Abstract
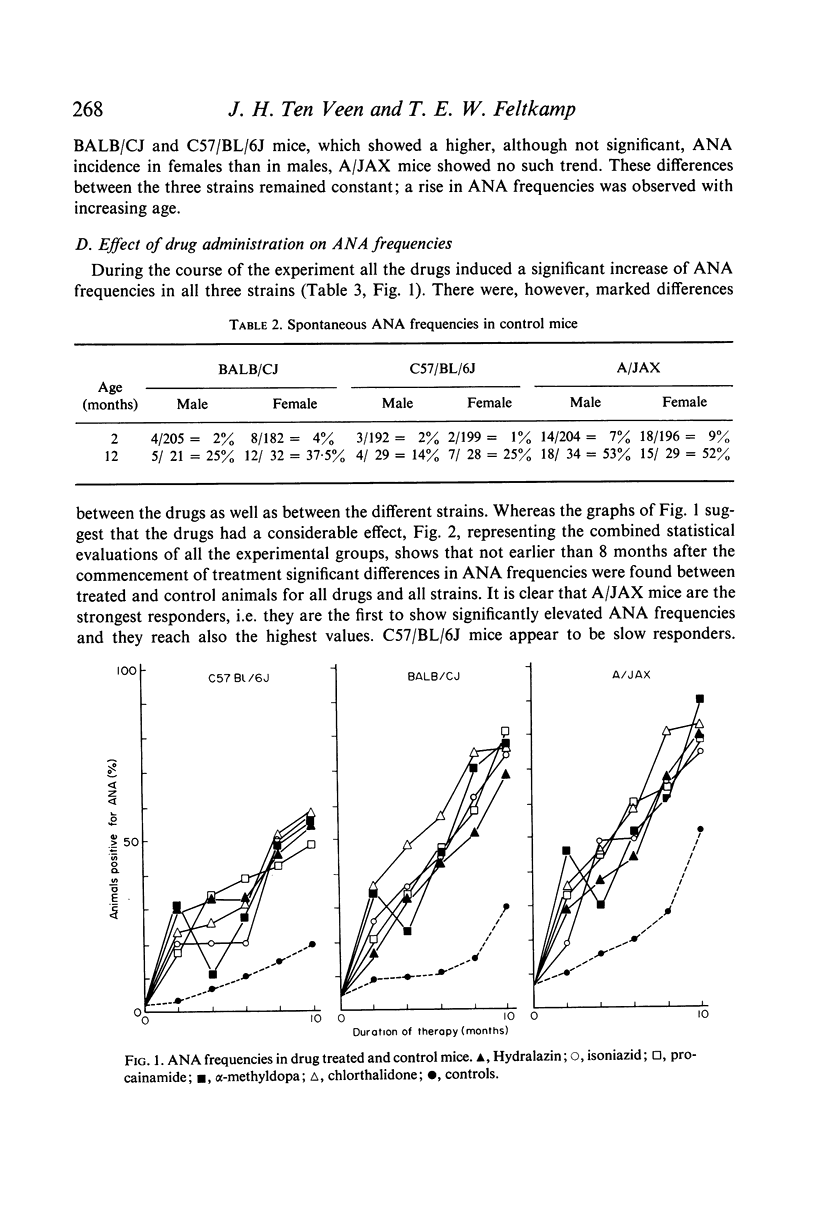
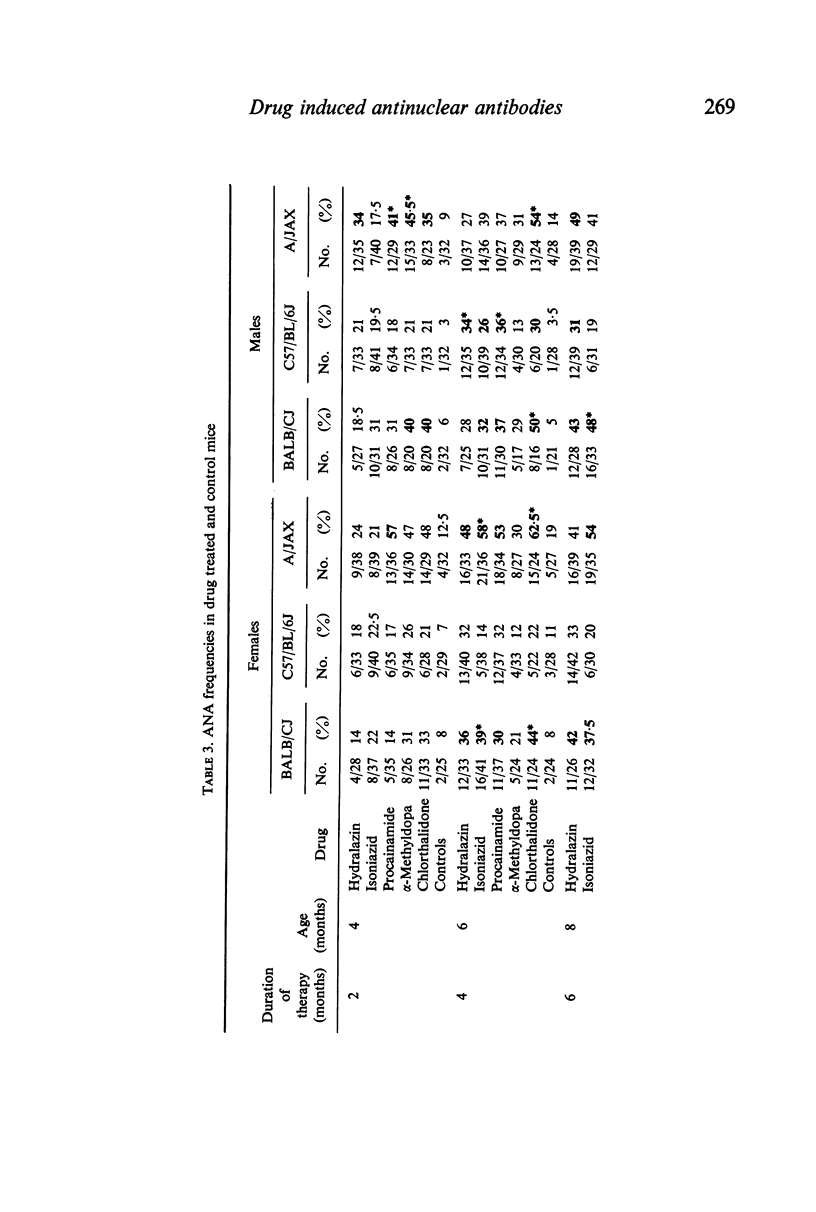
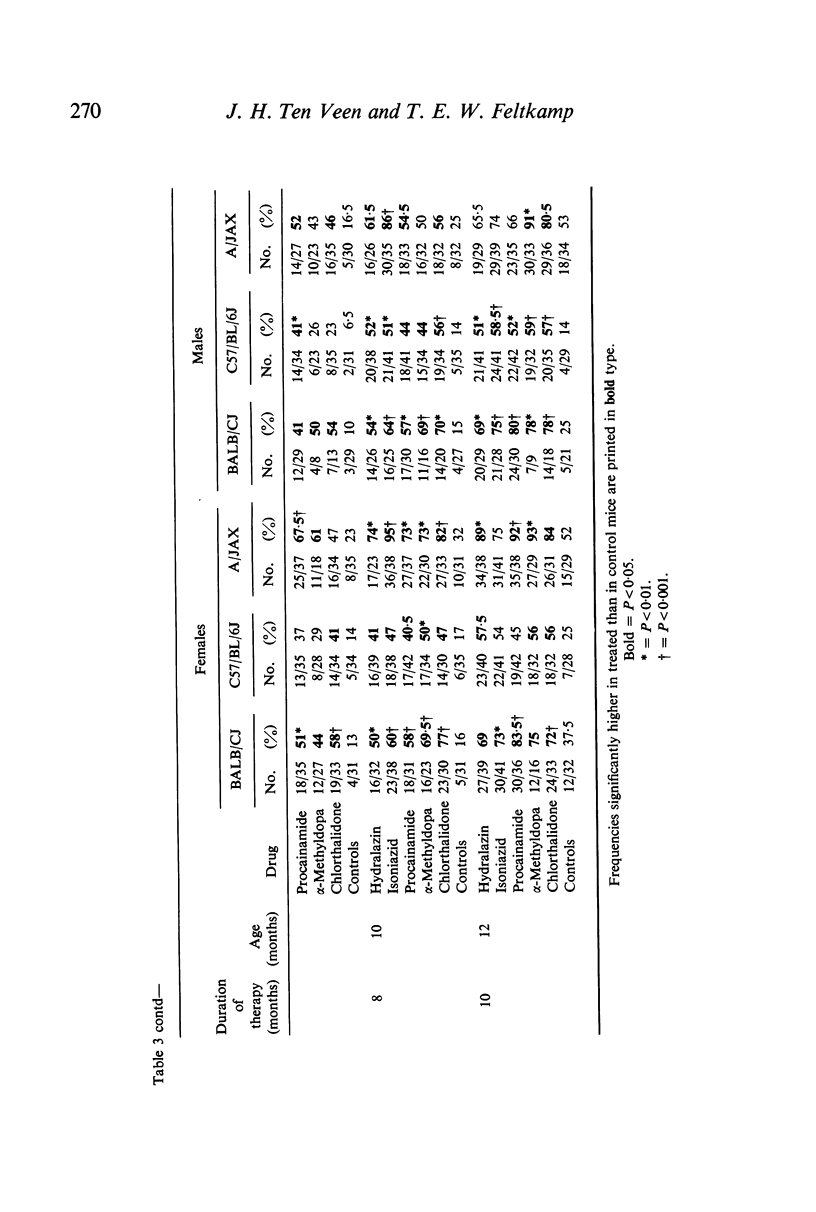
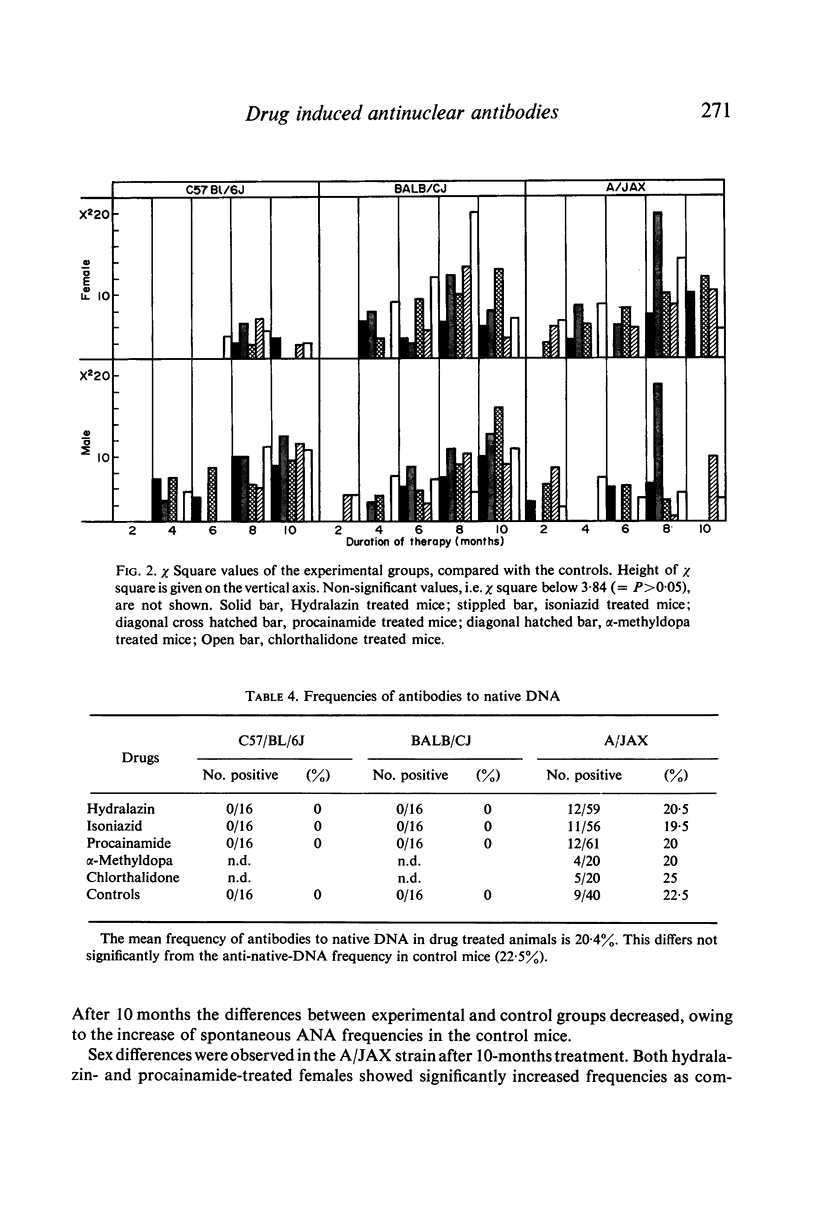
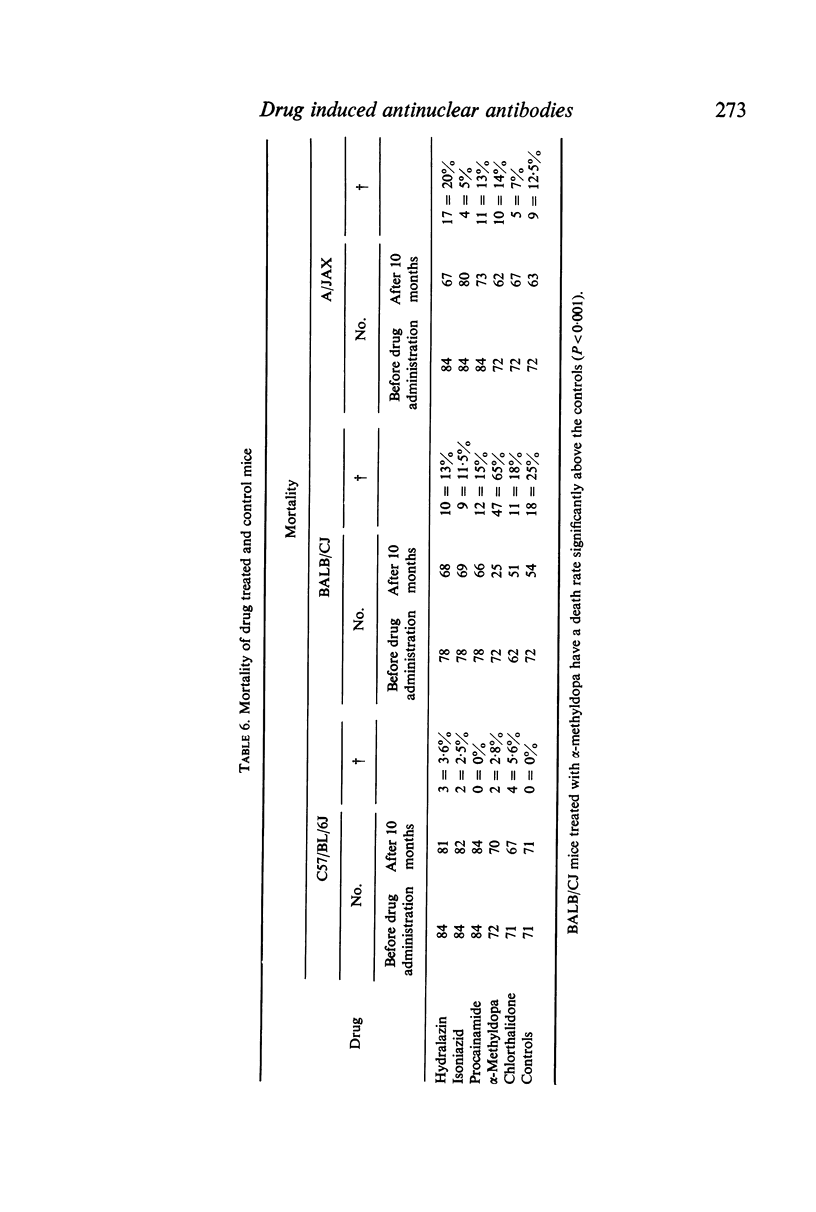
Hydralazin, isoniazid, procainamide, α-methyldopa and chlorthalidone were given orally to mice of three inbred strains: BALB/CJ, C57/BL/6J and A/JAX. All drugs significantly increased the frequency of antinuclear antibodies (ANA). The results were most marked after 8 months of treatment. Although a slight preponderance of females was observed for ANA frequencies in BALB/CJ and A/JAX mice, this was significant only for hydralazin- and procainamide-treated animals. C57/BL/6J males appeared to respond better than females. Genetical factors appear of importance in the induciton of drug induced lupus erythematosus (DILE).
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALARCON SEGOVIA D., WORTHINGTON J. W., WARD L. E., WAKIM K. G. LUPUS DIATHESIS AND THE HYDRALAZINE SYNDROME. N Engl J Med. 1965 Mar 4;272:462–466. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196503042720905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alarcón-Segovia D. Drug-induced lupus syndromes. Mayo Clin Proc. 1969 Sep;44(9):664–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alarcón-Segovia D., Fishbein E., Betancourt V. M. Antibodies to nucleoprotein and to hydrazide-altered soluble nucleoprotein in tuberculous patients receiving isoniazid. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Oct;5(4):429–437. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAVERMAN I. M., LERNER A. B. Hydralazine disease in the guinea-pig as an experimental model for lupus erythematosus. J Invest Dermatol. 1962 Oct;39:317–327. doi: 10.1038/jid.1962.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomgren S. E., Condemi J. J., Bignall M. C., Vaughan J. H. Antinuclear antibody induced by procainamide. A prospective study. N Engl J Med. 1969 Jul 10;281(2):64–66. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196907102810203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breckenridge A., Dollery C. T., Worlledge S. M., Holborow E. J., Johnson G. D. Positive direct Coombs tests and antinuclear factor in patients treated with methyldopa. Lancet. 1967 Dec 16;2(7529):1265–1267. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90387-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COMENS P. Experimental hydralazine disease and its similarity to disseminated lupus erythematosus. J Lab Clin Med. 1956 Mar;47(3):444–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannat A., Seligmann M. Induction by isoniazid and hydrallazine of antinuclear factors in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1968 Jan;3(1):99–105. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condemi J. J., Moore-Jones D., Vaughan J. H., Perry H. M. Antinuclear antibodies following hydralazine toxicity. N Engl J Med. 1967 Mar 2;276(9):486–491. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196703022760902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feltkamp T. E., Mees E. J., Nieuwenhuis M. G. Autoantibodies related to treatment with chlorthalidone and alpha-methyldopa. Acta Med Scand. 1970 Mar 3;187(3):219–223. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1970.tb02934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLEY H. L. EVIDENCE FOR A PREDISPOSITION TO RHEUMATIC DISEASES IN FAMILIES OF PATIENTS DEVELOPING DRUG-INDUCED SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS. Arthritis Rheum. 1964 Dec;7:684–686. doi: 10.1002/art.1780070608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hift W., Watson K. C. Systemic lupus erythematosus in a family. S Afr Med J. 1968 Aug 17;42(32):826–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hijmans W., Radema H., van Es L., Feltkamp T. E., van Loghem J. J., Schaap O. L. Cryoglobulins in New Zealand Black mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Feb;4(2):227–239. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Carr R. I., Agnello V., Fiezi T., Kunkel H. G. Antibodies to polynucleotides: distribution in human serums. Science. 1969 Dec 26;166(3913):1648–1649. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3913.1648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lappat E. J., Cawein M. J. A familial study of procainamide-induced systemic lupus erythematosus. A question of pharmacogenetic polymorphism. Am J Med. 1968 Dec;45(6):846–852. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(68)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molina J., Dubois E. L., Bilitch M., Bland S. L., Friou G. J. Procainamide-induced serologic changes in asymptomatic patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1969 Dec;12(6):608–614. doi: 10.1002/art.1780120608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monier J. C., Richard M. H., Thivolet J. Administration prolongée d'hydralazine chez le cobaye. Bilan sérologique et clinicopathologique. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol. 1968 Jan;13(1):67–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY H. M., Jr, SCHROEDER H. A. Syndrome simulating collagen disease caused by hydralazine (Apresoline). J Am Med Assoc. 1954 Feb 20;154(8):670–673. doi: 10.1001/jama.1954.02940420032009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg A. D., Pincus T., Talal N. DNA-binding assay for detection of anti-DNA antibodies in NZB-NZW F1 mice. J Immunol. 1969 Mar;102(3):788–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The T. H., Feltkamp T. E. Conjugation of fluorescein isothiocyanate to antibodies. II. A reproducible method. Immunology. 1970 Jun;18(6):875–881. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoburn R., Koffler D., Kunkel H. G. Distribution of antibodies to native DNA, single-stranded DNA, and double-stranded RNA in mouse serums. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Mar;136(3):711–714. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold R. T., Young F. E., Tan E. M., Farr R. S. Deoxyribonucleic acid antibody: a method to detect its primary interaction with deoxyribonucleic acid. Science. 1968 Aug 23;161(3843):806–807. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3843.806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Veen J. H., Feltkamp T. E. Formalinized chicken red cell nuclei as a simple antigen for standardized antinuclear factor determination. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Dec;5(6):673–678. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



