Abstract
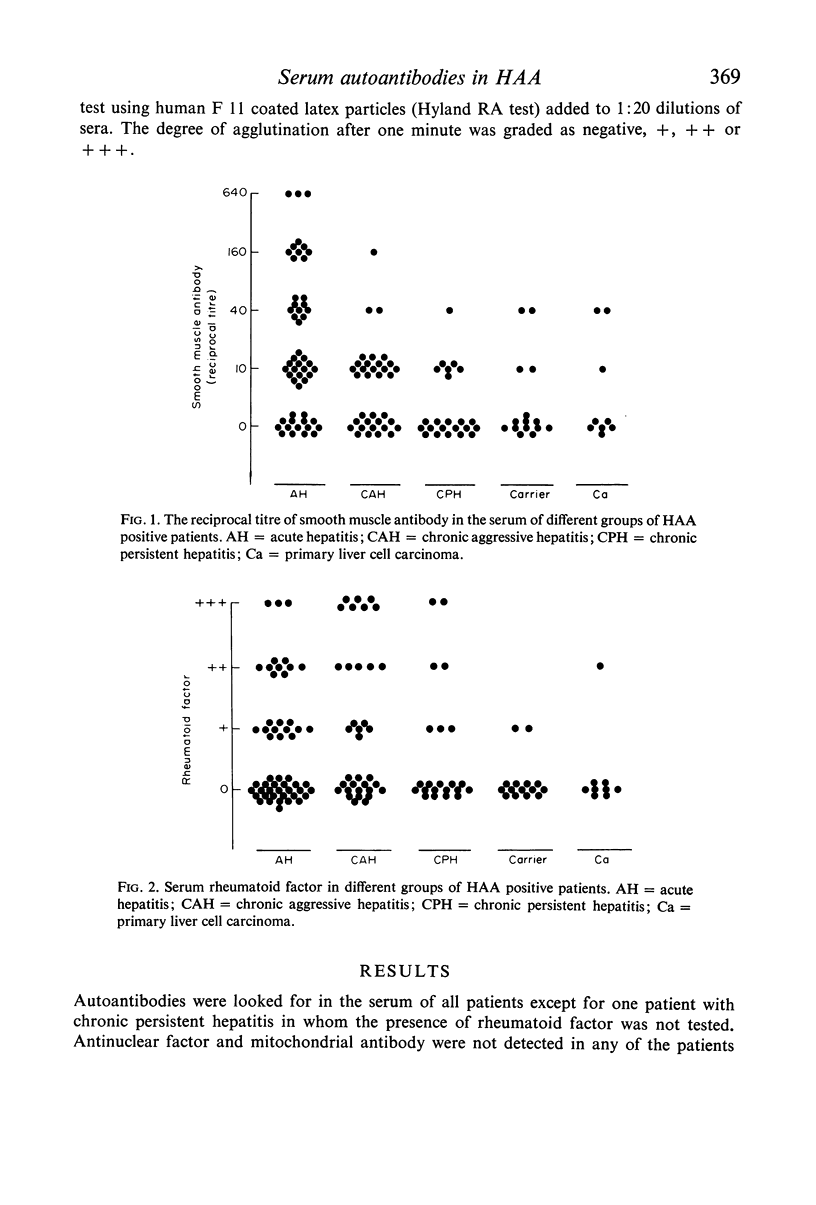
Sera from 134 HAA positive patients have been studied for the presence of a variety of autoantibodies. The patients were divided into groups dependent on the clinicopathological severity of the associated liver disease. Both smooth muscle antibody and rheumatoid factor were found in all groups of patients. However, their incidence and titre was higher in the groups of patients who had clinical and pathological evidence of the more active liver cell damage. As autoantibodies in viral infections may be an index of the presence of cell mediated immunity to the causative infective agent these results could support the hypothesis that cell mediated immunity is important in the pathogenesis of liver cell damage in HAA positive patients.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ajdukiewicz A. B., Fox R. A., Dudley F. J., Doniach D., Sherlock S. Immunological studies in an epidemic of infective, short-incubation hepatitis. Lancet. 1972 Apr 15;1(7755):803–805. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90795-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison A. C., Denman A. M., Barnes R. D. Cooperating and controlling functions of thymus-derived lymphocytes in relation to autoimmunity. Lancet. 1971 Jul 17;2(7716):135–140. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B. S., Gerstley B. J., Hungerford D. A., London W. T., Sutnick A. I. A serum antigen (Australia antigen) in Down's syndrome, leukemia, and hepatitis. Ann Intern Med. 1967 May;66(5):924–931. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-66-5-924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulkley B. H., Goldfinger S. E., Heizer W. D., Isselbacher K. J., Shulman N. R. Distinctions in chronic active hepatitis based on circulating hepatitis-associated antigen. Lancet. 1970 Dec 26;2(7687):1323–1326. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92356-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrow L. J., Holborow E. J., Brighton W. D. Reaction of human smooth muscle antibody with liver cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Aug 11;232(2):186–187. doi: 10.1038/newbio232186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrow L. J., Holborow E. J., Johnson G. D., Lamb S. G., Stewart J. S., Taylor P. E., Zuckerman A. J. Autoantibodies and the hepatitis-associated antigen in acute infective hepatitis. Br Med J. 1970 Jun 20;2(5711):693–695. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5711.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R. A., Niazi S. P., Sherlock S. Hepatitis-associated antigen in chronic liver disease. Lancet. 1969 Sep 20;2(7621):609–612. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90324-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles J. P., McCollum R. W., Berndtson L. W., Jr, Krugman S. Relation of Australia-SH antigen to the willowbrook MS-2 strain. N Engl J Med. 1969 Jul 17;281(3):119–122. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196907172810302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLBOROW J., JOHNSON G. D. ANTINUCLEAR FACTOR IN SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS. A CONSIDERATION OF THE IMMUNOFLUORESCENT METHOD OF DETECTING ANTINUCLEAR ANTIBODIES, WITH RESULTS OBTAINED IN A FAMILY STUDY. Arthritis Rheum. 1964 Apr;7:119–127. doi: 10.1002/art.1780070204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krugman S., Giles J. P. Viral hepatitis. New light on an old disease. JAMA. 1970 May 11;212(6):1019–1029. doi: 10.1001/jama.212.6.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. O., Dietrichson O., Elling P., Christoffersen P. Incidence and meaning of persistence of Australia antigen in patients with acute viral hepatitis: development of chronic hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1971 Nov 18;285(21):1157–1160. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197111182852101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M. An antigen detected in the blood during the incubation period of serum hepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):814–821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M. Role of serum hepatitis virus in chronic liver disease. Gastroenterology. 1971 May;60(5):913–921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherlock S., Fox R. A., Niazi S. P., Scheuer P. J. Chronic liver disease and primary liver-cell cancer with hepatitis-associated (Australia) antigen in serum. Lancet. 1970 Jun 13;1(7659):1243–1247. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91737-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vischer T. L. Australia antigen and autoantibodies in chronic hepatitis. Br Med J. 1970 Jun 20;2(5711):695–698. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5711.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright R. Australia antigen and smooth-muscle antibody in acute and chronic hepatitis. Lancet. 1970 Mar 7;1(7645):521–522. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(70)91605-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright R., McCollum R. W., Klatskin G. Australia antigen in acute and chronic liver disease. Lancet. 1969 Jul 19;2(7612):117–121. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92437-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegenfuss J. F., Jr, Miller J., Rossman D. Rheumatoid factor and Australia antigen. N Engl J Med. 1971 May 13;284(19):1104–1104. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197105132841919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


