Abstract
Purified monocytes and lymphocytes from peripheral blood of healthy human donors were tested in vitro for cytotoxicity against blood group A erythrocytes (RBC) treated with a human hyperimmune anti-A serum. Haemolysis was quantitated by the release of radioactivity from RBC pre-labelled with 51Cr-chromate.
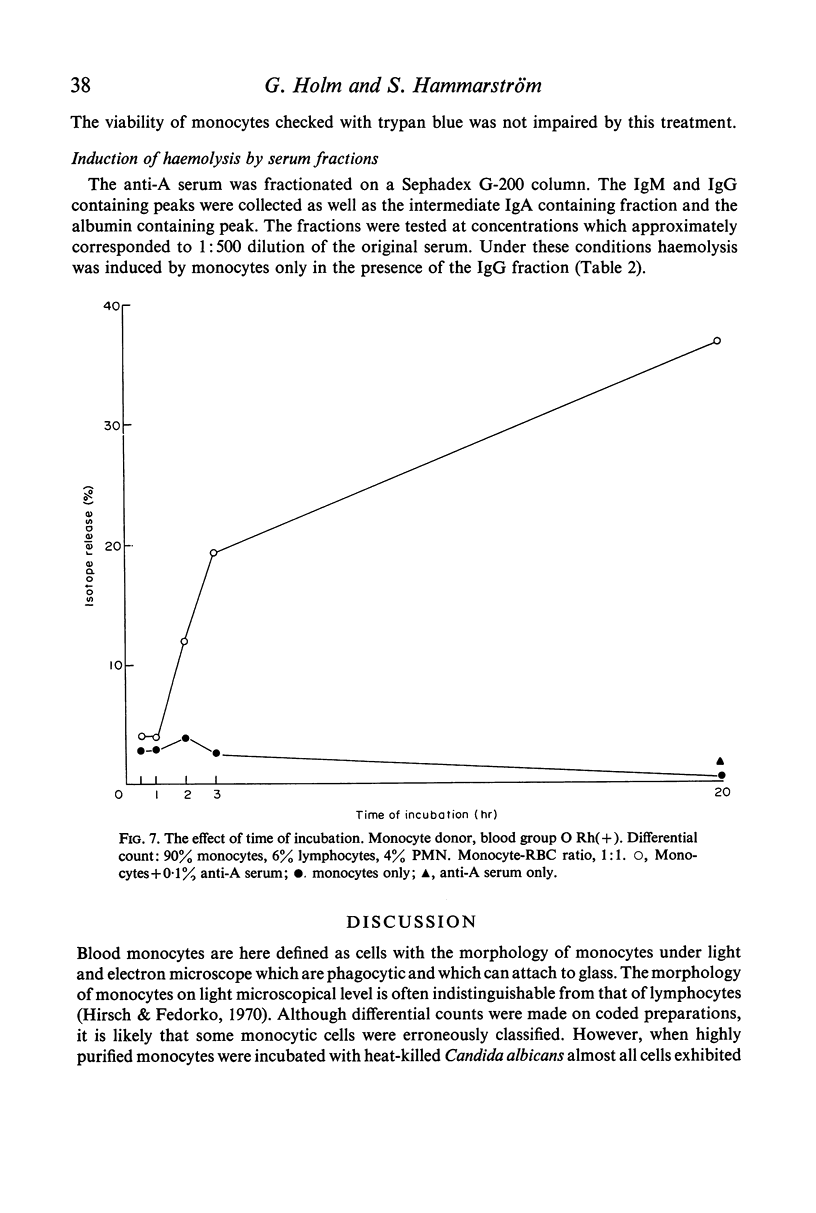
The antiserum contained high titre antibodies which agglutinated A-RBC. After separation of serum on a Sephadex G-200 column the IgG containing fraction agglutinated A-RBC and precipitated blood group A substance. No or only weak antibody activity was detected in the IgA- and IgM-containing fractions.
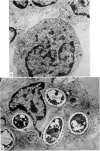
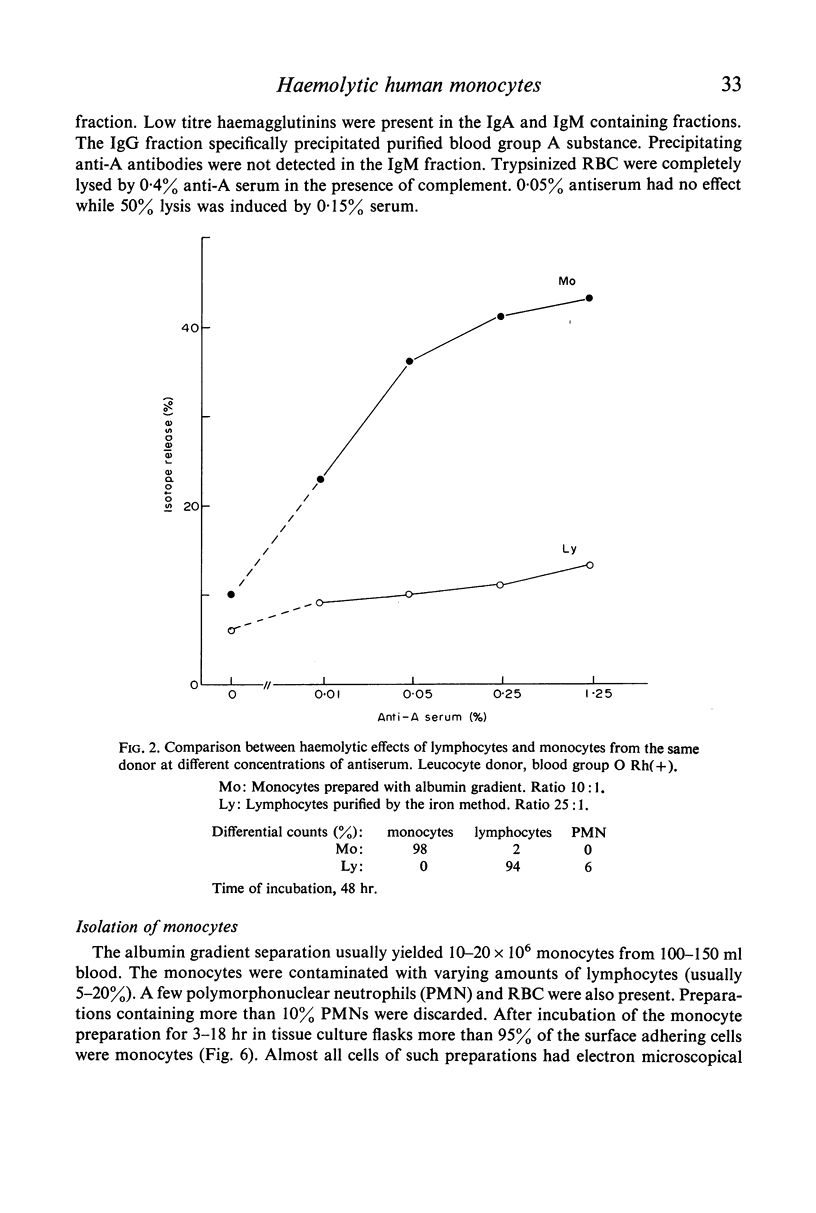
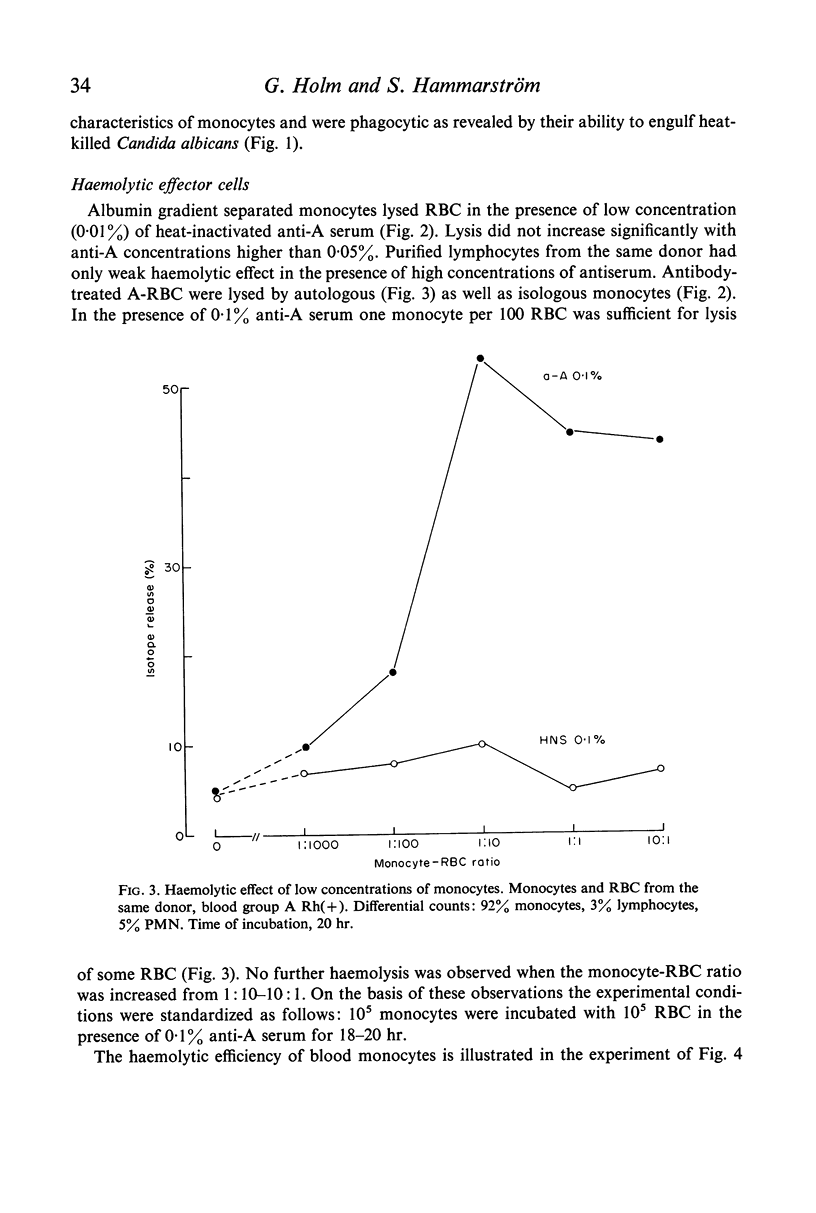
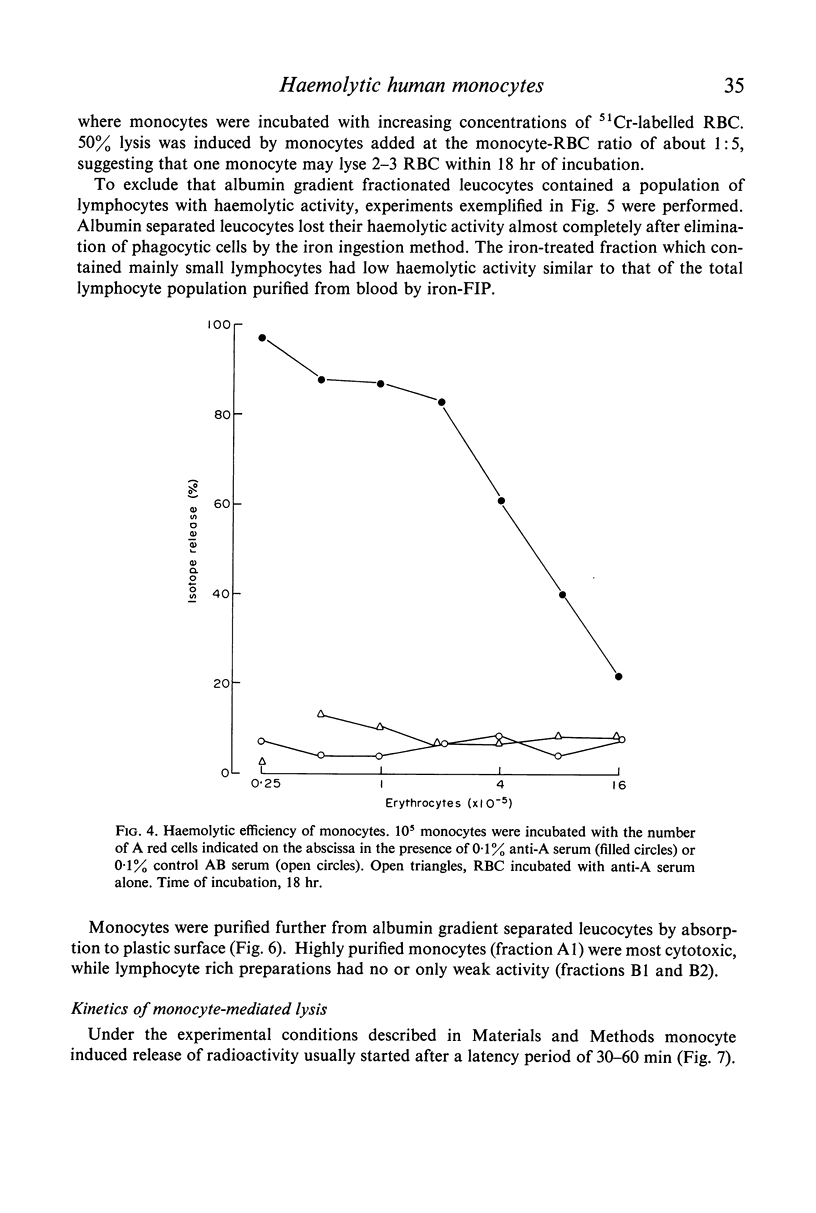
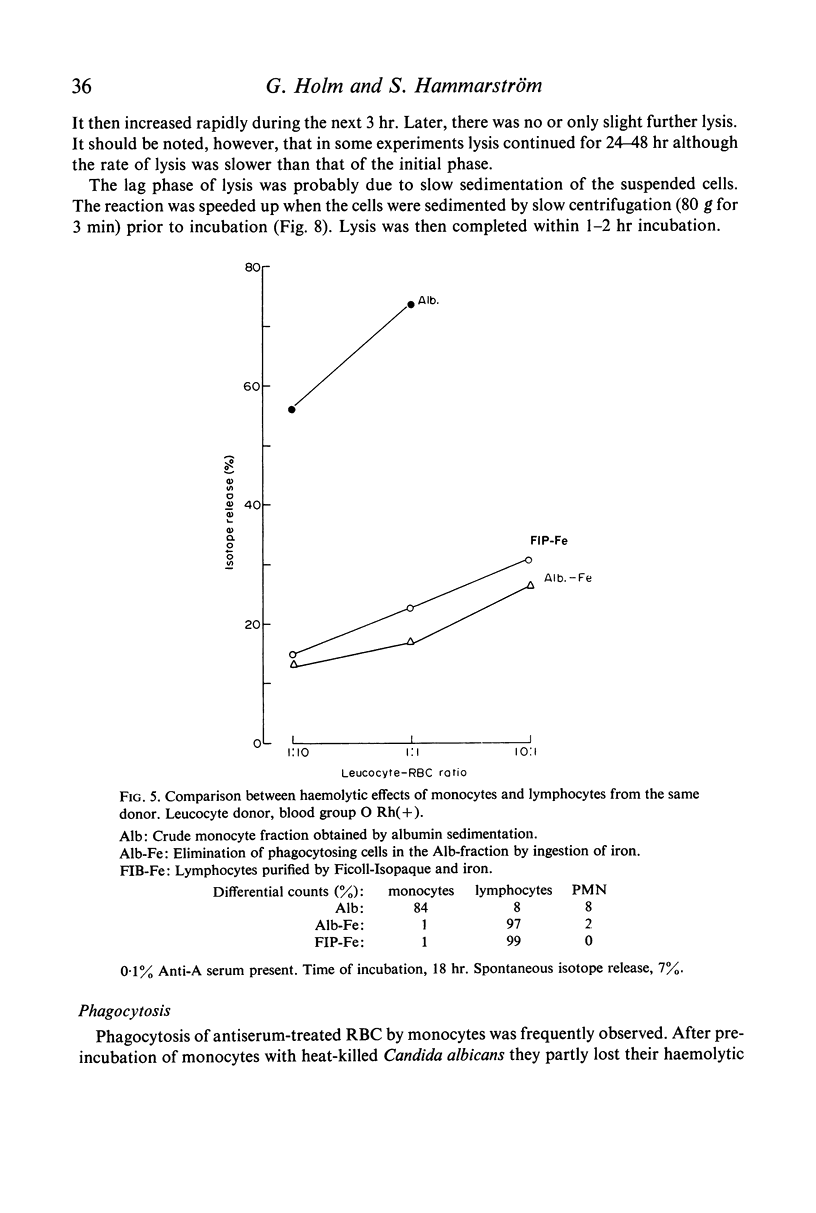
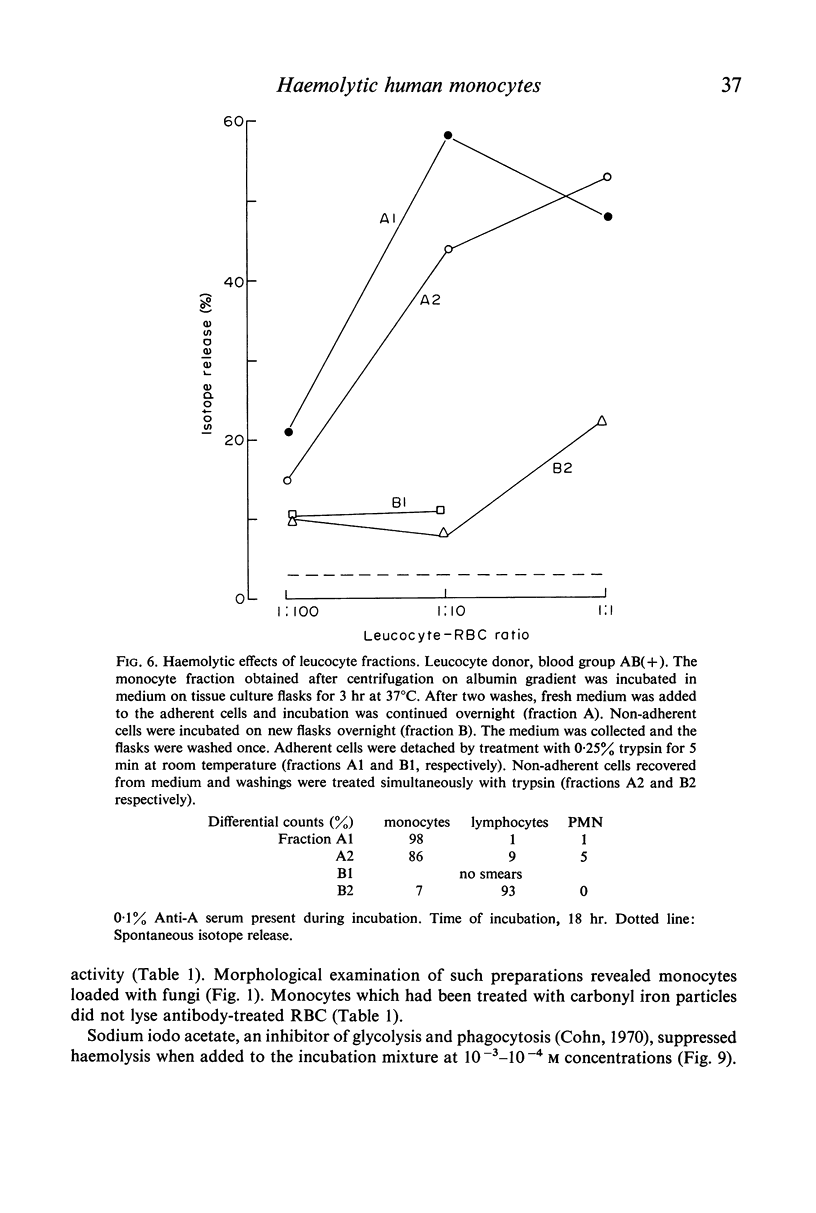
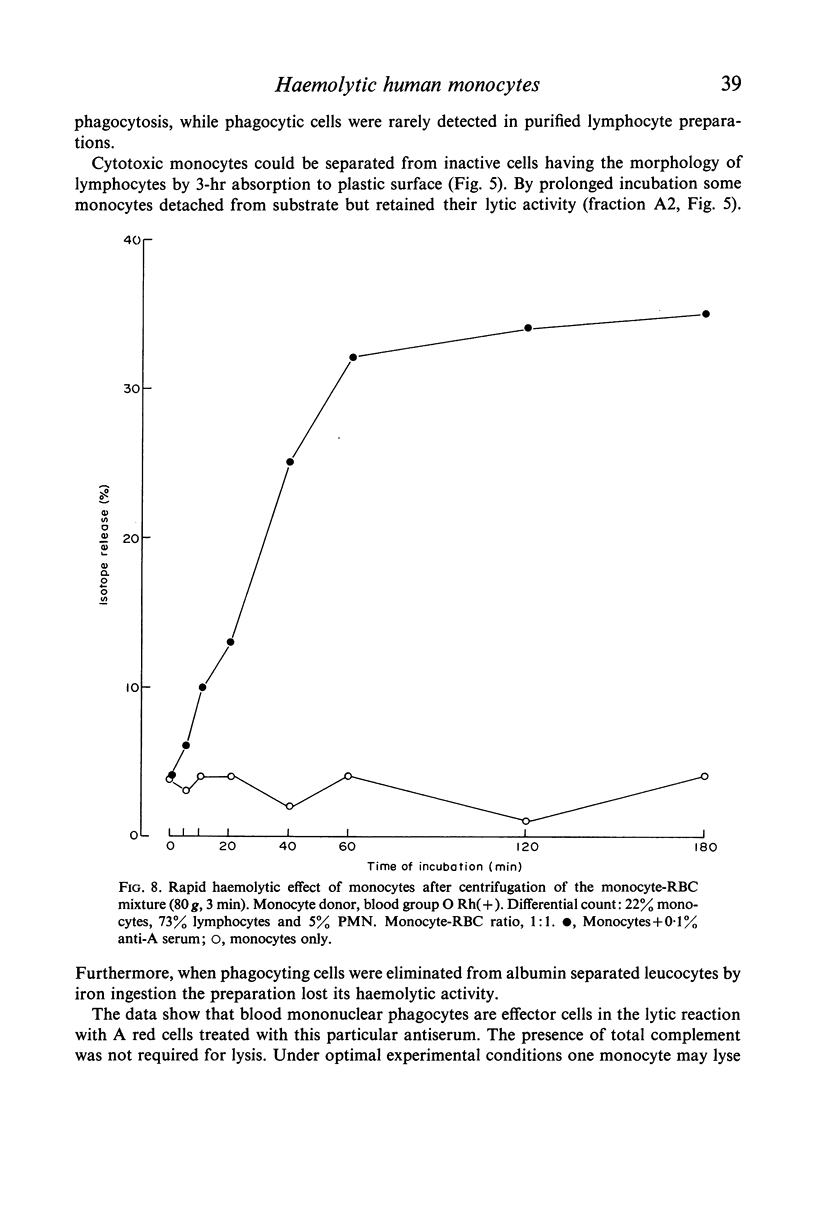
Purified monocytes added to a 100-fold excess of RBC in the presence of 0·1% antiserum induced some haemolysis. It was calculated that one monocyte was able to lyse 2–3 RBC within 18 hr incubation. In contrast, lymphocyte suspensions containing more than 97% small lymphocytes had no or only weak haemolytic activity at a lymphocyte-RBC ratio of 25: 1. The effector cells of the monocyte fraction adhered to glass and were eliminated by incubation with carbonyl iron. Phagocytosis by monocytes of antibody-treated RBC was frequently observed. Loading of monocytes by treatment with heat-killed Candida albicans or carbonyl iron particles suppressed their haemolytic action. Cytotoxicity was impaired after treatment of monocytes with 10−4 M sodium iodo acetate. After separation of serum on Sephadex G-200 column all monocyte induced haemolytic activity was found in the IgG containing fraction. It is assumed that haemolysis is induced by the interaction of monocytes with an IgG anti-A antibody of the antiserum.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson N., Gelfand E. W., Jandl J. H., Rosen F. S. The interaction between human monocytes and red cells. Specificity for IgG subclasses and IgG fragments. J Exp Med. 1970 Dec 1;132(6):1207–1215. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.6.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett W. E., Cohn Z. A. The isolation and selected properties of blood monocytes. J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 1;123(1):145–160. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biberfeld P. Uropod formation in phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) stimulated lymphocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Jun;66(2):433–445. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90698-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COULSON A. S., CHALMERS D. G. SEPARATION OF VIABLE LYMPHOCYTES FROM HUMAN BLOOD. Lancet. 1964 Feb 29;1(7331):468–469. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)90799-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dacie J. V. Autoimmune haemolytic anaemias. Br Med J. 1970 May 16;2(5706):381–386. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5706.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWALT T. J., GAJEWSKI M., McKENNA J. L. A new method for preparing buffy coat-poor blood. Transfusion. 1962 Jul-Aug;2:221–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.1962.tb00228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber H., Douglas S. D., Fudenberg H. H. The IgG receptor: an immunological marker for the characterization of mononuclear cells. Immunology. 1969 Jul;17(1):7–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber H., Douglas S. D., Nusbacher J., Kochwa S., Rosenfield R. E. IgG subclass specificity of human monocyte receptor sites. Nature. 1971 Feb 5;229(5284):419–420. doi: 10.1038/229419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LoBuglio A. F., Cotran R. S., Jandl J. H. Red cells coated with immunoglobulin G: binding and sphering by mononuclear cells in man. Science. 1967 Dec 22;158(3808):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3808.1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann P., Holm G. Cytotoxic effects of lymphoid cells in vitro. Adv Immunol. 1969;11:117–193. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60479-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann P., Perlmann H. Contactual lysis of antibody-coated chicken erythrocytes by purified lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1970 Sep;1(3):300–315. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Cohn Z. A. The origin and kinetics of mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1968 Sep 1;128(3):415–435. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.3.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Diesselhoff-Den Dulk M. M. The kinetics of promonocytes and monocytes in the bone marrow. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):813–828. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]