Abstract
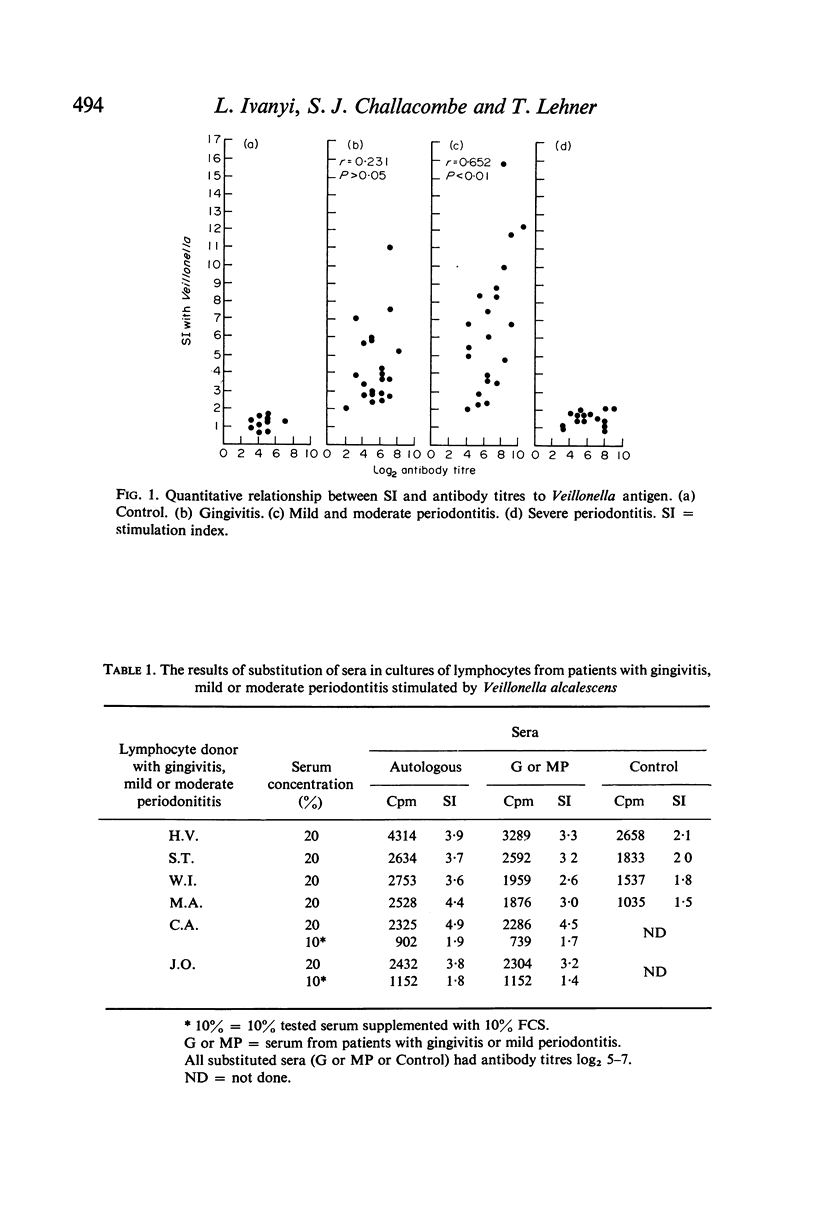
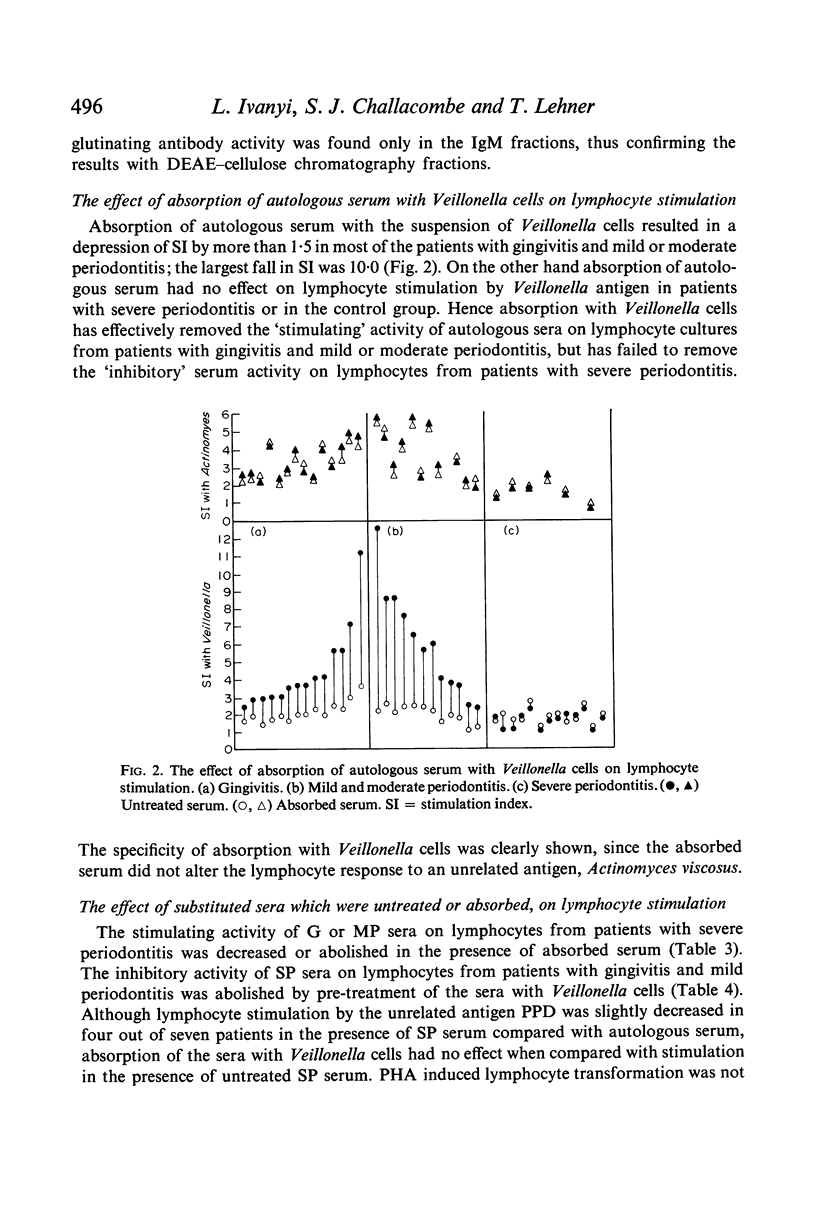
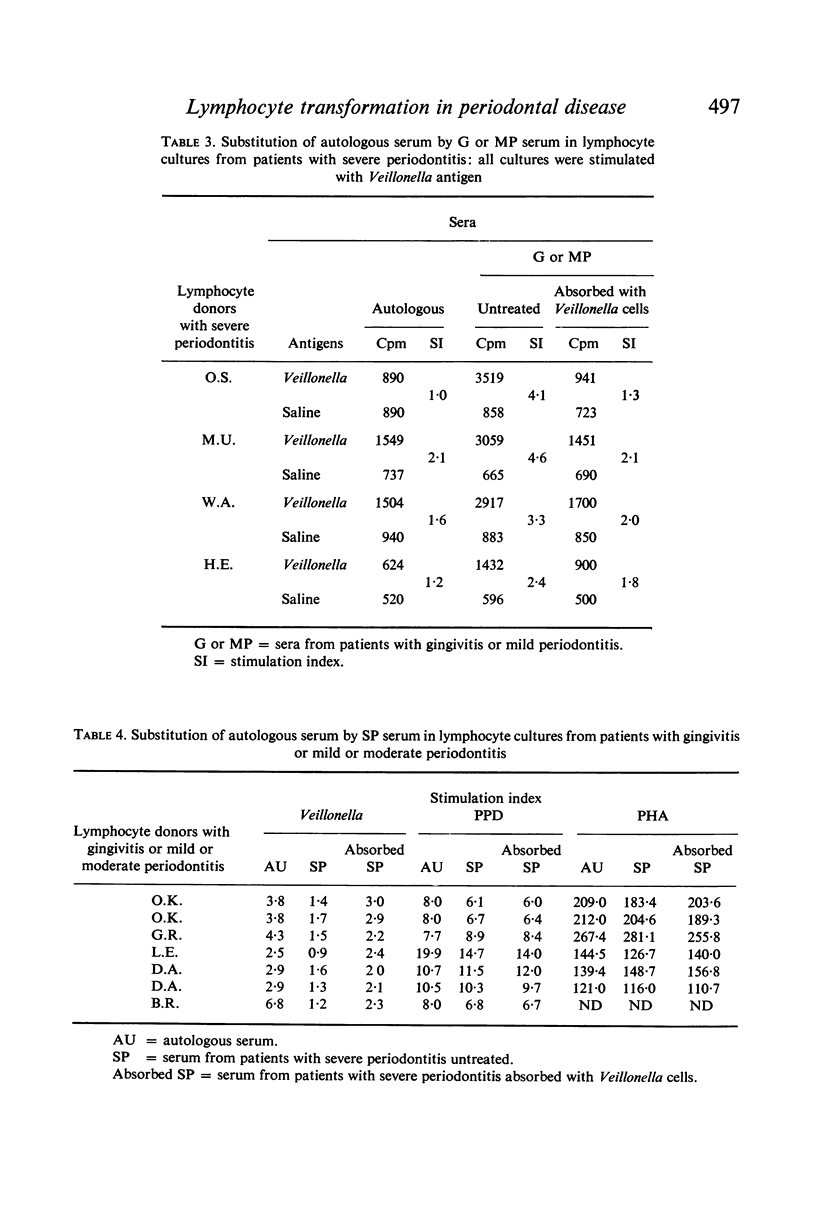
Peripheral blood lymphocytes from patients with periodontal disease were stimulated in vitro by sonicates of Veillonella alcalescens in the presence of autologous and substituted sera which were either untreated or absorbed with Veillonella cells. A significant positive correlation was found between the level of lymphocyte stimulation and IgM class of haemagglutinating antibody titres in patients with mild periodontitis (MP) (P<0·01) but not in those with gingivitis (G), severe periodontitis (SP) or in the control group (C). Absorption of autologous serum with a suspension of Veillonella cells resulted in a depression of lymphocyte stimulation by Veillonella antigen in G or MP patients, but had no effect on lymphocyte stimulation in SP patients. Furthermore, absorption with Veillonella abolished the stimulating activity of substituted G or MP sera on lymphocyte cultures from SP patients and the inhibitory activity of SP sera on lymphocyte cultures from G or MP patients. Serum absorption was specific, as it did not affect the mitogenic response of lymphocytes to Actinomyces viscosus, PPD or PHA. The data is interpreted in terms of modulation of lymphocyte responses in vitro by stimulating or inhibitory antibodies.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basten A., Sprent J., Miller J. F. Receptor for antibody-antigen complexes used to separate T cells from B cells. Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 9;235(58):178–180. doi: 10.1038/newbio235178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy R. Cellular immunity to autologous platelets and serum-blocking factors in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Lancet. 1972 Jan 1;1(7740):6–9. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennert G. The mechanism of antibody-induced stimulation and inhibition of the immune response. J Immunol. 1971 Apr;106(4):951–955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakhri O., Hobbs J. R. Target cell death without added complement after cooperation of 7S antibodies with non-immune lymphocytes. Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 9;235(58):177–178. doi: 10.1038/newbio235177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellström I., Hellström K. E., Allison A. C. Neonatally induced allograft tolerance may be mediated by serum-borne factors. Nature. 1971 Mar 5;230(5288):49–50. doi: 10.1038/230049a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellström K. E., Hellström I. Immunological enhancement as studied by cell culture techniques. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1970;24:373–398. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.24.100170.002105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry C., Jerne N. K. Competition of 19S and 7S antigen receptors in the regulation of the primary immune response. J Exp Med. 1968 Jul 1;128(1):133–152. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyi L., Lehner T. Stimulation of lymphocyte transformation by bacterial antigens in patients with periodontal disease. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 Nov;15(11):1089–1096. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90121-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyi L., Lehner T. The significance of serum factors in stimulation of lymphocytes from patients with periodontal disease by Veillonella alcalescens. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1971;41(4):620–627. doi: 10.1159/000230554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyi L., Wilton J. M., Lehner T. Cell-mediated immunity in periodontal disease; cytotoxicity, migration inhibition and lymphocyte transformation studies. Immunology. 1972 Jan;22(1):141–145. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagarlamoody S. M., Aust J. C., Tew R. H., McKhann C. F. In vitro detection of cytotoxic cellular immunity against tumor-specific antigens by a radioisotopic technique. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1346–1350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein W. J., Jr Lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity in vitro. Effect of enhancing antisera. J Exp Med. 1971 Nov 1;134(5):1238–1252. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.5.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY H. B., SOBER H. A. A simple chromatographic method for preparation of gamma globulin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Jan;103:250–252. doi: 10.3181/00379727-103-25476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T. Characterization of mucosal antibodies in recurrent aphthous ulceration and Behcet's syndrome. Arch Oral Biol. 1969 Jul;14(7):843–853. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(69)90174-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Parish C. R. Regulation of the immune response by antibody. I. Suppression of antibody formation and concomitant enhancement of cell-mediated immunity by passive antibody. Cell Immunol. 1972 May;4(1):66–85. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modabber F., Coons A. H. Antibody cytophilic for lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1972 May;108(5):1447–1452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim J. J. Modulation of in vitro lymphocyte transformation by antibodies: enhancement by antigen-antibody complexes and inhibition by antibody excess. Cell Immunol. 1972 Mar;3(3):341–360. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90243-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paraskevas F., Lee S. T., Orr K. B., Israels L. G. A receptor for Fc on mouse B-lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1972 May;108(5):1319–1327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhr J. W. Passive sensitization of lymphocytes and macrophages by antigen-antibody complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1599–1606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


