Abstract
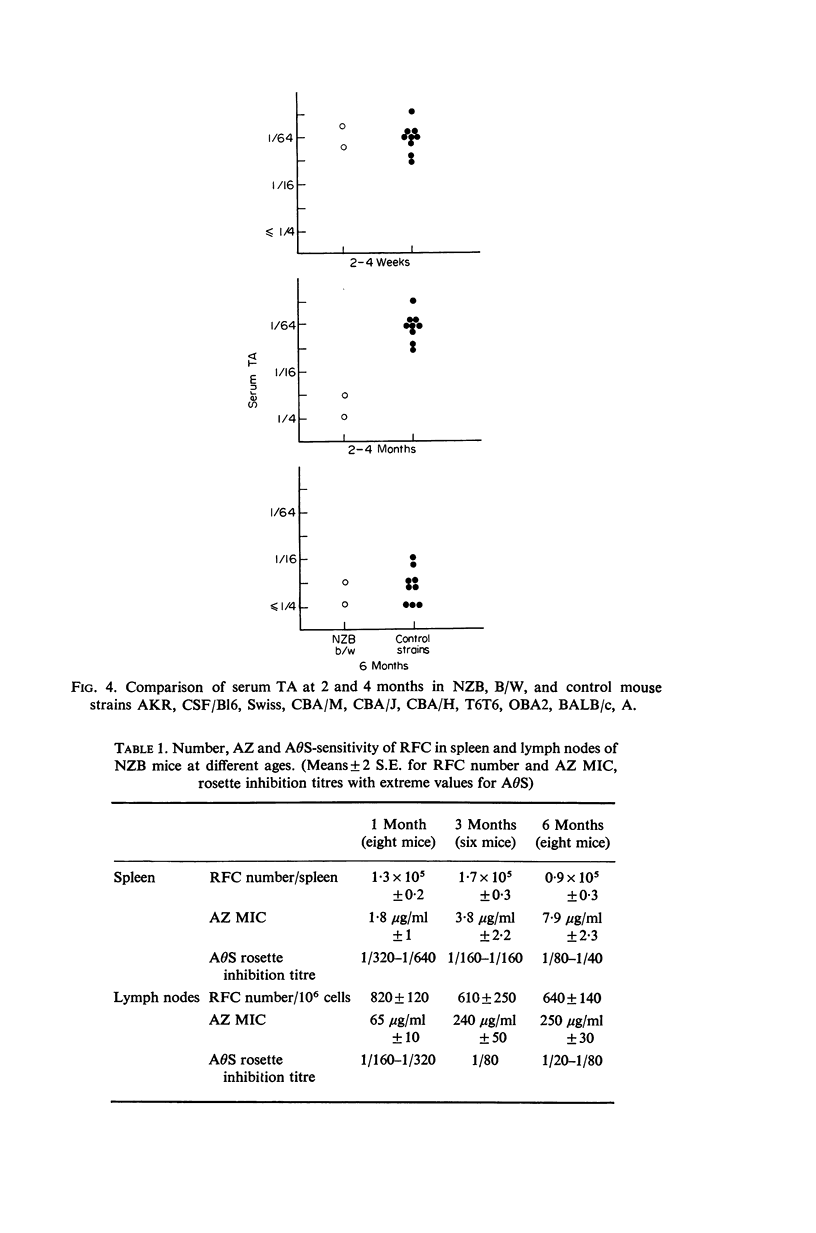
New Zealand Black (NZB) mice and (B/W) F1 hybrids have a normal level of serum `thymic activity' (TA) at birth but this level decreases prematurely between the third and sixth weeks of life. At 2 months, NZB and NZ (B/W) F1 mice have no significant TA, whereas TA is still at birth's level in six control mouse strains and remains at this level until the fourth to the sixth month. Six weeks after the decline of serum TA, NZB mice show disappearance of theta-positive lymph node rosette-forming cells (RFC) and 2 weeks later, progressive decrease in spleen RFC sensitivity to anti-theta serum (AΘS) and azathioprine (AZ) as in neonatally thymectomized CBA mice. Normal AZ and AΘS sensitivity of spleen and lymph node RFC is reconstituted by in vitro or in vivo treatment by thymic extracts. The early thymic abnormalities found in NZB mice are in keeping with the thymic medullar epithelium atrophy reported in newborn NZB mice.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALARCON SEGOVIA D., GALBRAITH R. F., MALDONADO J. E., HOWARD F. M., Jr SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS FOLLOWING THYMECTOMY FOR MYSTHENIA GRAVIS. REPORT OF TWO CASES. Lancet. 1963 Sep 28;2(7309):662–665. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90456-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURNET F. M., HOLMES M. C. THYMIC CHANGES IN THE MOUSE STRAIN NZB IN RELATION TO THE AUTO-IMMUNE STATE. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:229–241. doi: 10.1002/path.1700880129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach J. F., Dardenne M. Absence d'hormone thymique dans le sérum de souris NZB et NZBXNZW et de malades atteints de lupus érythémateux disséminé. J Urol Nephrol (Paris) 1972 Dec;78(12):994–997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach J. F., Dardenne M. Antigen recognition by T lymphocytes. II. Similar effects of azathioprine, antilymphocyte serum, and anti-theta serum on rosette-forming lymphocytes in normal and neonatally thymectomized mice. Cell Immunol. 1972 Jan;3(1):11–21. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90221-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach J. F., Dardenne M. Antigen recognition by T lymphocytes. Thymus and marrow dependence of spontaneous rosette forming cells in the mouse. Cell Immunol. 1972 Jan;3(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90220-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach J. F., Dardenne M., Goldstein A. L., Guha A., White A. Appearance of T-cell markers in bone marrow rosette-forming cells after incubation with thymosin, a thymic hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2734–2738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach J. F., Dardenne M. Thymus dependency of rosette-forming cells: evidence for a circulating thymic hormone. Transplant Proc. 1972 Sep;4(3):345–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey T. P. Azathioprine (Imuran) administration and the development of malignant lymphomas in NZB mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1968 May;3(4):305–312. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. L., Jr Incorporation of sulfate by the mouse thymus: its relation to secretion by medullary epithelial cells and to thymic lymphopoiesis. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):927–957. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denman A. M., Denman E. J. Depletion of long-lived lymphocytes in old New Zealand black mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Apr;6(4):457–472. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A. L., Guha A., Zatz M. M., Hardy M. A., White A. Purification and biological activity of thymosin, a hormone of the thymus gland. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1800–1803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMES M. C., GORIE J., BURNET F. M. Transmission by splenic cells of an autoimmune disease occurring spontaneously in mice. Lancet. 1961 Sep 16;2(7203):638–639. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)90313-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howie J. B., Helyer B. J. The immunology and pathology of NZB mice. Adv Immunol. 1968;9:215–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60444-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. H., Dixon F. J. Genesis of antinuclear antibody in NZB-W mice: role of genetic factors and of viral infections. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Jun;6(6):829–839. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmel E., Hurd E. R., Ziff M. Differential effects of 6-mercaptopurine and cyclophosphamide on autoimmune phenomena in NZB mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Feb;8(2):355–362. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leventhal B. G., Talal N. Response of NZB and NZB-NZW spleen cells to mitogenic agents. J Immunol. 1970 Apr;104(4):918–923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton J. I., Siegel B. V. Response of NZB mice to foreign antigen and development of autoimmune disease. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1969 Feb;6(1):78–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Playfair J. H. Strain differences in the immune responses of mice. 3. A raised tolerance threshold in NZB thymus cells. Immunology. 1971 Dec;21(6):1037–1043. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodey G. E., Good R. A., Yunis E. J. Progressive loss in vitro of cellular immunity with ageing in strains of mice susceptible to autoimmune disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Sep;9(3):305–311. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon J. C., Benveniste J. The immune response in NZBxNZW F1 hybrid mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Feb;4(2):213–225. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai T., Mellors R. C. Natural thymocytotoxic autoantibody and reactive antigen in New Zealand black and other mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1412–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staples P. J., Talal N. Relative inability to induce tolerance in adult NZB and NZB-NZW F1 mice. J Exp Med. 1969 Jan 1;129(1):123–139. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutman O., Yunis E. J., Good R. A. Deficient immunologic functions of NZB mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Apr;127(4):1204–1207. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thivolet J., Monier J. C., Ruel J. P., Richard M. H. Antinuclear autoantibodies in Swiss mice thymectomized at birth. Nature. 1967 Jun 10;214(5093):1134–1136. doi: 10.1038/2141134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J. L., Poulter L. W. Selective depletion of lymphoid tissue by cyclophosphamide. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Feb;10(2):285–296. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman B. H., Raff M. C., East J. T and B lymphocytes in New Zealand black mice. An analysis of the theta, TL and MBLA markers. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 May;11(1):1–11. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir D. M., McBride W., Naysmith J. D. Immune response to a soluble protein antigen in NZB mice. Nature. 1968 Sep 21;219(5160):1276–1277. doi: 10.1038/2191276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatz M. M., Mellors R. C., Lance E. M. Changes in lymphoid populations of ageing CBA and NZB mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Mar;8(3):491–500. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries M. J., Hijmans W. Pathological changes of thymic epithelial cells and autoimmune disease in NZB, NZW and (NZB x NZW)F1 mice. Immunology. 1967 Feb;12(2):179–196. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


