Abstract
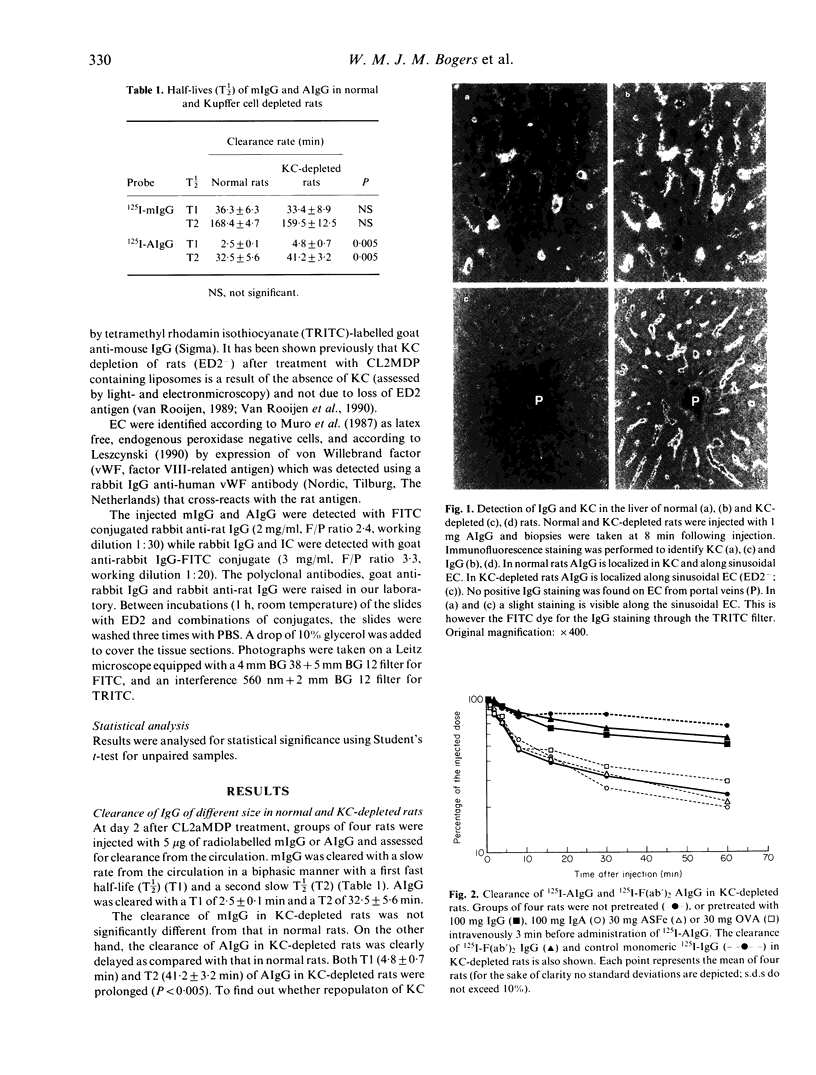
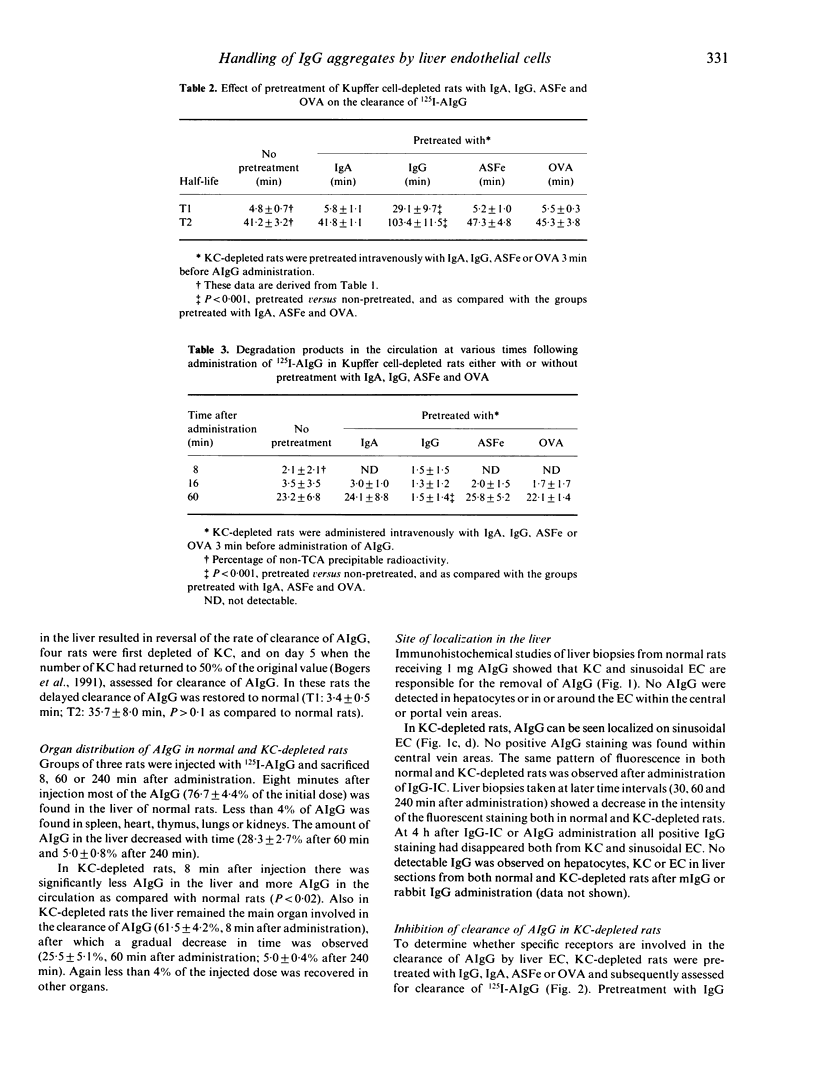
In the present study we have investigated the clearance kinetics and tissue distribution of monomeric (m) IgG and soluble aggregates of IgG (AIgG) and immune complexes (IC) in normal and Kupffer cell (KC) depleted rats. In normal rats, clearance of mIgG occurred in a biphasic manner with a first half-life (T1/2) (T1) of 36.3 +/- 6.3 min and a second T1/2 (T2) of 168.4 +/- 4.7 min. AIgG composed of 20-27 IgG molecules per aggregate were cleared significantly faster than mIgG with a T1 of 2.5 +/- 0.1 min and a T2 of 32.5 +/- 5.6 min. KC depletion did not have a significant effect on the clearance rate of mIgG (T1: 33.4 +/- 8.9 min; T2; 159.5 +/- 12.5 min), while clearance of AIgG was delayed significantly with T1 4.8 +/- 0.7 min and T2 41.2 +/- 3.2 min. Eight minutes after injection, 77% of AIgG was found in the liver in normal rats while 62% was found in the liver of KC-depleted rats. Double immunofluorescence studies indicated that AIgG in the liver was associated with KC and endothelial cells (EC) in normal rats. In KC-depleted rats, AIgG was strongly associated with EC. A similar staining pattern was observed when IgG-immune IC were administered. The clearance of AIgG in KC-depleted rats was inhibited fully by pre-administration of high concentrations of IgG but not by pretreatment with IgA. asialofetuin (ASFe) or ovalbumin (OVA). Aggregated F(ab')2IgG was cleared with a comparable rate to mIgG from the circulation, again suggesting Fc gamma receptor-mediated elimination of AIgG by EC. There was a reduced degradation of AIgG in rats depleted of KC as compared with normal rats. These data suggest binding and degradation of AIgG by EC in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENACERRAF B., SEBESTYEN M., COOPER N. S. The clearance of antigen antibody complexes from the blood by the reticuloendothelial system. J Immunol. 1959 Feb;82(2):131–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blouin A., Bolender R. P., Weibel E. R. Distribution of organelles and membranes between hepatocytes and nonhepatocytes in the rat liver parenchyma. A stereological study. J Cell Biol. 1977 Feb;72(2):441–455. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.2.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogers W. M., Gorter A., Janssen D. J., Rits M., Bazin H., van Es L. A., Daha M. R. The involvement of Kupffer cells in the clearance of high molecular weight rat IgA aggregates in rats. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Jun;31(6):679–689. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb02819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogers W. M., Gorter A., Stuurman M. E., Van Es L. A., Daha M. R. Clearance kinetics and tissue distribution of aggregated human serum IgA in rats. Immunology. 1989 Jun;67(2):274–280. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogers W. M., Stad R. K., Janssen D. J., Prins F. A., van Rooijen N., van Es L. A., Daha M. R. Kupffer cell depletion in vivo results in clearance of large-sized IgA aggregates in rats by liver endothelial cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jul;85(1):128–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05693.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra C. D., Döpp E. A., Joling P., Kraal G. The heterogeneity of mononuclear phagocytes in lymphoid organs: distinct macrophage subpopulations in the rat recognized by monoclonal antibodies ED1, ED2 and ED3. Immunology. 1985 Mar;54(3):589–599. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halma C., Daha M. R., van Furth R., Camps J. A., Evers-Schouten J. H., Pauwels E. K., Lobatto S., Van Es L. A. Elimination of soluble 123I-labelled aggregates of human immunoglobulin G in humans; the effect of splenectomy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Jul;77(1):62–66. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kijlstra A., Knutson D. W., van der Lelij A., van Es L. A. Characteristics of soluble immune complexes prepared from oligovalent DNP conjugates and anti-DNP antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1977;17(3-4):263–277. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90109-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kijlstra A., Van Es L. A., Daha M. R. Enhanced degradation of soluble immunoglobulin aggregates by macrophages in the presence of complement. Immunology. 1979 Jul;37(3):673–680. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson D. W., Kijlstra A., Van Es L. A. Association and dissociation of aggregated IgG from rat peritoneal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1368–1381. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leszczynski D. Interleukin-1 alpha inhibits the effects of gamma-interferon and tumor necrosis factor alpha on the expression of the major histocompatibility antigens by the rat endothelium. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jan;136(1):229–237. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobatto S., Daha M. R., Voetman A. A., Evers-Schouten J. H., Van Es A. A., Pauwels E. K., Van Es L. A. Clearance of soluble aggregates of human immunoglobulin G in healthy volunteers and chimpanzees. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Jul;69(1):133–141. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muro H., Shirasawa H., Maeda M., Nakamura S. Fc receptors of liver sinusoidal endothelium in normal rats and humans. A histologic study with soluble immune complexes. Gastroenterology. 1987 Nov;93(5):1078–1085. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90572-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulford K., Souhami R. L. The surface properties and antigen-presenting function of hepatic non-parenchymal cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Dec;46(3):581–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifai A., Mannik M. Clearance of circulating IgA immune complexes is mediated by a specific receptor on Kupffer cells in mice. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):125–137. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifai A., Schena F. P., Montinaro V., Mele M., D'Addabbo A., Nitti L., Pezzullo J. C. Clearance kinetics and fate of macromolecular IgA in patients with IgA nephropathy. Lab Invest. 1989 Oct;61(4):381–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan U. S., Schultz D. R., Del Vecchio P. J., Ryan J. W. Endothelial cells of bovine pulmonary artery lack receptors for C3b and for the Fc portion of immunoglobulin G. Science. 1980 May 16;208(4445):748–749. doi: 10.1126/science.7367890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli J. A., Taylor R. P. Physiological and pathological aspects of circulating immune complexes. Kidney Int. 1989 Apr;35(4):993–1003. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shingu M., Hashimoto Y., Johnson A. R., Hurd E. R. The search for Fc receptors on human tissues and human endothelial cells in culture. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1981 Jun;167(2):147–155. doi: 10.3181/00379727-167-41140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skogh T., Blomhoff R., Eskild W., Berg T. Hepatic uptake of circulating IgG immune complexes. Immunology. 1985 Aug;55(4):585–594. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffan A. M., Gendrault J. L., McCuskey R. S., McCuskey P. A., Kirn A. Phagocytosis, an unrecognized property of murine endothelial liver cells. Hepatology. 1986 Sep-Oct;6(5):830–836. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tax W. J., van de Winkel J. G. Human Fc gamma receptor II: a standby receptor activated by proteolysis? Immunol Today. 1990 Sep;11(9):308–310. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90125-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rooijen N., Kors N., vd Ende M., Dijkstra C. D. Depletion and repopulation of macrophages in spleen and liver of rat after intravenous treatment with liposome-encapsulated dichloromethylene diphosphonate. Cell Tissue Res. 1990 May;260(2):215–222. doi: 10.1007/BF00318625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rooijen N. The liposome-mediated macrophage 'suicide' technique. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Nov 13;124(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90178-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veerhuis R., van Es L. A., Daha M. R. In vivo modulation of rat complement activities by infusion of anti-H antibodies. Immunobiology. 1985 Sep;170(3):133–145. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(85)80086-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Laan-Klamer S. M., Atmosoerodjo-Briggs J. E., Harms G., Hoedemaeker P. J., Hardonk M. J. A histochemical study about the involvement of rat liver cells in the uptake of heterologous immune complexes from the circulation. Histochemistry. 1985;82(5):477–482. doi: 10.1007/BF02450483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Laan-Klamer S. M., Harms G., Atmosoerodjo-Briggs J., Hoedemaeker P. J., Hardonk M. J. Hepatic uptake of autologous immune complexes in the rat. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Apr;23(4):441–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Laan-Klamer S. M., Harms G., Atmosoerodjo J. E., Meijer D. K., Hardonk M. J., Hoedemaeker P. J. Studies on the mechanism of binding and uptake of immune complexes by various cell types of rat liver in vivo. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Jan;23(1):127–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb01950.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


