Abstract
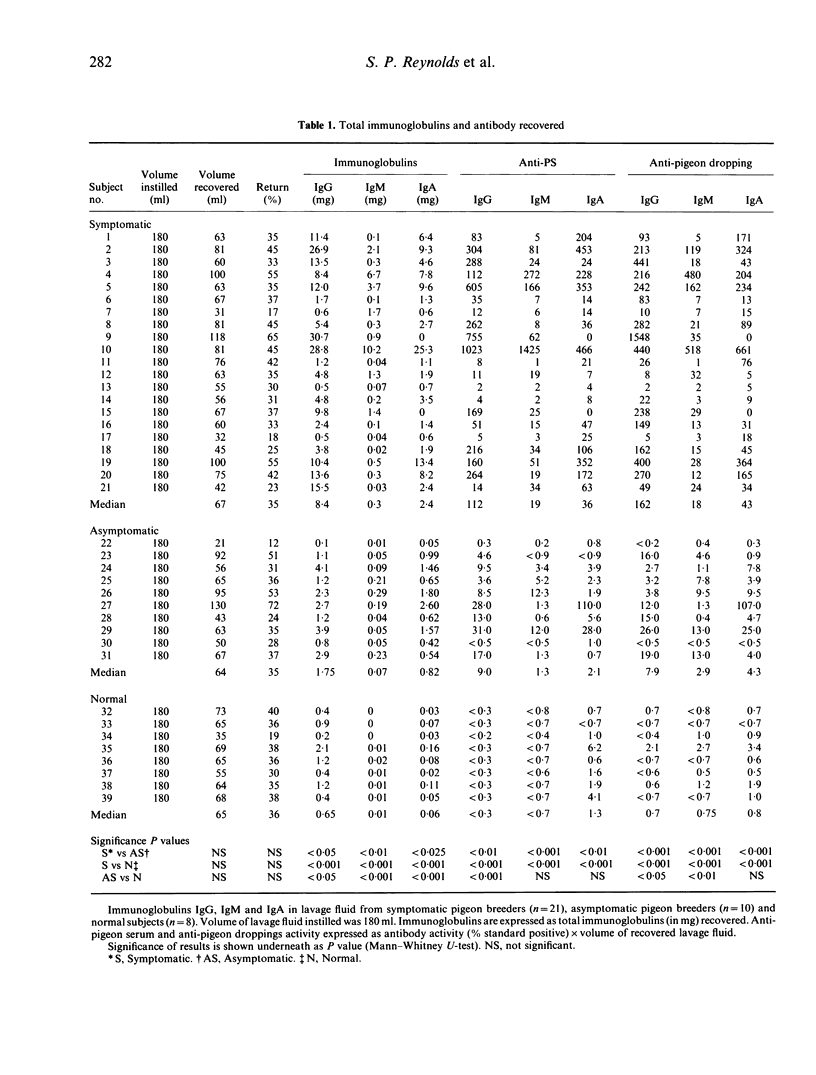
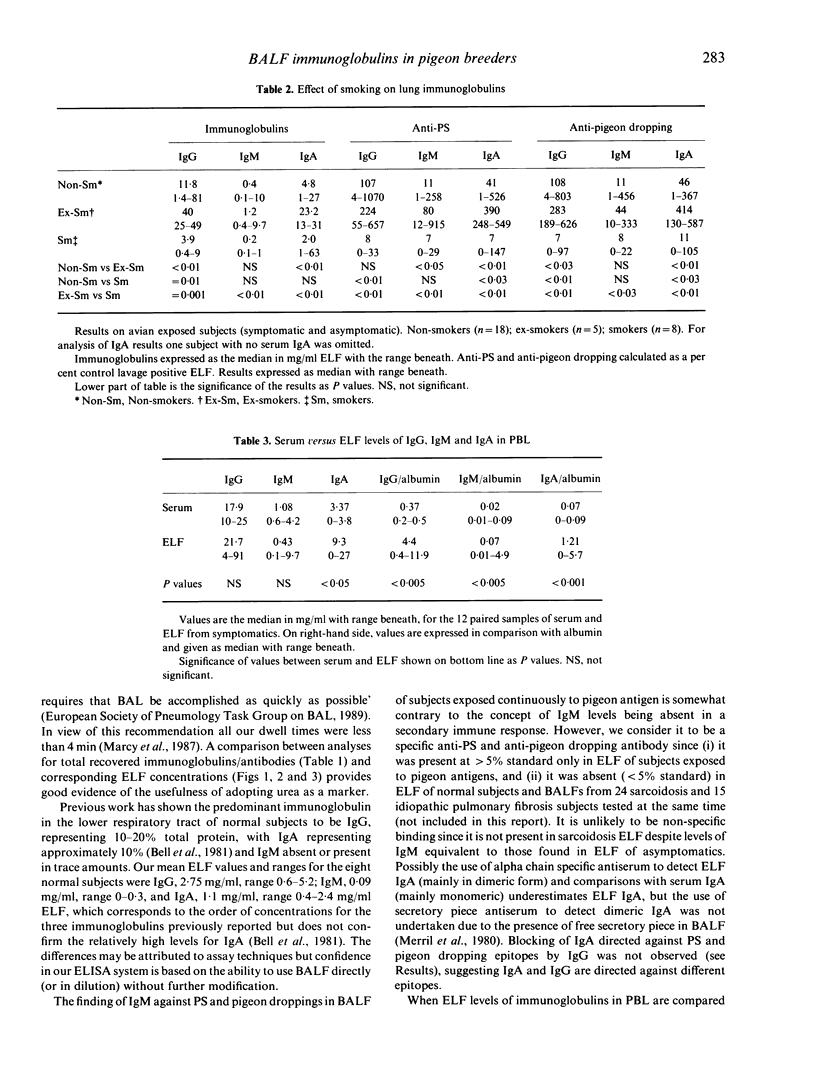
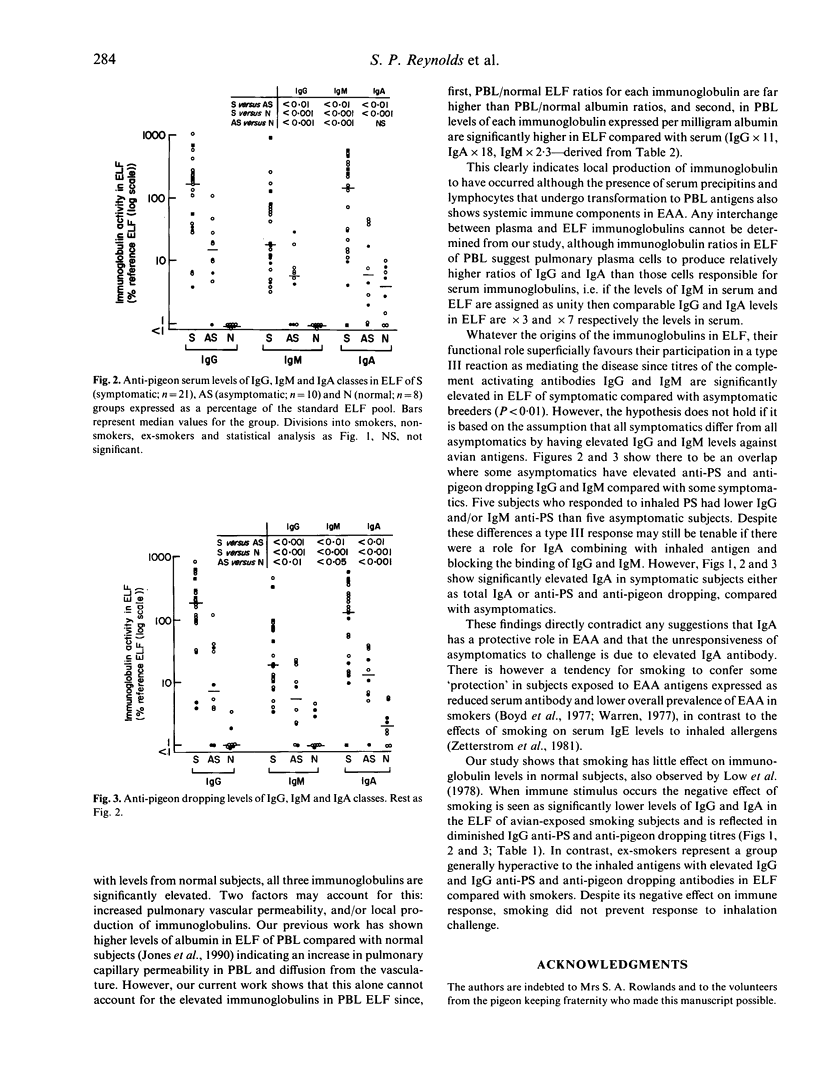
Twenty-one symptomatic subjects with pigeon breeders' lung (PBL) and 10 asymptomatic pigeon breeders, with a similar exposure to pigeon antigens, underwent bronchoalveolar lavage. Total IgG, IgM and IgA in lavage fluid were determined as were specific antibody levels against antigens in pigeon serum and droppings. Results were converted to levels in epithelial lining fluid (ELF) using lavage and serum urea ratios. It was found that symptomatics represent a group that is hyperreactive to pigeon antigens compared with the asymptomatic group with significantly higher IgG, IgM, IgA levels as well as specific antibody levels against pigeon serum and droppings. Paired serum and ELF samples from 12 symptomatic subjects showed significantly elevated IgG, IgM and IgA levels in ELF compared with serum when values were expressed in terms of albumin. This strongly supports the concept of local production of immunoglobulins within the lung after inhaling immunogens as opposed to their diffusion from the vasculature. Results for IgA indicate that any putative protective role for this immunoglobulin is not valid in relation to the prevention of extrinsic allergic alveolitis. Analysis of smoking habits, lung immunoglobulins and response to inhalation challenge confirm the negative influence of smoking on total and functional lung immunoglobulins; however, levels in the ELF of ex-smokers suggest that the effect of smoking is not permanent. Smoking did not prevent responses to inhalation challenge.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell D. Y., Haseman J. A., Spock A., McLennan G., Hook G. E. Plasma proteins of the bronchoalveolar surface of the lungs of smokers and nonsmokers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jul;124(1):72–79. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boren M. N., Moore V. L., Abramoff P., Fink J. N. Pigeon breeder's disease. Antibody response of man against a purified component of pigeon dropping extract. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1977 Jul;8(1):108–115. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(77)90098-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Fjellanger I., Gjeruldsen S. T. Localization of immunoglobulins in human nasal mucosa. Immunochemistry. 1967 Jan;4(1):57–60. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(67)90197-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. H., Cockcroft A. Inhalation challenge in humidifier fever. Clin Allergy. 1981 May;11(3):227–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1981.tb01588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. H., Davies B. H. Inhalation challenge and skin testing in farmer's lung. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1981 Jul;68(1):58–64. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(81)90124-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. H., Wagner J. C., Seal R. M. Pulmonary responses to particulate materials capable of activating the alternative pathway of complement. Clin Allergy. 1976 Mar;6(2):155–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1976.tb01893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink J. N., Tebo T., Barboriak J. J. Differences in the immune responses of pigeon breeders to pigeon serum proteins. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Aug;74(2):325–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrick D. J., Marshall R., Faux J. A., Krall J. M. Positive "alveolar" responses to antigen inhalation provocation tests: their validity and recognition. Thorax. 1980 Jun;35(6):415–427. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.6.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Fauci A. S. Immunolgic reactivity of the lung. V. Regulatory effects of antibody on the pulmonary immune response to locally administered antigen. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1728–1733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Gadek J. E., Kawanami O., Ferrans V. J., Crystal R. G. Inflammatory and immune processes in the human lung in health and disease: evaluation by bronchoalveolar lavage. Am J Pathol. 1979 Oct;97(1):149–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. P., Edwards J. H., Reynolds S. P., Peters T. J., Davies B. H. A comparison of albumin and urea as reference markers in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from patients with interstitial lung disease. Eur Respir J. 1990 Feb;3(2):152–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low R. B., Davis G. S., Giancola M. S. Biochemical analyses of bronchoalveolar lavage fluids of healthy human volunteer smokers and nonsmokers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Nov;118(5):863–875. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.5.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M. A., Dvorak K. J., Worman L. W., DeCosse J. J. Immunoglobulin content in the bronchial washings of patients with benign and malignant pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 1976 Sep 23;295(13):694–698. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197609232951303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcy T. W., Merrill W. W., Rankin J. A., Reynolds H. Y. Limitations of using urea to quantify epithelial lining fluid recovered by bronchoalveolar lavage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jun;135(6):1276–1280. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.6.1276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Tello F. J., Braun D. G., Blanc W. A. Immunoglobulin production in bronchial mucosa and bronchial lymph nodes, particularly in cystic fibrosis of the pancreas. J Immunol. 1968 Nov;101(5):989–1003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSharry C., Banham S. W., Lynch P. P., Boyd G. Antibody measurement in extrinsic allergic alveolitis. Eur J Respir Dis. 1984 May;65(4):259–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill W. W., Goodenberger D., Strober W., Matthay R. A., Naegel G. P., Reynolds H. Y. Free secretory component and other proteins in human lung lavage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Jul;122(1):156–161. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.1.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore V. L., Schanfield M. S., Fink J. N., Fudenberg H. H. Immunoglobulin allotypes in symptomatic and asymptomatic pigeon breeders. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 May;149(1):307–310. doi: 10.3181/00379727-149-38795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson R., Wang J. L., Fink J. N., Calvanico N. J., Roberts M. IgA and IgG antibody activities of serum and bronchoalveolar fluid from symptomatic and asymptomatic pigeon breeders. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Nov;120(5):1113–1118. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.5.1113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys J., Hutchcroft B. J. Bronchial provocation tests in etiologic diagnosis and analysis of asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 Dec;112(6):829–859. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.112.6.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REED C. E., BARBEE R. A. PIGEON-BREEDERS' LUNG: A NEWLY OBSERVED INTERSTITIAL PULMONARY DISEASE. JAMA. 1965 Jul 26;193:261–265. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03090040005001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennard S. I., Basset G., Lecossier D., O'Donnell K. M., Pinkston P., Martin P. G., Crystal R. G. Estimation of volume of epithelial lining fluid recovered by lavage using urea as marker of dilution. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Feb;60(2):532–538. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.60.2.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes C. N., Wenzel F. J., Lawton B. R., Emanuel D. A. The pulmonary pathology of farmer's lung disease. Chest. 1982 Feb;81(2):142–146. doi: 10.1378/chest.81.2.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Newball H. H. Analysis of proteins and respiratory cells obtained from human lungs by bronchial lavage. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Oct;84(4):559–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rácz P., Tenner-Rácz K., Myrvik Q. N., Fainter L. K. Functional architecture of bronchial associated lymphoid tissue and lymphoepithelium in pulmonary cell-mediated reactions in the rabbit. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1977 Jul;22(1):59–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sennekamp J., Lange G., Nerger K., Berdel D., Meier-Sydow J. Human antibodies against antigens of the sparrow, blackbird, weaver finch, canary, budgerigar, pigeon and hen using the indirect immunofluorescent technique. Clin Allergy. 1981 Jul;11(4):375–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1981.tb01608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valeyre D., Saumon G., Bladier D., Amouroux J., Pré J., Battesti J. P., Georges R. The relationships between noninvasive explorations in pulmonary sarcoidosis of recent origin, as shown in bronchoalveolar lavage, serum, and pulmonary function tests. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Jul;126(1):41–45. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS J. V. Inhalation and skin tests with extracts of hay and fungi in patients with farmer's lung. Thorax. 1963 Jun;18:182–196. doi: 10.1136/thx.18.2.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warr G. A., Martin R. R., Sharp P. M., Rossen R. D. Normal human bronchial immunoglobulins and proteins: effects of cigarette smoking. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Jul;116(1):25–30. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.116.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren C. P. Extrinsic allergic alveolitis: a disease commoner in non-smokers. Thorax. 1977 Oct;32(5):567–569. doi: 10.1136/thx.32.5.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger S. E., Kelman J. A., Elson N. A., Young R. C., Jr, Reynolds H. Y., Fulmer J. D., Crystal R. G. Bronchoalveolar lavage in interstitial lung disease. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Oct;89(4):459–466. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-4-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetterström O., Osterman K., Machado L., Johansson S. G. Another smoking hazard: raised serum IgE concentration and increased risk of occupational allergy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Nov 7;283(6301):1215–1217. doi: 10.1136/bmj.283.6301.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


