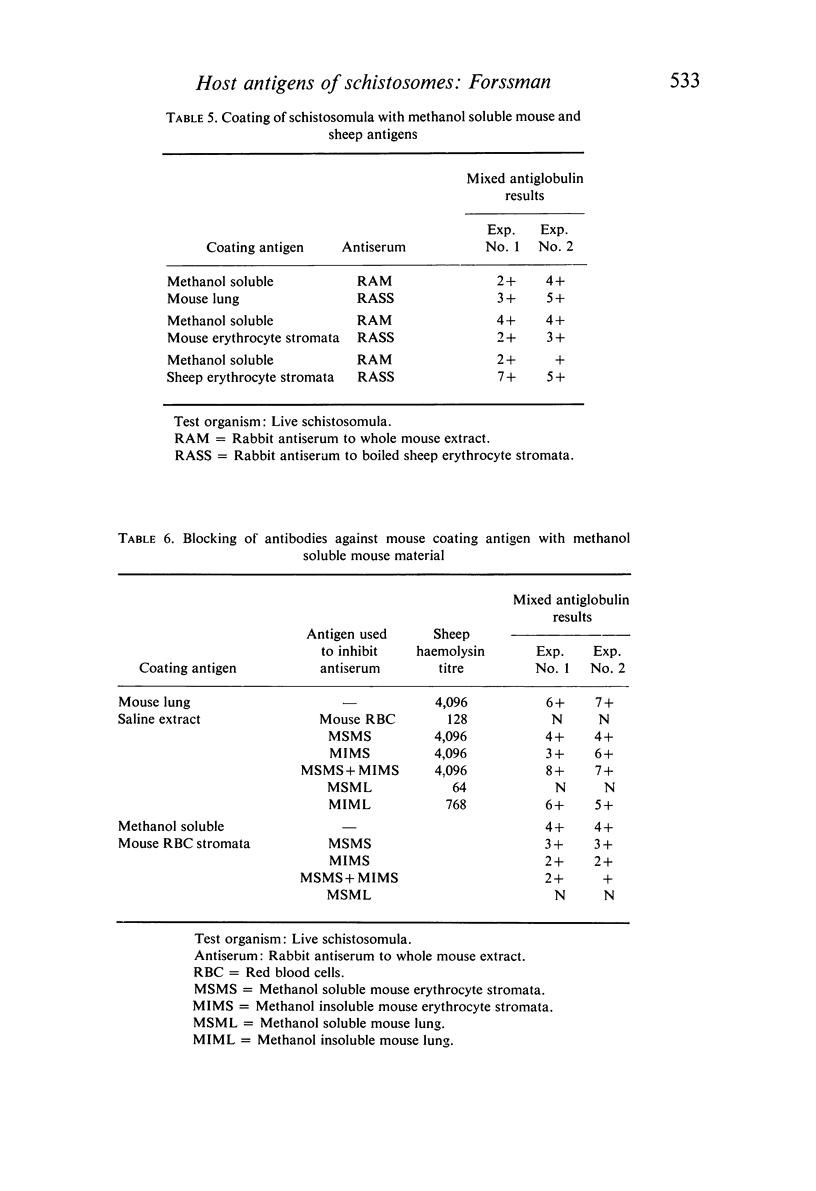
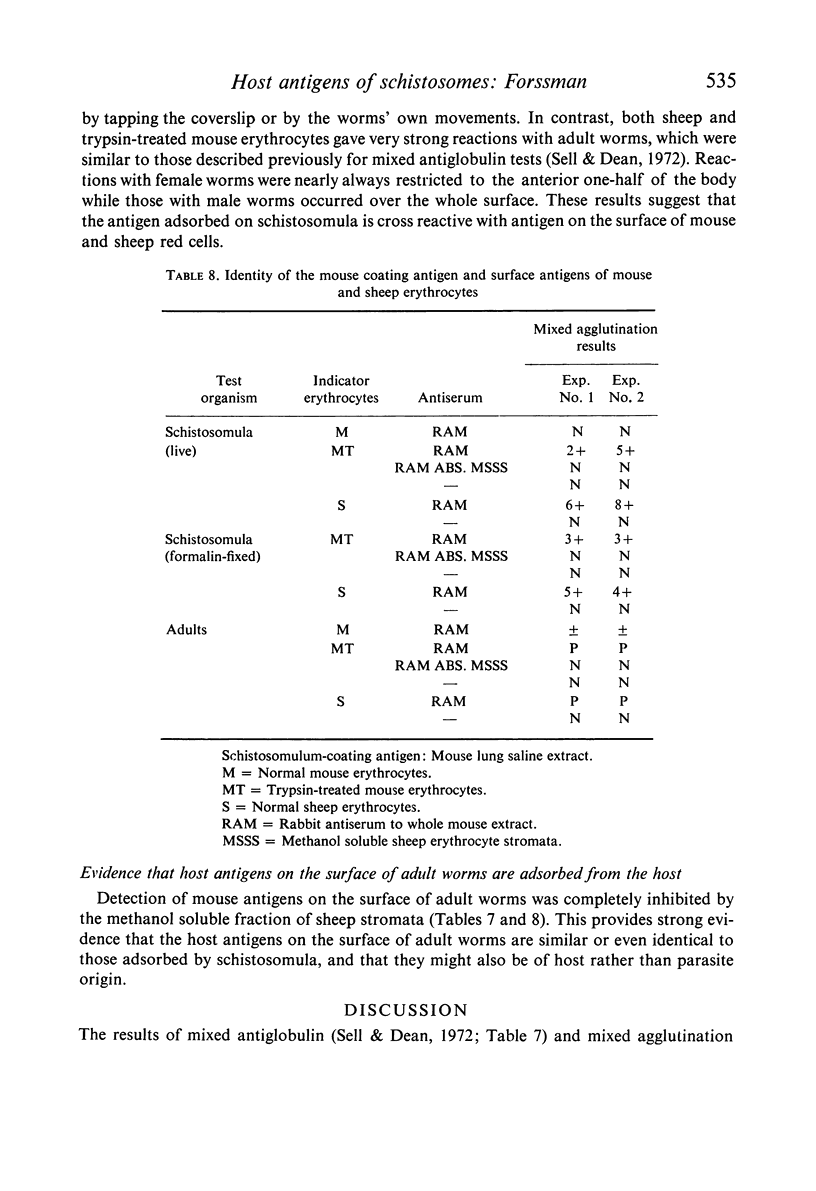
A study was made of the nature of mouse (host) antigens adsorbed by schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. Using the mixed antiglobulin test, extracts of a number of individual mouse tissues were tested for their ability to coat schistosomula. All were effective to some extent, with the greatest activity being found in extracts of the lung and spleen. Antibodies against the schistosomulum-coating antigen as well as surface host antigens of adult Schistosoma mansoni were removed by absorbing with erythrocytes from a number of Forssman-positive but not Forssman-negative animal species. These antibodies were also absorbed by Forssman-positive guineapig kidney extract and methanol soluble (Forssman-positive) but not insoluble fractions of sheep erythrocyte stromata and mouse lungs. Schistosomula could be coated in vitro with methanol soluble fractions of mouse lung and erythrocytes and sheep erythrocytes. Though both mouse and sheep coating antigens reacted with anti-mouse and anti-sheep antibodies, reactions were stronger with the homologous antiserum. It was concluded that schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni adsorb from mice an antigen similar but not identical to the Forssman antigen of sheep erythrocytes, and that this antigen is also found on the surface of adult worms.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COOMBS R. R., POUT D. D., SOULSBY E. J. GLOBULIN, POSSIBLY OF ANTIBODY NATURE, COMBINING WITH THE CUTICLE OF LIVE TURBATRIX ACETI. Exp Parasitol. 1965 Jun;16:311–317. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(65)90052-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron A., Biguet J., Rose F., Vernes A. Les antigènes de Schistosoma mansoni. II. Etude immunoélectrophorétique comparée de divers stades larvaires et des adults des deux sexes. Aspects immunologiques des relations hote-parasite de la cervaire et de l'adulte de S. mansoni. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 Nov;109(5):798–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron A., Biguet J., Vernes A., Afchain D. Structure antigénique des helminthes. Aspects immunologiques des relations hote-parasite. Pathol Biol. 1968 Feb;16(3):121–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. A., Smithers S. R., Terry R. J. "Host" antigens associated with schistosomes: observations on their attachment and their nature. Parasitology. 1970 Aug;61(1):87–94. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000040889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIDSOHN I., STERN K. Further studies on natural antisheep agglutinins in mice of inbred strains. Cancer Res. 1950 Sep;10(9):571–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damian R. T. Common antigens between adult Schistosoma mansoni and the laboratory mouse. J Parasitol. 1967 Feb;53(1):60–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogarth-Scott R. S. Naturally occurring antibodies to the cuticle of nematodes. Parasitology. 1968 Feb;58(1):221–226. doi: 10.1017/s003118200007356x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huntley C. C., Lyerly A. D., Patterson M. V. Isohemagglutinins in parasitic infections. JAMA. 1969 May 19;208(7):1145–1148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusel J. R. The penetration of human epidermal sheets by the cercariae of Schistosoma mansoni and the collection of schistosomula. Parasitology. 1970 Feb;60(1):89–96. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000077271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDUC E. H., TANAKA N. A study of the cellular distribution of Forssman antigen in various species. J Immunol. 1956 Sep;77(3):198–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLIVER-GONZALEZ J. Anti-egg precipitins in the serum of humans infected with Schistosoma mansoni. J Infect Dis. 1954 Jul-Aug;95(1):86–91. doi: 10.1093/infdis/95.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp H. J., Borsos T. Forssman antigen and antibody: preparation of water soluble antigen and measurement of antibody concentration by precipitin analysis, by C'1a fixation and by hemolytic activity. J Immunol. 1966 Jun;96(6):913–919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell K. W., Dean D. A. Surface antigens on Schistosoma mansoni. I. Demonstration of host antigens on schistosomula and adult worms using the mixed antiglobulin test. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Nov;12(3):315–324. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithers S. R., Terry R. J., Hockley D. J. Host antigens in schistosomiasis. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 Feb 25;171(1025):483–494. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithers S. R., Terry R. J. The infection of laboratory hosts with cercariae of Schistosoma mansoni and the recovery of the adult worms. Parasitology. 1965 Nov;55(4):695–700. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000086248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. F., Soulsby E. J. Antigenic analysis of the developmental stagesof Ascaris suum. II. Host components. Exp Parasitol. 1970 Jun;27(3):362–367. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(70)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


