Abstract
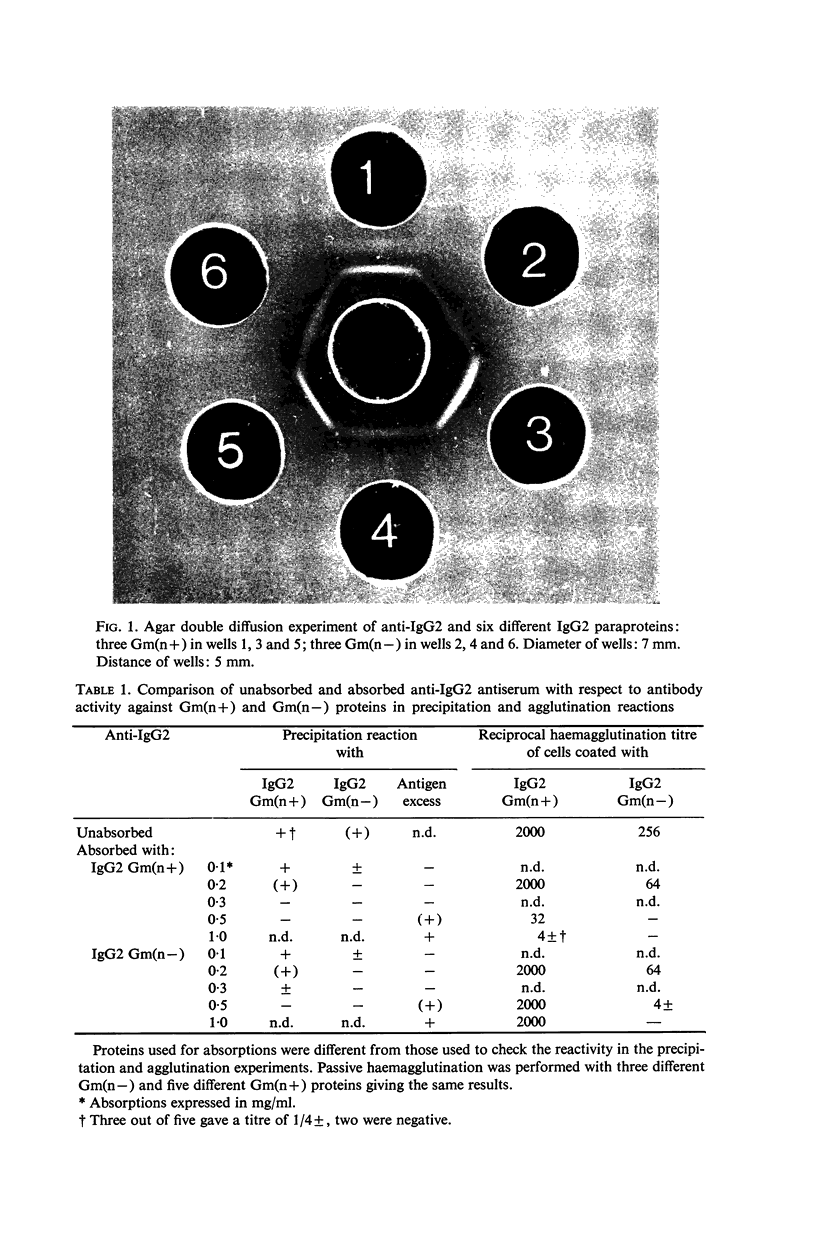
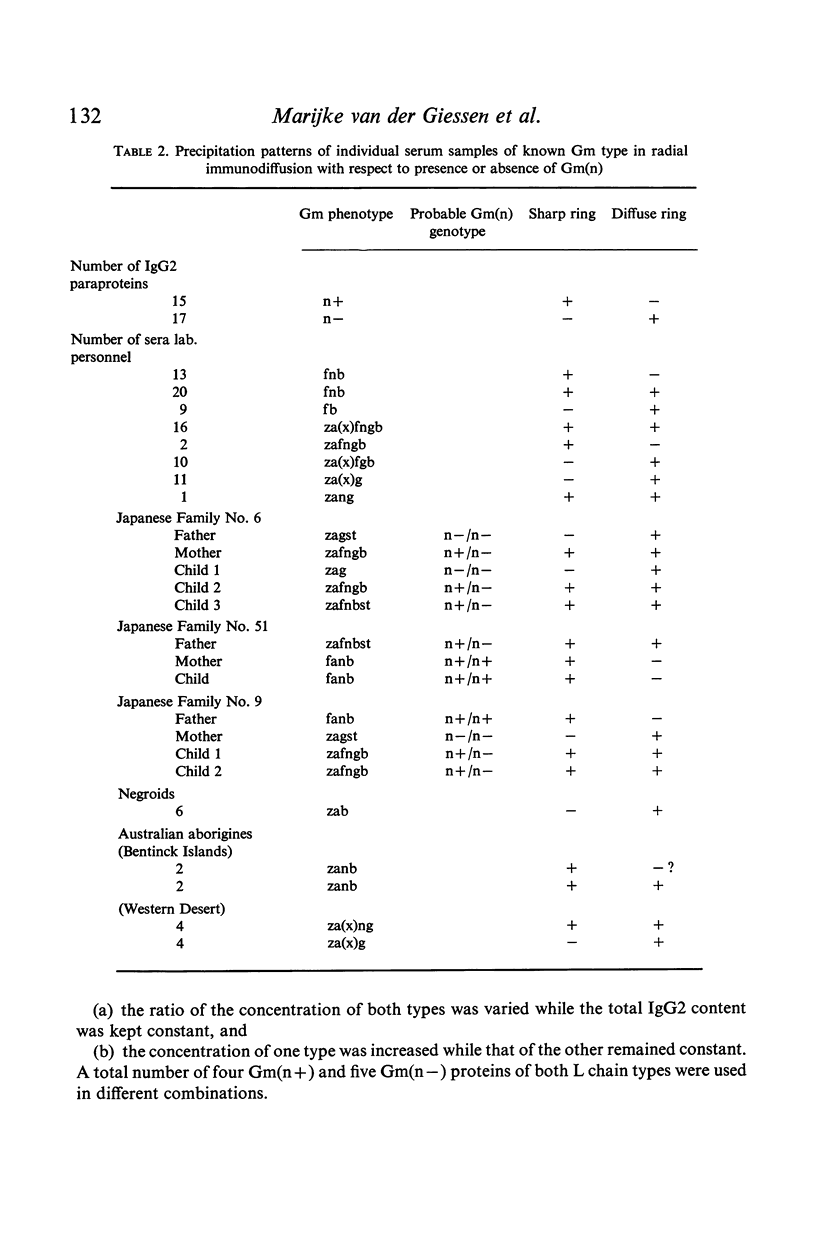
A monkey antiserum was obtained by immunization with Gm(n+) IgG2 proteins. After it had been rendered specific for the IgG2 subclass, it was shown to contain antibodies of two specificities, i.e. anti-γ2 and anti-Gm(n). Precipitation and haemagglutination experiments, using unabsorbed antiserum and antiserum absorbed with Gm(n+) or Gm(n−) proteins, made it clear that the anti-Gm(n) was unable to form precipitates with Gm(n+) proteins without the assistance of anti-γ2 antibodies. Results obtained in radial immunodiffusion with serum samples of known Gm genotype showed that the antiserum differentiates three types of individuals: homozygous Gm(n− /n−), heterozygous Gm(n+ /n−) and homozygous Gm(n+ /n+).
The amount of IgG2 present in serum samples from seventy-four individuals of variable Gm types was determined by comparison with a standard serum. It was found that the mean level of female sera (4·2 mg/ml) was higher than that of male sera (3·3 mg/ml). It was further shown that the IgG2 level was correlated with Gm(n). The total IgG2 content of individuals possessing the Gm(n) marker was higher than that of individuals of otherwise identical Gm type but lacking this factor. In individuals heterozygous for Gm(n) the level of Gm(n+) protein was significantly higher than that of Gm(n−) protein.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALLIEUX R. E., BERNIER G. M., TOMINAGA K., PUTNAM F. W. GAMMA GLOBULIN ANTIGENIC TYPES DEFINED BY HEAVY CHAIN DETERMINANTS. Science. 1964 Jul 10;145(3628):168–170. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3628.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREY H. M., KUNKEL H. G. H CHAIN SUBGROUPS OF MYELOMA PROTEINS AND NORMAL 7S GAMMA-GLOBULIN. J Exp Med. 1964 Aug 1;120:253–266. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay F. C., Hull M. G., Torrigiani G. The transfer of human IgG subclasses from mother to foetus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Sep;9(3):355–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber H., Fudenberg H. H. Receptor sites of human monocytes for IgG. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1968;34(1):18–31. doi: 10.1159/000230091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Ishizaka K., Salmon S., Fudenberg H. Biologic activities of aggregated gamma-globulin. 8. Aggregated immunoglobulins of different classes. J Immunol. 1967 Jul;99(1):82–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferis R., Weston P. D., Stanworth D. R., Clamp J. R. Relationship between the papain sensitivity of human gammaG immunoglobulins and their heavy chain subclass. Nature. 1968 Aug 10;219(5154):646–649. doi: 10.1038/219646b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNKEL H. G., ALLEN J. C., GREY H. M., MARTENSSON L., GRUBB R. A RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE H CHAIN GROUPS OF 7S GAMMA-GLOBULIN AND THE GM SYSTEM. Nature. 1964 Jul 25;203:413–414. doi: 10.1038/203413a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalff M. W. A population study on serum immunoglobulin levels. Clin Chim Acta. 1970 May;28(2):277–289. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(70)90092-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel H. G., Yount W. J., Litwin S. D. Genetically determined antigen of the Ne subgroup of gamma-globulin: detection by precipitin analysis. Science. 1966 Nov 25;154(3752):1041–1043. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3752.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A., Skvaril F., Steinberg A. G., Van Loghem E., Terry W. D. Correlations between the concentrations of the four sub-classes of IgG and Gm Allotypes in normal human sera. J Immunol. 1972 Jan;108(1):195–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A., Skvaril F., van Loghem E., Kleemola M. Human IgG subclasses in maternal and fetal serum. Vox Sang. 1971 Dec;21(6):481–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1971.tb04808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A., Terry W. D., Waldmann T. A. Metabolic properties of IgG subclasses in man. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):673–680. doi: 10.1172/JCI106279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POULIK M. D., SHUSTER J. HETEROGENEITY OF H CHAINS OF MYELOMA PROTEINS: SUSCEPTIBILITY TO PAPAIN AND TRYPSIN. Nature. 1964 Nov 7;204:577–579. doi: 10.1038/204577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L., Fishkin B. G., Grey H. M. Catabolism of human gammaG-immunoglobulins of different heavy chain subclasses. I. Catabolism of gammaG-myeloma proteins in man. J Clin Invest. 1968 Oct;47(10):2323–2330. doi: 10.1172/JCI105917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRY W. D., FAHEY J. L. SUBCLASSES OF HUMAN GAMMA-2-GLOBULIN BASED ON DIFFERENCES IN THE HEAVY POLYPEPTIDE CHAINS. Science. 1964 Oct 16;146(3642):400–401. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3642.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry W. D., Fahley J. L., Steinberg A. G. GM and INV factors in subclasses of human IgG. J Exp Med. 1965 Dec 1;122(6):1087–1102. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.6.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry W. D. Skin-sensitizing activity related to gamma- polypeptide chain characteristics of human IgG. J Immunol. 1965 Dec;95(6):1041–1047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount W. J., Kunkel H. G., Litwin S. D. Studies of the Vi (gamma-2c) subgroup of gamma-globulin. A relationship between concentration and genetic type among normal individuals. J Exp Med. 1967 Jan 1;125(1):177–190. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]