Abstract
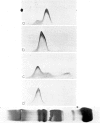
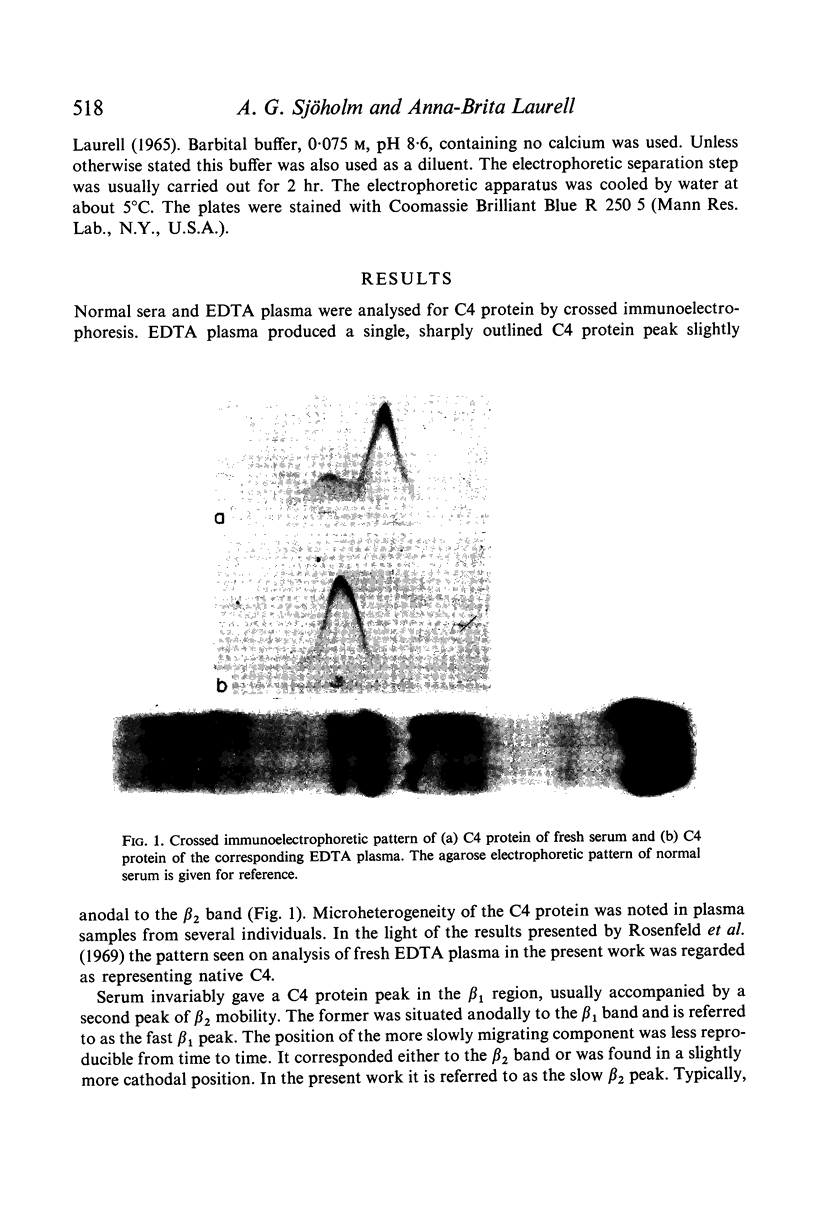
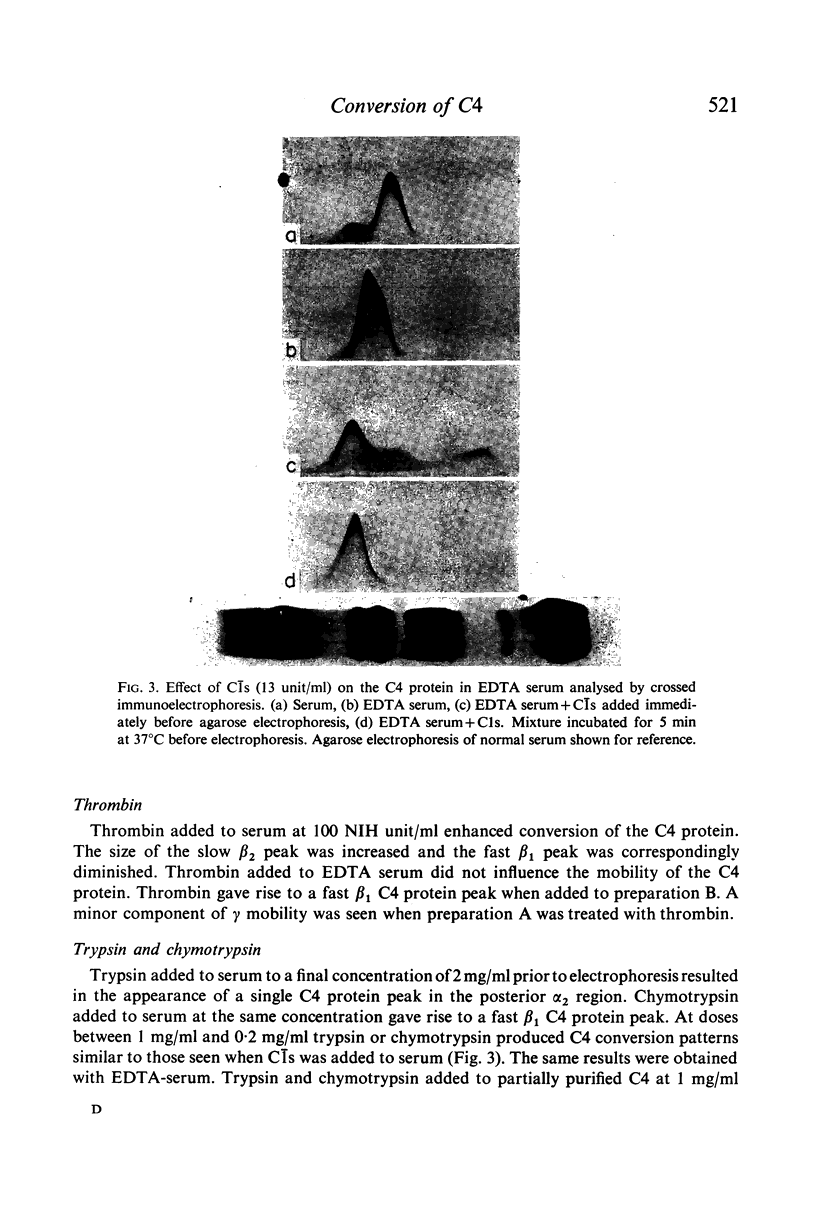
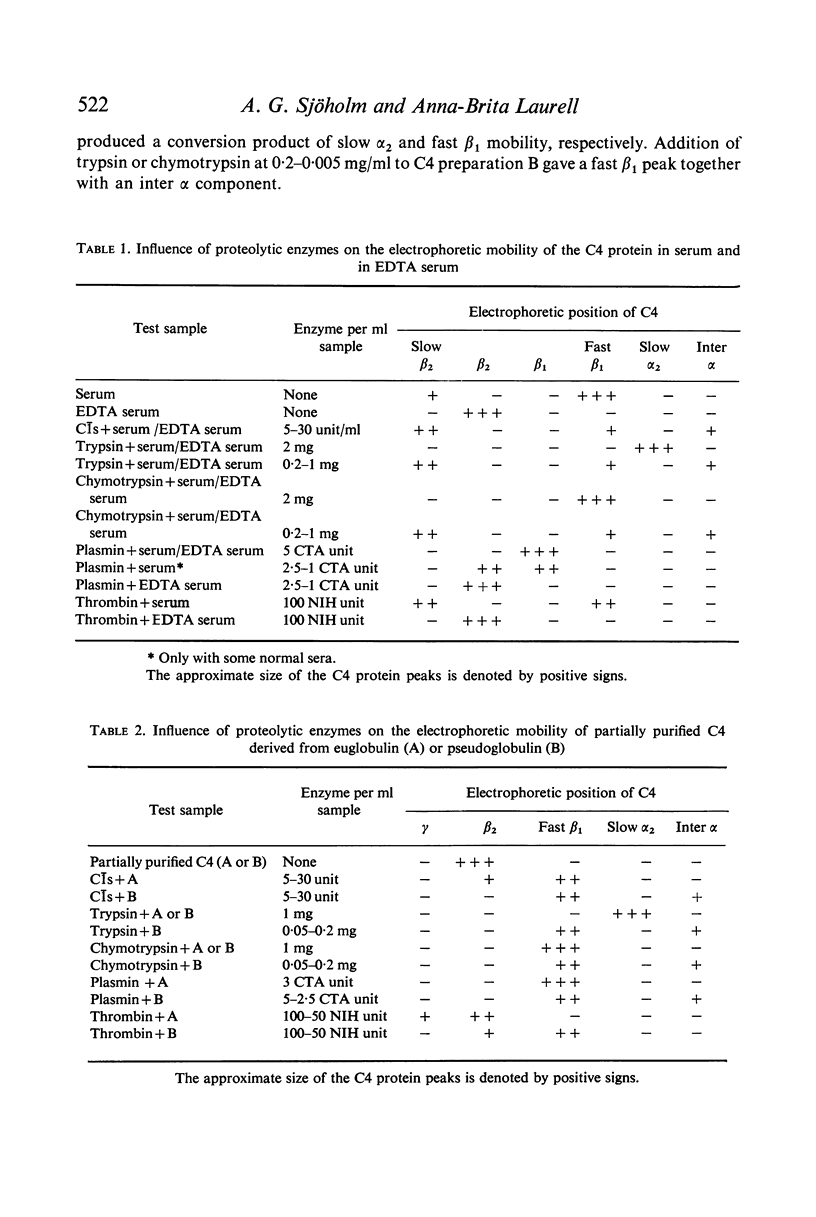
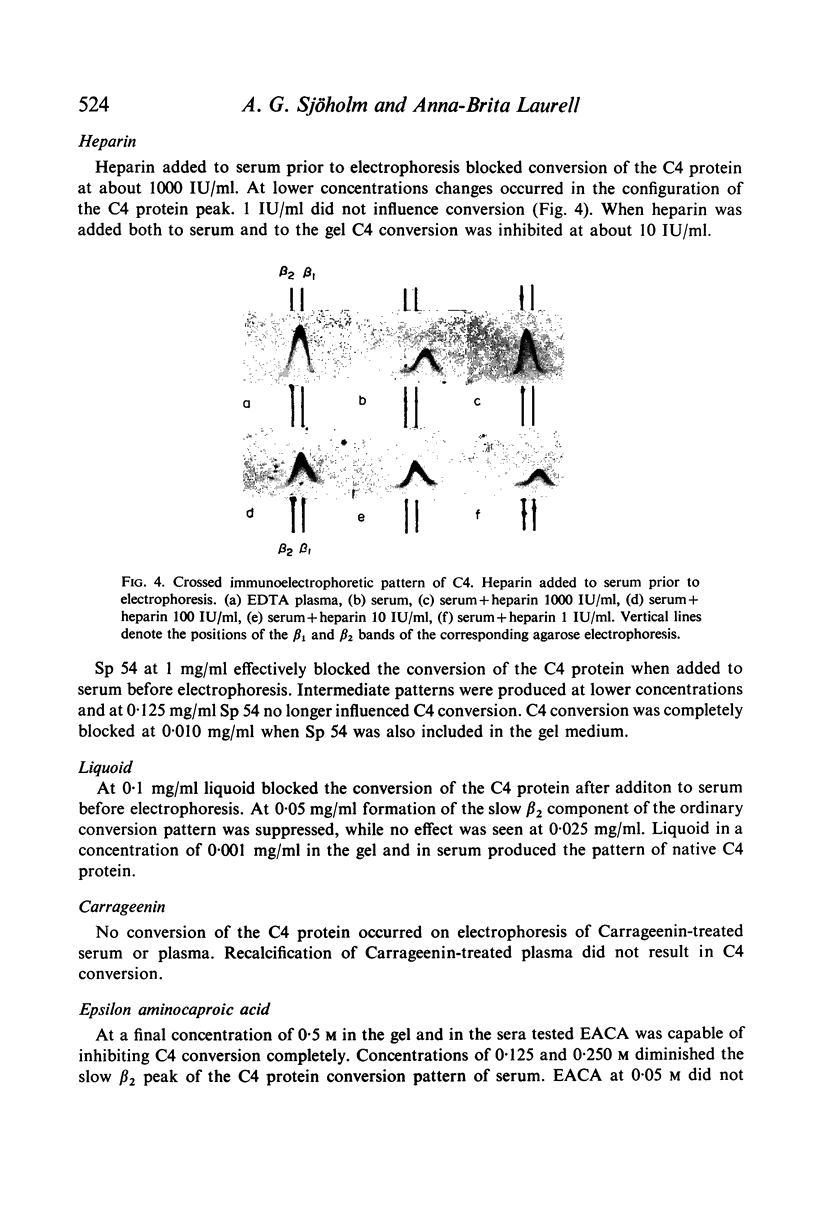
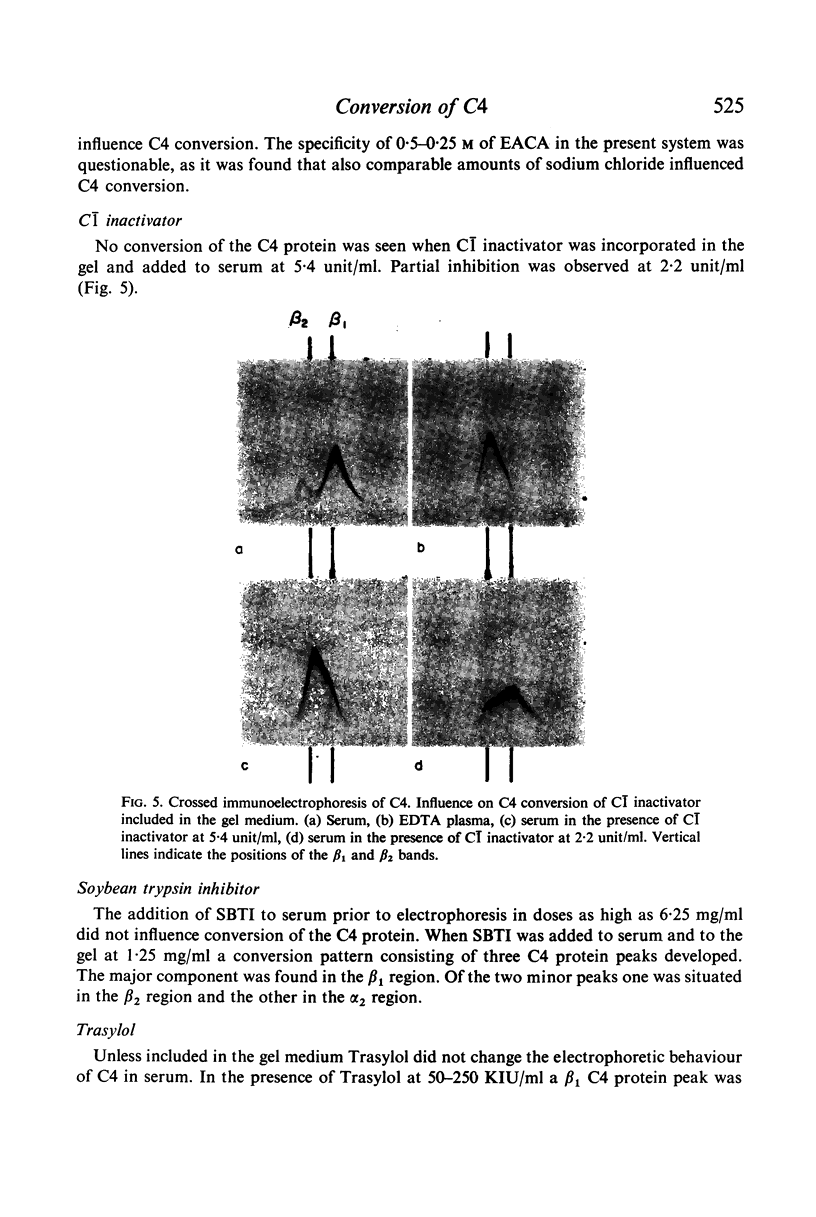
C4 in EDTA plasma and partially purified C4 give a β2 peak on crossed immunoelectrophoresis. During electrophoresis C4 in serum is converted to a product of fast β1 mobility, usually accompanied by a slow β2 peak. Conversion in serum is inhibited by EDTA. Storage of serum at room temperature results in a gradual increase of the slow β2 peak. Storage of EDTA plasma changes the configuration of the native β2 peak. C[unk]s, trypsin, chymotrypsin, plasmin or thrombin added to partially purified C4 is capable of producing a fast β1 C4 protein peak. C[unk]s, trypsin and chymotrypsin give this conversion product also when added to EDTA serum. C[unk]s, trypsin and chymotrypsin also give rise to a show β2 and an inter α C4 conversion product in serum, probably consisting of complex formations between C4 and other serum proteins. Enzyme inhibitors known to interfere with C[unk] inhibit the conversion of C4 in serum on agarose electrophoresis. The results suggest that such conversion is caused by an activation of C1 during electrophoresis.
Full text
PDF


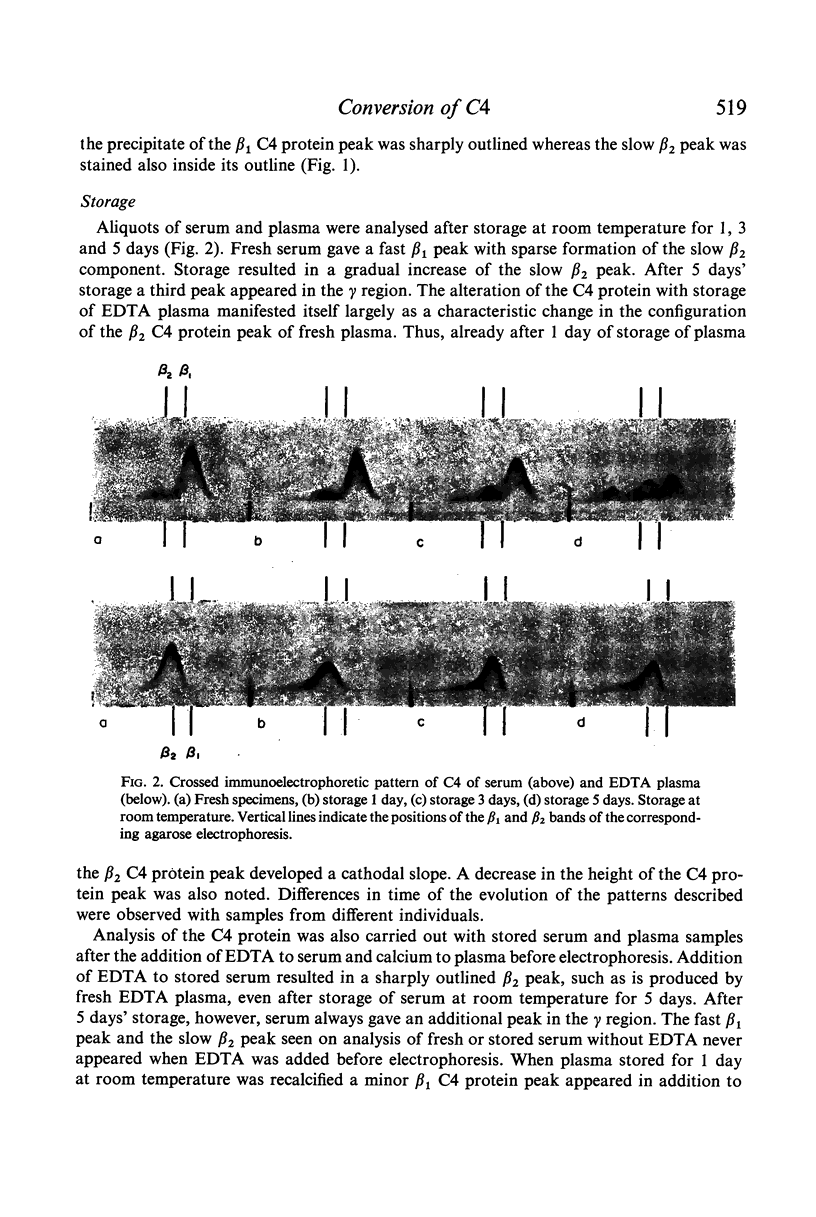






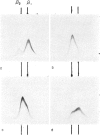
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORSOS T., RAPP H. J., CRISLER C. THE INTERACTION BETWEEN CARRAGEENAN AND THE FIRST COMPONENT OF COMPLEMENT. J Immunol. 1965 May;94:662–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back N., Steger R. Effect of inhibitors on kinin-releasing activity of proteases. Fed Proc. 1968 Jan-Feb;27(1):96–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breckenridge R. T., Ratnoff O. D. The Role of Proaccelerin in Human Blood Coagulation. Evidence that Proaccelerin Is Converted to a Prothrombin-converting Principle by Activated Stuart Factor: With Notes on the Anticoagulant Action of Soybean Trypsin Inhibitor, Protamine Sulfate, and Hexadimethrine Bromide. J Clin Invest. 1965 Feb;44(2):302–314. doi: 10.1172/JCI105144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budzko D. B., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Cleavage of the fourth component of human complement (C4) by C1 esterase: isolation and characteristics of the low molecular weight product. Immunochemistry. 1970 Feb;7(2):227–234. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson V. H. Mechanisms of activation of C'1 esterase in hereditary angioneurotic edema plasma in vitro. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):411–429. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FJELLSTROM K. E. Preparation of complement reagents by means of gel filtration. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1962;54:439–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes C. D., Pensky J., Ratnoff O. D. Inhibition of activated Hageman factor and activated plasma thromboplastin antecedent by purified serum C1 inactivator. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Nov;76(5):809–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAINES A. L., LEPOW I. H. STUDIES ON HUMAN C'1-ESTERASE. I. PURIFICATION AND ENZYMATIC PROPERTIES. J Immunol. 1964 Mar;92:456–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEIMBURGER N., SCHWICK G. [Fibrin agar electrophoresis. 1. Description of the method]. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1962 Jul 15;7:432–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedner U., Nilsson I. M. Comparison between a direct and an indirect method for determining plasminogen. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1971 Oct 31;26(2):289–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. J., Kline D. L., Alkjaersig N. Assay methods and standard preparations for plasmin, plasminogen and urokinase in purified systems, 1967-1968. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1969 Apr 30;21(2):259–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEPOW I. H., NAFF G. B., TODD E. W., PENSKY J., HINZ C. F. Chromatographic resolution of the first component of human complement into three activities. J Exp Med. 1963 Jun 1;117:983–1008. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.6.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEPOW I. H., RATNOFF O. D., LEVY L. R. Studies on the activation of a proesterase associated with partially purified first component of human complement. J Exp Med. 1958 Mar 1;107(3):451–474. doi: 10.1084/jem.107.3.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE L., OSLER A. G., MAYER M. M. Studies on the role of Ca++ and Mg++ in complement fixation and immune hemolysis. III. The respective roles of Ca++ and Mg++ in immune hemolysis. J Immunol. 1953 Nov;71(5):374–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY L. R., LEPOW I. H. Assay and properties of serum inhibitor of C'l-esterase. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Aug-Sep;101:608–611. doi: 10.3181/00379727-101-25034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell A. B., Lundh B., Malmquist J. Inability of a highly purified streptokinase preparation to inactivate complement in serum. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;64(3):318–328. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.64.3.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell A. B., Mårtensson U. C1 inactivator protein complexed with albumin in plasma from a patient with angioneurotic edema. Eur J Immunol. 1971 Apr;1(2):146–149. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830010215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell A. B., Sjöholm A., Johnson U. Quantitation of the fourth complement component by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Sep;7(3):423–430. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loos M., Borsos T., Rapp H. J. Activation of the first component of complement evidence for an internal activation step. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):683–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J., LEPOW I. H. C'1 ESTERASE EFFECT ON ACTIVITY AND PHYSICOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF THE FOURTH COMPONENT OF COMPLEMENT. J Exp Med. 1965 May 1;121:819–833. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.5.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naff G. B., Ratnoff O. S. The enzymatic nature of C'1r. Conversion of C'1s to C'1 esterase and digestion of amino acid esters by C'1r. J Exp Med. 1968 Oct 1;128(4):571–593. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.4.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., LEPOW I. H. Some properties of an esterase derived from preparations of the first component of complement. J Exp Med. 1957 Aug 1;106(2):327–343. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnoff O. D., Pensky J., Ogston D., Naff G. B. The inhibition of plasmin, plasma kallikrein, plasma permeability factor, and the C'1r subcomponent of the first component of complement by serum C'1 esterase inhibitor. J Exp Med. 1969 Feb 1;129(2):315–331. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. I., Ruddy S., Austen K. F. Structural polymorphism of the fourth component of human complement. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2283–2292. doi: 10.1172/JCI106194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR F. B., Jr, FUDENBERG H. INHIBITION OF THE C'-1 COMPONENT OF COMPLEMENT BY AMINO ACIDS. Immunology. 1964 Jul;7:319–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vroon D. H., Schultz D. R., Zarco R. M. The separation of nine components and two inactivators of components of complement in humansserum. Immunochemistry. 1970 Jan;7(1):43–61. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walb D., Loos M., Hadding U. In vitro-Untersuchungen über Angriffspunkt und Wirkungsunterschiede zum Heparin. Antikomplementäre Wirkung eines semisynthetischen Pentosan-Polysulfo-Esters. Z Naturforsch B. 1971 May;26(5):403–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]