Abstract
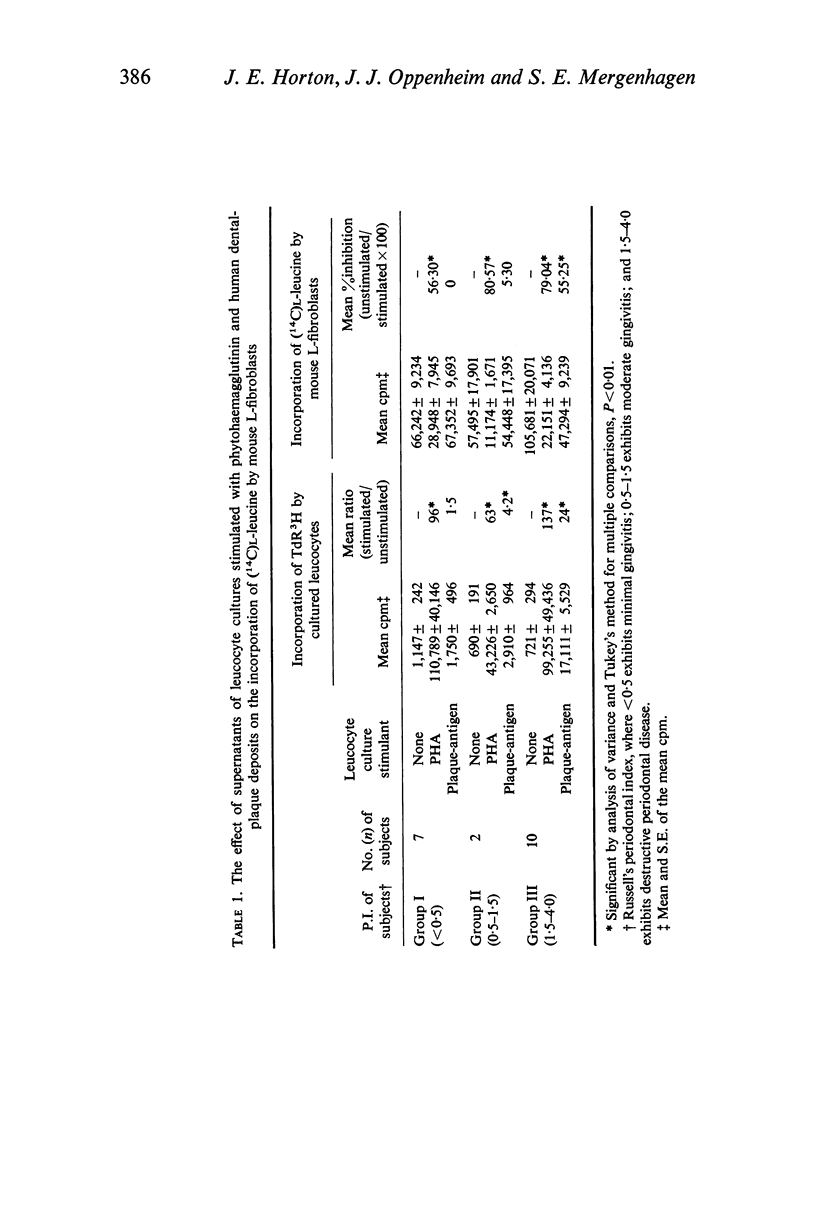
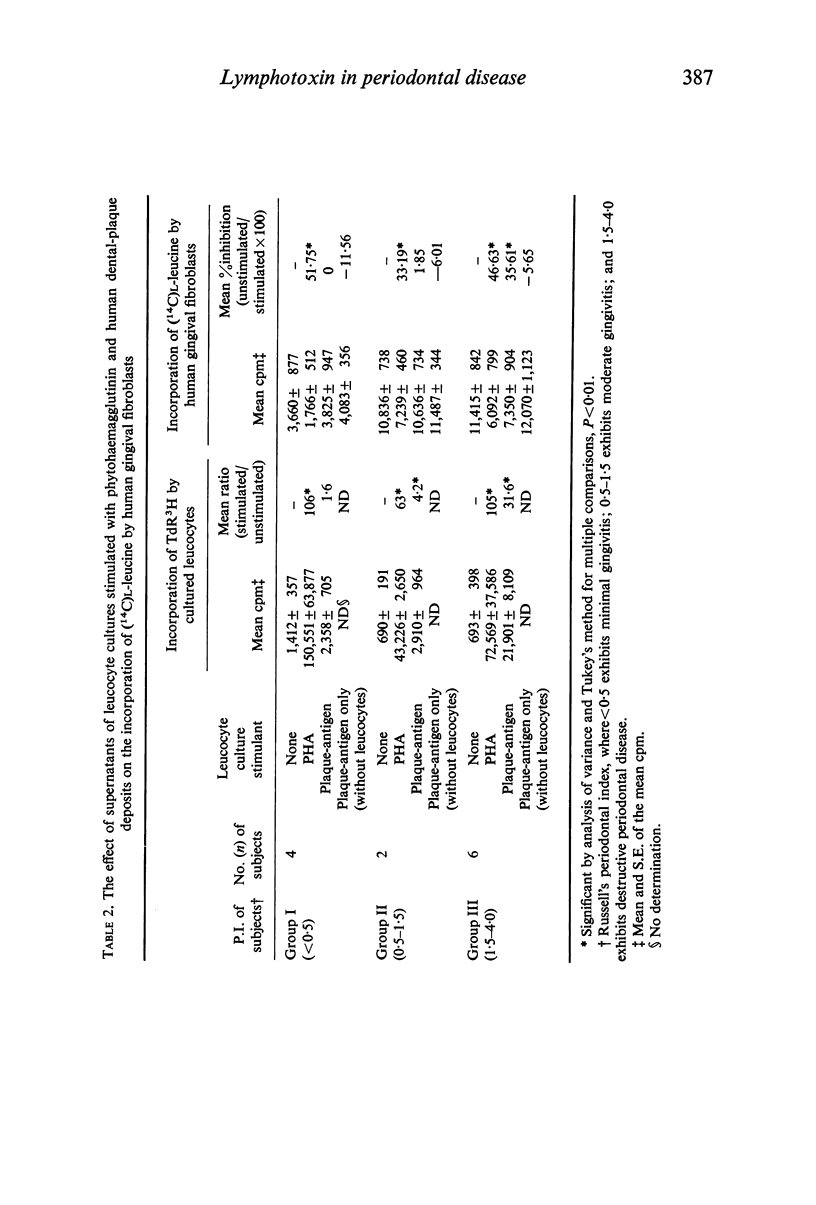
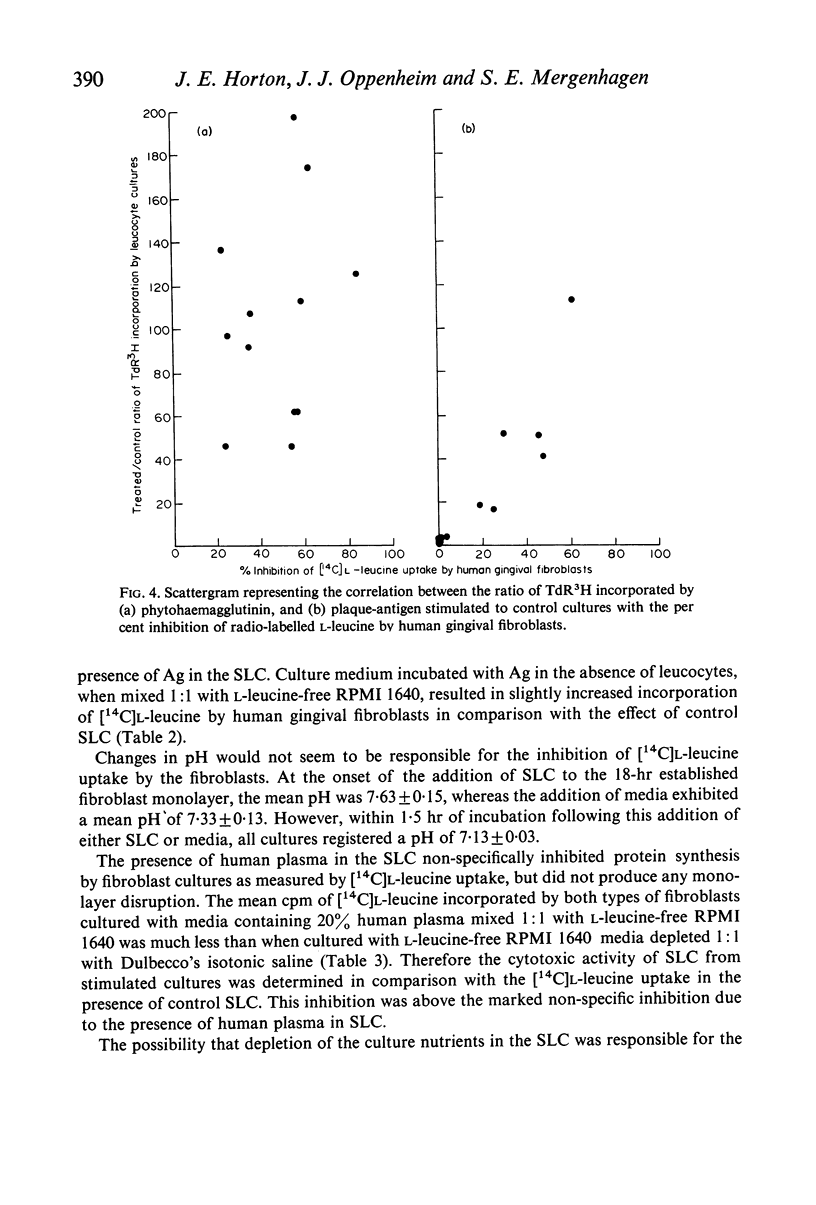
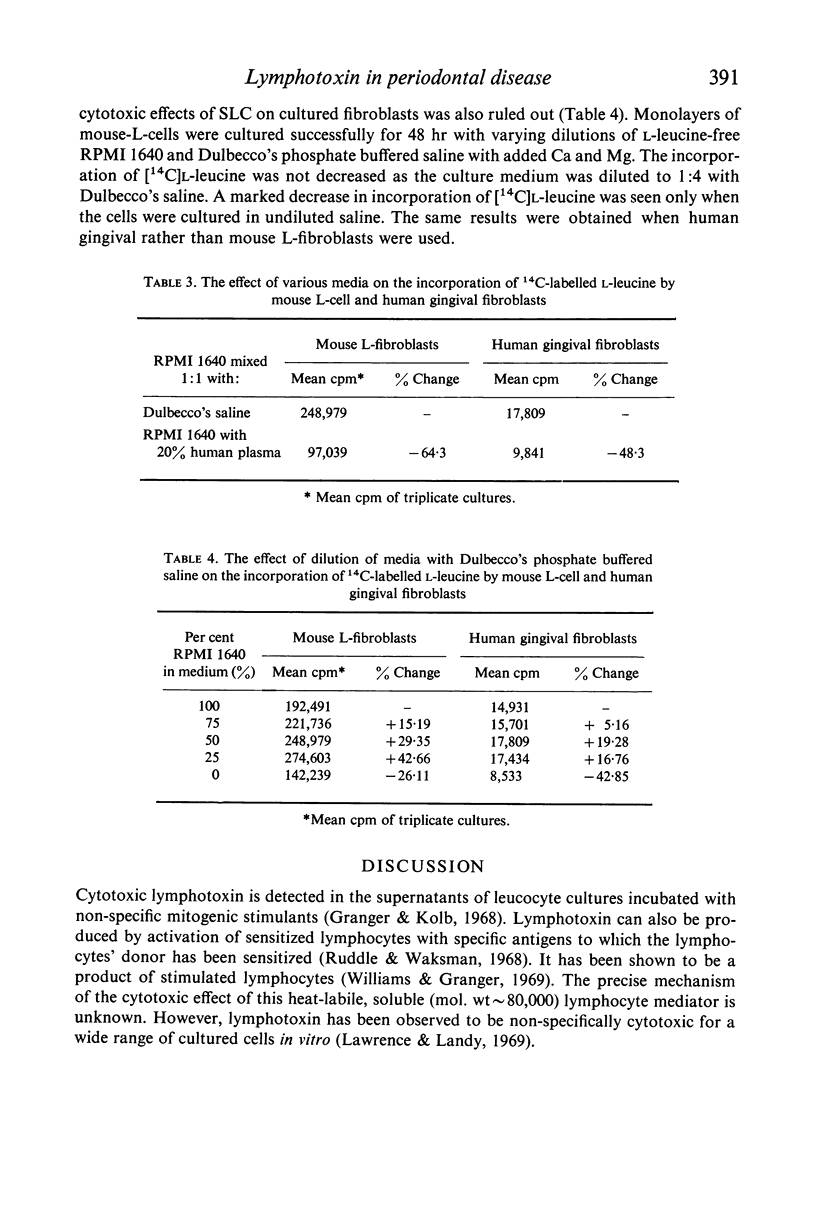
Leucocyte cultures from subjects with periodontal disease when stimulated by human dental-plaque deposit material, or phytohaemagglutinin, produce a soluble factor, lymphotoxin, which is cytotoxic for fibroblasts in vitro. The cytotoxic effect was determined from the degree of inhibition of incorporation of 14C-labelled L-leucine by in vitro cultures of human gingival or mouse L-fibroblasts exposed to supernatants from such cultures. Inhibition of protein synthesis by the fibroblasts was not due to either depletion of nutrients or direct toxicity of the antigenic dental-plaque material. Both plaque-stimulated leucocyte culture supernatants from clinically normal subjects and unstimulated leucocyte culture supernatants from subjects with periodontal disease were significantly less inhibitory than supernatants of plaque-stimulated leucocyte cultures from subjects with periodontal disease. This production of lymphotoxin by leucocytes stimulated with antigen(s) present in dental plaque-deposits may reflect a mechanism of tissue destruction by sensitized lymphocytes present in the tissues of subjects with periodontal disease.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloom B. R., Bennett B. Mechanism of a reaction in vitro associated with delayed-type hypersensitivity. Science. 1966 Jul 1;153(3731):80–82. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3731.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaparas S. D., Thor D. E., Godfrey H. P., Baer H., Hedrick S. R. Tuberculin-active carbohydrate that induces inhibition of macrophage migration but not lymphocyte transformation. Science. 1970 Nov 6;170(3958):637–639. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3958.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger G. A., Kolb W. P. Lymphocyte in vitro cytotoxicity: mechanisms of immune and non-immune small lymphocyte mediated target L cell destruction. J Immunol. 1968 Jul;101(1):111–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton J. E., Leikin S., Oppenheim J. J. Human lymphoproliferative reaction to saliva and dental plaque-deposits: an in vitro correlation with periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 1972 Sep;43(9):522–527. doi: 10.1902/jop.1972.43.9.522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton J. E., Raisz L. G., Simmons H. A., Oppenheim J. J., Mergenhagen S. E. Bone resorbing activity in supernatant fluid from cultured human peripheral blood leukocytes. Science. 1972 Sep 1;177(4051):793–795. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4051.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyi L., Lehner T. Stimulation of lymphocyte transformation by bacterial antigens in patients with periodontal disease. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 Nov;15(11):1089–1096. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90121-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyi L., Wilton J. M., Lehner T. Cell-mediated immunity in periodontal disease; cytotoxicity, migration inhibition and lymphocyte transformation studies. Immunology. 1972 Jan;22(1):141–145. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer J. J., Granger G. A. An improved in vitro assay for lymphotoxin. Cell Immunol. 1972 Jan;3(1):144–149. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90235-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim J. J., Wolstencroft R. A., Gell P. G. Delayed hypersensitivity in the guinea-pig to a protein-hapten conjugate and its relationship to in vitro transformation of lymph node, spleen, thymus and peripheral blood lymphocytes. Immunology. 1967 Jan;12(1):89–102. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter J. B. Cytotoxin(s) produced by human lymphocytes: inhibition by anti-inflammatory steroids and anti-malarial drugs. Cell Immunol. 1971 Apr;2(2):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(71)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick E., Turk J. L. The biological activities of soluble lymphocyte products. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Jan;10(1):1–23. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSSELL A. L. A system of classification and scoring for prevalence surveys of periodontal disease. J Dent Res. 1956 Jun;35(3):350–359. doi: 10.1177/00220345560350030401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddle N. H., Waksman B. H. Cytotoxicity mediated by soluble antigen and lymphocytes in delayed hypersensitivity. 3. Analysis of mechanism. J Exp Med. 1968 Dec 1;128(6):1267–1279. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.6.1267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Altman L. C., Hausman M. S., Mergenhagen S. E. Human mononuclear leukocyte chemotaxis: a quantitative assay for humoral and cellular chemotactic factors. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):857–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Remold H. G., David J. R. Leukotactic factor produced by sensitized lymphocytes. Science. 1969 Mar 7;163(3871):1079–1081. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3871.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. W., Granger G. A. Lymphocyte in vitro cytotoxicity: correlation of derepression with release of lymphotoxin from human lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1969 Aug;103(2):170–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




