Abstract
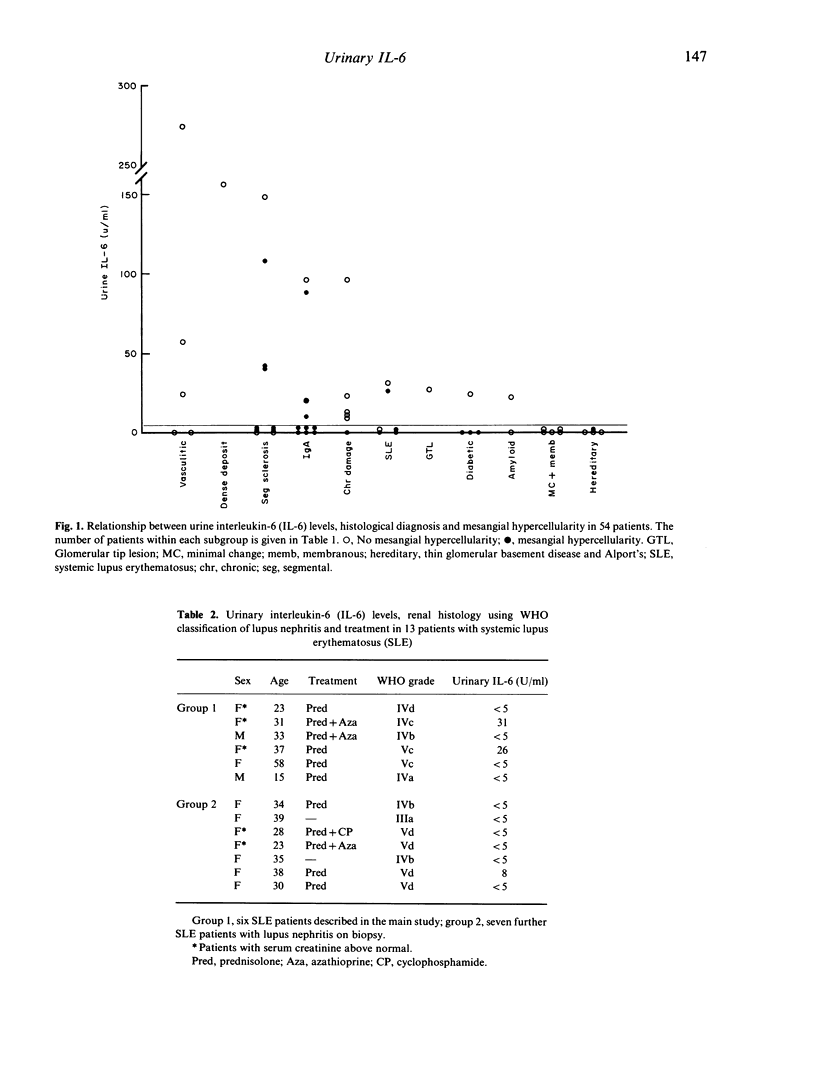
A prospective study of plasma and urinary interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels was performed in 54 patients undergoing renal biopsy to determine whether detectable urinary IL-6 was a reliable marker for mesangial proliferation. Interleukin-6 was found in both the urine and plasma of seven patients, the urine alone of 15 patients, and the plasma alone of two patients. Interleukin-6 was not detected in the urine or the plasma of the remaining 30 patients, the urine of 10 healthy controls or the urine of 10 patients with rheumatoid arthritis with raised plasma IL-6. Interleukin-6 was found in the urine of only one out of an additional seven patients with lupus nephritis. Urinary IL-6 was associated with a variety of renal abnormalities and was not restricted to those with mesangial hypercellularity. Furthermore, many patients with mesangial hypercellularity did not have detectable urinary IL-6. There was no correlation between urinary IL-6 and plasma IL-6, urinary albumin excretion or urinary creatinine. These results suggest that IL-6 detected in the urine is a marker of renal IL-6 production, but not specifically of mesangial hypercellularity. The patients with IL-6 in the urine had a mean serum creatinine significantly higher than those without IL-6. It is not possible to distinguish at present whether IL-6 contributes to renal dysfunction or whether it reflects renal damage.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaman M., Howie A. J., Hardwicke J., Michael J., Adu D. The glomerular tip lesion: a steroid responsive nephrotic syndrome. Clin Nephrol. 1987 May;27(5):217–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boswell J. M., Yui M. A., Burt D. W., Kelley V. E. Increased tumor necrosis factor and IL-1 beta gene expression in the kidneys of mice with lupus nephritis. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 1;141(9):3050–3054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boswell J. M., Yui M. A., Endres S., Burt D. W., Kelley V. E. Novel and enhanced IL-1 gene expression in autoimmune mice with lupus. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):118–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta B., Panayi G. S. Interleukin-6 in serum of patients with polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1990 Dec;29(6):456–458. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/29.6.456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohi K., Iwano M., Muraguchi A., Horii Y., Hirayama T., Ogawa S., Shiiki H., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Ishikawa H. The prognostic significance of urinary interleukin 6 in IgA nephropathy. Clin Nephrol. 1991 Jan;35(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floege J., Topley N., Wessel K., Kaever V., Radeke H., Hoppe J., Kishimoto T., Resch K. Monokines and platelet-derived growth factor modulate prostanoid production in growth arrested, human mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1990 Mar;37(3):859–869. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich P. C., Castell J. V., Andus T. Interleukin-6 and the acute phase response. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 1;265(3):621–636. doi: 10.1042/bj2650621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helle M., Boeije L., Aarden L. A. Functional discrimination between interleukin 6 and interleukin 1. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Oct;18(10):1535–1540. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssiau F. A., Devogelaer J. P., Van Damme J., de Deuxchaisnes C. N., Van Snick J. Interleukin-6 in synovial fluid and serum of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory arthritides. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Jun;31(6):784–788. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein B., Zhang X. G., Jourdan M., Content J., Houssiau F., Aarden L., Piechaczyk M., Bataille R. Paracrine rather than autocrine regulation of myeloma-cell growth and differentiation by interleukin-6. Blood. 1989 Feb;73(2):517–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le J. M., Vilcek J. Interleukin 6: a multifunctional cytokine regulating immune reactions and the acute phase protein response. Lab Invest. 1989 Dec;61(6):588–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble B., Ren K., Taverne J., Dipirro J., Van Liew J., Dijkstra C., Janossy G., Poulter L. W. Mononuclear cells in glomeruli and cytokines in urine reflect the severity of experimental proliferative immune complex glomerulonephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 May;80(2):281–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suematsu S., Matsuda T., Aozasa K., Akira S., Nakano N., Ohno S., Miyazaki J., Yamamura K., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. IgG1 plasmacytosis in interleukin 6 transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7547–7551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbanski A., Schwarz T., Neuner P., Krutmann J., Kirnbauer R., Köck A., Luger T. A. Ultraviolet light induces increased circulating interleukin-6 in humans. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Jun;94(6):808–811. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12874666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Oers M. H., Van der Heyden A. A., Aarden L. A. Interleukin 6 (IL-6) in serum and urine of renal transplant recipients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Feb;71(2):314–319. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



