Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERG O., KAELLEN B. EFFECT OF MONONUCLEAR BLOOD CELLS FROM MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS PATIENTS ON NEUROGLIA IN TISSUE CULTURE. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1964 Jul;23:550–559. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196407000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORNSTEIN M. B., CRAIN S. M. FUNCTIONAL STUDIES OF CULTURED BRAIN TISSUES AS RELATED TO "DEMYELINATIVE DISORDERS". Science. 1965 May 28;148(3674):1242–1244. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3674.1242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker H. W., Balla J. I., Burger H. G., Ebeling P., Mackay I. R. Multiple sclerosis and autoimmune diseases. Aust N Z J Med. 1972 Aug;2(3):256–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1972.tb03071.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
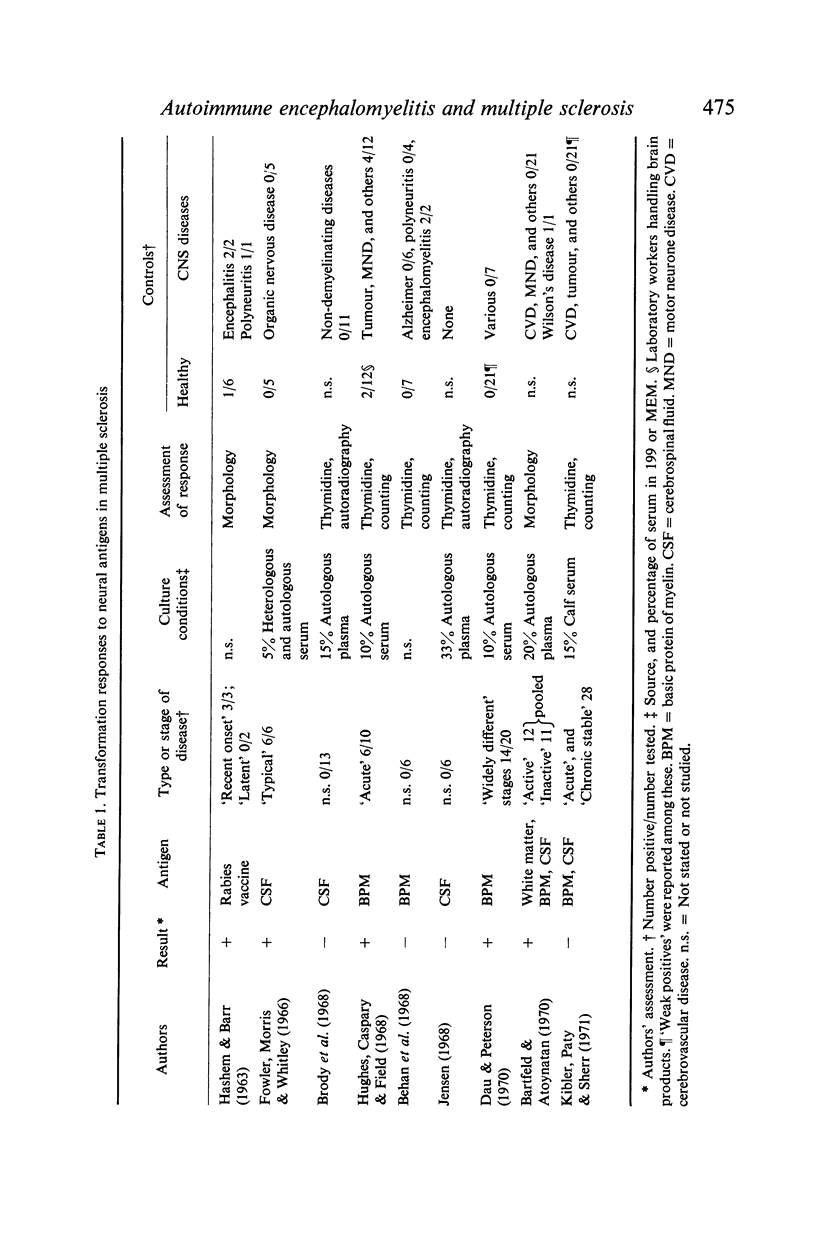
- Bartfeld H., Atoynatan T. In vitro delayed (cellular) hypersensitivity in multiple sclerosis to central nervous system antigens. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;39(4):361–367. doi: 10.1159/000230364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartfeld H., Atoynatan T. Lymphocyte transformation in multiple sclerosis. Br Med J. 1970 Apr 11;2(5701):91–92. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5701.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behan P. O., Behan W. M., Feldman R. G., Kies M. W. Cell-mediated hypersensitivity to neural antigens. Occurrence in human patients and nonhuman primates with neurological diseases. Arch Neurol. 1972 Aug;27(2):145–152. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1972.00490140049008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behan P. O., Geschwind N., Lamarche J. B., Lisak R. P., Kies M. W. Delayed hypersensitivity to encephalitogenic protein in disseminated encephalomyelitis. Lancet. 1968 Nov 9;2(7576):1009–1012. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91299-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein M. B., Crain S. M. Lack of correlation between changes in bioelectric functions and myelin in cultured CNS tissues chronically exposed to sera from animals with EAE. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1971 Jan;30(1):129–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody J. A. Epidemiology of multiple sclerosis and a possible virus aetiology. Lancet. 1972 Jul 22;2(7769):173–176. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91340-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody J. A., Harlem M. M., Kurtzke J. F., White L. R. Unsuccessful attempt to induce transformation by cerebrospinal fluid in cultured lymphocytes from patients with multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1968 Jul 25;279(4):202–204. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196807252790408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell B., Vogel P. J., Fisher E., Lorenz R. Myelin basic protein administration in multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol. 1973 Jul;29(1):10–15. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490250028003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnegie P. R. Amino acid sequence of the encephalitogenic basic protein from human myelin. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(1):57–67. doi: 10.1042/bj1230057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspary E. A., Hughes D., Field E. J. On the mode of action of antilymphocytic serum: experiments on electrophoretic mobility of macrophages in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Sep;7(3):395–400. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerf J. A., Carels G. Multiple sclerosis: serum factor producing reversible alterations in bioelectric responses. Science. 1966 May 20;152(3725):1066–1068. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3725.1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coates A. S., Lennon V. A. Lymphocytes binding basic protein of myelin; cytophilic serum antibody and effect of adjuvant. Immunology. 1973 Mar;24(3):425–434. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dau P. C., Peterson R. D. Transformation of lymphocytes from patients with multiple sclerosis. Use of encephalitogen of human origin, with a report of a trial of immunosuppressive therapy in multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol. 1970 Jul;23(1):32–40. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1970.00480250036006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon F. J. Presidential address. Pathogenesis of immunologic disease. J Immunol. 1972 Aug;109(2):187–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling P. C., Kim S. U., Murray M. R., Cook S. D. Serum 19S and 7S demyelinating antibodies in multiple sclerosis. J Immunol. 1968 Nov;101(5):1101–1104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunkley P. R., Coates A. S., Carnegie P. R. Communications. Encephalitogenic activity of peptides from the smaller basic protein of rat myelin. J Immunol. 1973 Jun;110(6):1699–1701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einstein E. R., Chao L. P., Csejtey J. Suppression of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by chemically modified encephalitogen. Immunochemistry. 1972 Oct;9(10):1013–1019. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90111-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einstein E. R., Csejtey J., Dalal K. B., Adams C. W., Bayliss O. B., Hallpike J. F. Proteolytic activity and basic protein loss in and around multiple sclerosis plaques: combined biochemical and histochemical observations. J Neurochem. 1972 Mar;19(3):653–662. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01382.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eylar E. H., Brostoff S., Hashim G., Caccam J., Burnett P. Basic A1 protein of the myelin membrane. The complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 25;246(18):5770–5784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eylar E. H., Brostoff S., Jackson J., Carter H. Allergic encephalomyelitis in monkeys induced by a peptide from the A1 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):617–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasanaro G., Gentile A., Stella L. Prospettive per una terapia immunologica della sclerosi multipla. Acta Neurol (Napoli) 1972 Jul-Aug;27(4):367–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field E. J., Caspary E. A. Lymphocyte sensitisation: an in-vitro test for cancer? Lancet. 1970 Dec 26;2(7687):1337–1341. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92361-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field E. J. Delayed hypersensitivity studies: some applications of cell electrophoresis. J R Coll Physicians Lond. 1972 Apr;6(3):316–326. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field E. J. Role of viral infection and autoimmunity in aetiology and pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Lancet. 1973 Feb 10;1(7798):295–297. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91542-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field E. J. Slow virus infections of the nervous system. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1969;8:129–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler I., Morris C. E., Whitley T. Lymphocyte transformation in mutliple sclerosis induced by cerebrospinal fluid. N Engl J Med. 1966 Nov 10;275(19):1041–1044. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196611102751904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerstl B., Uyeda C. T., Hunt H., Eng L. F. A physiological mechanism preventing experimental allergic encephalitis. Immunology. 1972 Sep;23(3):395–403. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASHEM N., BARR M. L. MITOGENIC EFFECT OF RABIES VACCINE ON CULTURES OF LYMPHOCYTES IN DISEASES OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Lancet. 1963 Nov 16;2(7316):1029–1030. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes D., Caspary E. A., Field E. J. Lymphocyte trnsformation induced by encephalitogenic factor in multiple sclerosis and other neurological diseases. Lancet. 1968 Dec 7;2(7580):1205–1207. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91690-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen M. K. Lymphocyte transformation in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand. 1968;44(2):200–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1968.tb05566.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. B., Wiśniewski H. M., Raine C. S., Eylar E. H., Terry R. D. Specific binding of peroxidase-labeled myelin basic protein in allergic encephalomyelitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2694–2698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karniely Y., Mozes E., Shearer G. M., Sela M. The role of thymocytes and bone marrow cells in defining the response to the dinitrophenyl hapten attached to positively and negatively charged synthetic polypeptide carriers. Cell fractionation over charged columns. J Exp Med. 1973 Jan 1;137(1):183–195. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kibler R. F., Paty D. W., Sherr V. Immunology of multiple sclerosis. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis. 1971;49:95–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kies M. W., Driscoll B. F., Seil F. J., Alvord E. C., Jr Myelination inhibition factor: dissociation from induction of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Science. 1973 Feb 16;179(4074):689–690. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4074.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamoureux G., Thibeault G., Richer G., Bernard C. Induction de l'encéphalite allergique expérimentale avec des encéphalitogènes humains de synthèse. Union Med Can. 1972 Apr;101(4):674–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon V. A., Carnegie P. R. Immunopharmacological disease: a break in tolerance to receptor sites. Lancet. 1971 Mar 27;1(7700):630–633. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91557-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon V. A., Whittingham S., Carnegie P. R., McPherson T. A., Mackay I. R. Detection of antibodies to the basic protein of human myelin by radioimmunoassay and immunofluorescence. J Immunol. 1971 Jul;107(1):56–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon V. A., Wilks A. V., Carnegie P. R. Immunologic properties of the main encephalitogenic peptide from the basic protein of human myelin. J Immunol. 1970 Nov;105(5):1223–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon V., Feldmann M., Crawford M. The detection of autoantibody-forming cells. II. Cells in lymph nodes and central nervous system containing antibody to myelin basic protein. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1972;43(5):749–758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon V., Feldmann M. The detection of autoantibody-forming cells. I. An assay for plaque-forming cells to the basic protein of myelin in guinea-pigs. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1972;42(4):627–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon V., Mackay I. R. Binding of 125 I myelin basic protein by serum and cerebrospinal fluid. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Aug;11(4):595–603. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S., Sowinski R. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in inbred and outbred mice. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):139–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link H. Oligoclonal immunoglobulin G in multiple sclerosis brains. J Neurol Sci. 1972 May;16(1):103–114. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(72)90105-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisak R. P., Heinze R. G., Falk G. A., Kies M. W. Search for anti-encephalitogen antibody in human demyelinative diseases. Neurology. 1968 Jan;18(1 Pt 2):122–128. doi: 10.1212/wnl.18.1_part_2.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumsden C. E. Properties and significance of the demyelinating antibody in multiple sclerosis. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1969;36(Suppl):247–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumsden C. E. The immunogenesis of the multiple sclerosis plaque. Brain Res. 1971 May 21;28(3):365–390. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90052-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay I. R., Morris P. J. Association of autoimmune active chronic hepatitis with HL-A1,8. Lancet. 1972 Oct 14;2(7781):793–795. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92149-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson T. A., Carnegie P. R. Radioimmunoassay with gel filtration for detecting antibody to basic proteins of myelin. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Nov;72(5):824–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar J. H., Fraser K. B., Haire M., Connolly J. H., Shirodaria P. V., Hadden D. S. Immunoglobulin M specific for measles and mumps in multiple sclerosis. Br Med J. 1971 May 15;2(5758):378–380. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5758.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minderhoud J. M., Smith J. K. Immunological activity of blood lymphocyte fractions. A study by the macrophage electrophoretic mobility method. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Apr;10(4):571–579. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito S., Namerow N., Mickey M. R., Terasaki P. I. Multiple sclerosis: association with HL-A3. Tissue Antigens. 1972;2(1):1–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1972.tb00111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann J. W., Ziegler D. K. Therapeutic trial of immunosuppressive agents in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 1972 Dec;22(12):1268–1271. doi: 10.1212/wnl.22.12.1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATERSON P. Y. Transfer of allergic encephalomyelitis in rats by means of lymph node cells. J Exp Med. 1960 Jan 1;111:119–136. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson P. Y., Hanson M. A. Cyclophosphamide inhibition of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis and cellular transfer of the disease in Lewis rats. J Immunol. 1969 Dec;103(6):1311–1316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson P. Y. Immune processes and infectious factors in central nervous system disease. Annu Rev Med. 1969;20:75–100. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.20.020169.000451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick J., Lindstrom J. Autoimmune response to acetylcholine receptor. Science. 1973 May 25;180(4088):871–872. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4088.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prineas J. Paramyxovirus-like particles associated with acute demyelination in chronic relapsing multiple sclerosis. Science. 1972 Nov 17;178(4062):760–763. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4062.760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prineas J., Raine C. S., Wísniewski H. An ultrastructural study of experimental demyelination and remyelination. 3. Chronic experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the central nervous system. Lab Invest. 1969 Dec;21(6):472–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard J. A., Moore J. L., Sutherland W. H., Joslin C. A. Macrophage-electrophoretic-mobility (M.E.M.) test for malignant disease. An independent confirmation. Lancet. 1972 Sep 23;2(7778):627–629. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)93018-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raine C. S., Bornstein M. B. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: an ultrastructural study of experimental demyelination in vitro. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1970 Apr;29(2):177–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riekkinen P., Rinne U. K., Savolainen H., Palo J., Kivalo E., Arstila A. Studies on the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Basic proteins in the myelin and white matter of multiple sclerosis, subacute sclerosing panencephalitis and postvaccinal leucoencephalitis. Eur Neurol. 1971;5(4):229–244. doi: 10.1159/000114075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocklin R. E., Sheremata W. A., Feldman R. G., Kies M. W., David J. R. The Guillain-Barré syndrome and multiple sclerosis. In vitro cellular responses to nervous-tissue antigens. N Engl J Med. 1971 Apr 15;284(15):803–808. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197104152841501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seil F. J., Falk G. A., Kies M. W., Alvord E. C., Jr The in vitro demyelinating activity of sera from guinea pigs sensitized with whole CNS and with purified encephalitogen. Exp Neurol. 1968 Dec;22(4):545–555. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(68)90148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira R., Chou F. C., McKneally S., Urban E., Kibler R. F. Biologicl activity and synthesis of an encephalitogenic determinant. Science. 1971 Aug 20;173(3998):736–738. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3998.736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberberg D., Lisak R., Zweiman B. Multiple sclerosis unaffected by azathioprine in pilot study. Arch Neurol. 1973 Mar;28(3):210–212. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490210090017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitler L. E., Von Muller C. M., Fudenberg H. H., Eylar E. H. Experimental allergic encephalitis. Dissociation of cellular immunity to brain protein and disease production. J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):156–174. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandgaard S., Jorgensen P. N. Delayed hypersensitivity to myelin antigen in multiple sclerosis investigated with the leucocyte migration method. Acta Neurol Scand. 1972;48(2):243–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1972.tb07545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanborg R. H. Antigen-induced inhibition of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. I. Inhibition in guinea pigs injected with non-encephalitogenic modified myelin basic protein. J Immunol. 1972 Sep;109(3):540–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tourtellotte W. On cerebrospinal fluid immunoglobulin-G (IgG) quotients in multiple sclerosis and other diseases. A review and a new formula to estimate the amount of IgG synthesized per day by the central nervous system. J Neurol Sci. 1970 Mar;10(3):279–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(70)90156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Noort S., Stjernholm R. L. Lymphotoxic activity in multiple sclerosis serum. Neurology. 1971 Aug;21(8):783–793. doi: 10.1212/wnl.21.8.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAKSMAN B. H. Further study of skin reactions in rabbits with experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: reactions to tests with purified white matter fractions; use of a quantitative technique for evaluating sensitivity production of sensitization and disease by intradermal injection of antigen without adjuvants. J Infect Dis. 1956 Nov-Dec;99(3):258–269. doi: 10.1093/infdis/99.3.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner L. P., Johnson R. T., Herndon R. M. Viral infections and demyelinating diseases. N Engl J Med. 1973 May 24;288(21):1103–1110. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197305242882106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittingham S., Bencina B., Carnegie P. R., McPherson T. A. Properties of antibodies produced in rabbits to human myelin and myelin basic protein. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1972;42(2):250–263. doi: 10.1159/000230610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaşargil M. G. Intracranial microsurgery. Proc R Soc Med. 1972 Jan;65(1):15–16. doi: 10.1177/003591577206500106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yung L. L., Diener E., McPherson T. A., Barton M. A., Hyde H. A. Antigen-binding lymphocytes in normal man and guinea pig to human encephalitogenic protein. J Immunol. 1973 May;110(5):1383–1387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


