Abstract
Antibodies produced in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (RRP) patients treated with lymphoblastoid interferon (lyIFN) may neutralize antiviral activity or may only bind to lyIFN. These antibodies were characterized for immunoglobulin class, IgG subclass, and light chain type by an indirect immunoassay. Serum dilutions were incubated on lyIFN-coated plates and the presence of antibody detected using peroxidase-conjugated goat antibodies to each human immunoglobulin class and light chain isotype, or using MoAbs to each human IgG subclass. Neutralizing activity was measured as the inhibition of lyIFN antiviral activity for Vervet monkey cells challenged with Semliki Forest Virus. Among antibody-positive patients, 12% produced IgM coincident with IgG, and 25% produced IgA coincident with IgG. Thus, antibody responses in patients treated with lyIFN are not exclusively of IgG class. The predominant lyIFN-specific subclasses were IgG1 and IgG3, which occurred in 70% and 83% of patients, respectively. An IgG4 response was detected in two patients who also had antibody of other isotypes; no IgG2 antibody was detected in any patient. Antibodies were not IgG subclass-restricted, a trend which was more pronounced in patients having neutralizing antibody than non-neutralizing antibody. Light chain molecules of lyIFN-specific antibody were of both kappa and lambda isotypes, with kappa chains occurring most frequently. Among patients having non-neutralizing antibodies, monotypic light chains occurred in 65% of the patients, whereas no patient with neutralizing antibody had monotypic light chain antibody. Sera from 599 normal human volunteers were assayed for antibody, and seven were found to be immunoreactive to lyIFN. Only one serum of the seven was positive for neutralizing activity.
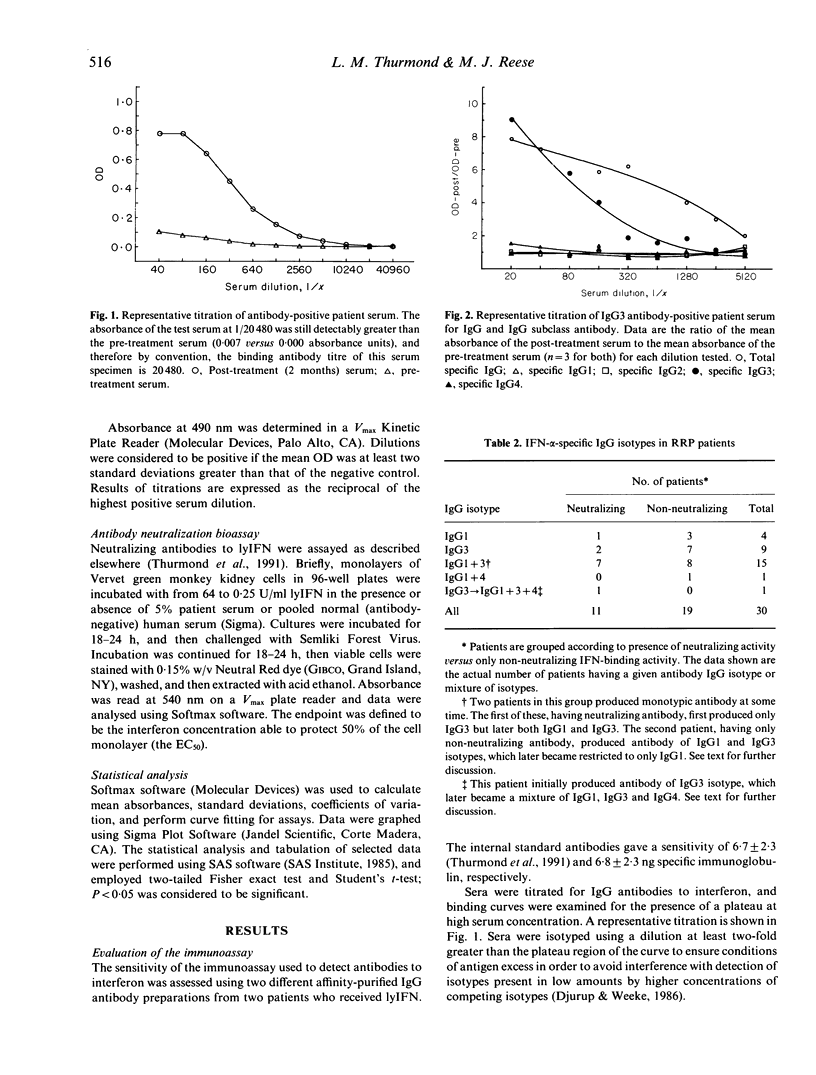
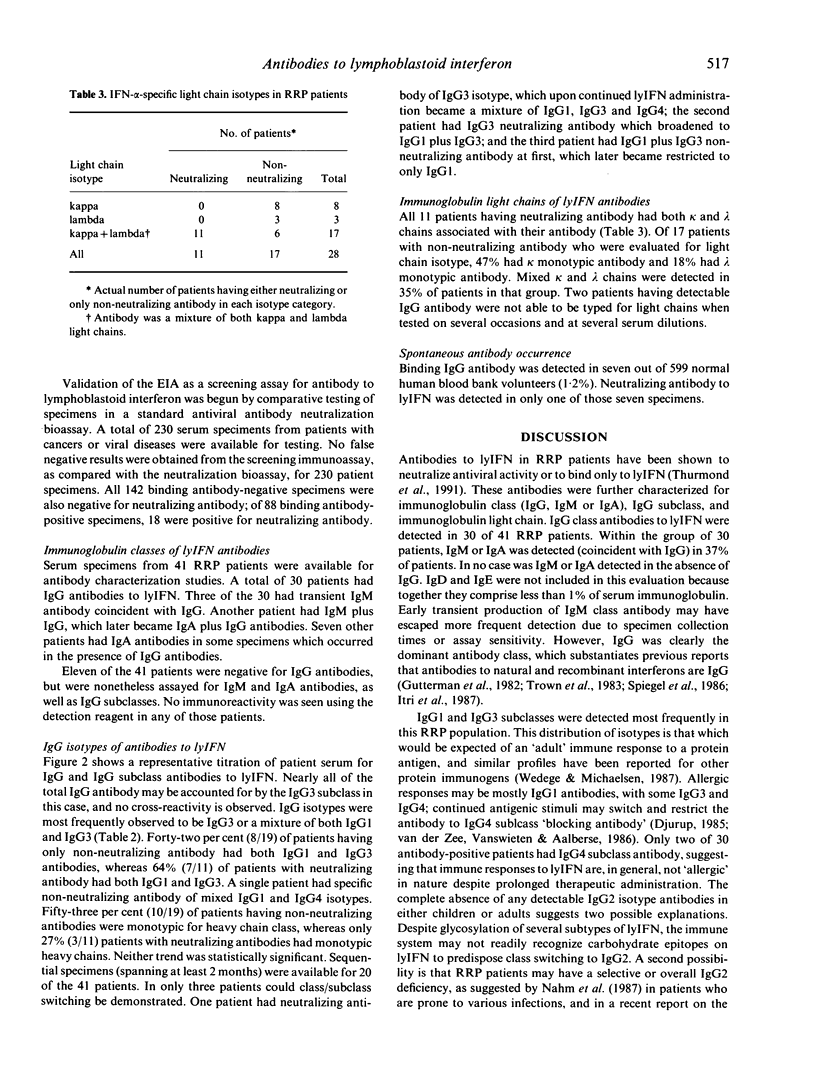
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. Human immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):12745–12748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djurup R. The subclass nature and clinical significance of the IgG antibody response in patients undergoing allergen-specific immunotherapy. Allergy. 1985 Oct;40(7):469–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1985.tb00253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djurup R., Weeke B. Methods of detecting IgG subclass proteins and antibodies. Monogr Allergy. 1986;19:86–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutterman J. U., Fine S., Quesada J., Horning S. J., Levine J. F., Alexanian R., Bernhardt L., Kramer M., Spiegel H., Colburn W. Recombinant leukocyte A interferon: pharmacokinetics, single-dose tolerance, and biologic effects in cancer patients. Ann Intern Med. 1982 May;96(5):549–556. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-5-549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström L., Smith C. I. IgG subclass changes in response to vaccination. Monogr Allergy. 1986;19:241–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström L., Smith C. I. IgG subclasses in bacterial infections. Monogr Allergy. 1986;19:122–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itri L. M., Campion M., Dennin R. A., Palleroni A. V., Gutterman J. U., Groopman J. E., Trown P. W. Incidence and clinical significance of neutralizing antibodies in patients receiving recombinant interferon alfa-2a by intramuscular injection. Cancer. 1987 Feb 1;59(3 Suppl):668–674. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19870201)59:3+<668::aid-cncr2820591317>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S. J., Sullivan L. M., Salfi M., Grossberg H., Spiegel R. J., Leibowitz P. J., Oden E. M., Kelsey D. K., Treuhaft M. W. Minimal antigenicity of intron A in human recipients demonstrated by three analytical methods. J Biol Response Mod. 1988 Oct;7(5):447–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferis R., Reimer C. B., Skvaril F., de Lange G., Ling N. R., Lowe J., Walker M. R., Phillips D. J., Aloisio C. H., Wells T. W. Evaluation of monoclonal antibodies having specificity for human IgG sub-classes: results of an IUIS/WHO collaborative study. Immunol Lett. 1985;10(3-4):223–252. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(85)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. J., Itri L. M. Safety and tolerance of recombinant interferon alfa-2a (Roferon-A) in cancer patients. Cancer. 1986 Apr 15;57(8 Suppl):1709–1715. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19860415)57:8+<1709::aid-cncr2820571315>3.0.co;2-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashima H., Leventhal B., Clark K., Cohen S., Dedo H., Donovan D., Fearon B., Gardiner L., Goepfert H., Lusk R. Interferon alfa-n1 (Wellferon) in juvenile onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: results of a randomized study in twelve collaborative institutions. Laryngoscope. 1988 Mar;98(3):334–340. doi: 10.1288/00005537-198803000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. I., Heiner D. C., Wara D. Development of serum IgG subclass levels in children. Monogr Allergy. 1986;19:108–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leventhal B. G., Kashima H. K., Weck P. W., Mounts P., Whisnant J. K., Clark K. L., Cohen S., Dedo H. H., Donovan D. J., Fearon B. W. Randomized surgical adjuvant trial of interferon alfa-n1 in recurrent papillomatosis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1988 Oct;114(10):1163–1169. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1988.01860220097032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsiota P., Saron M. F., Guillon J. C., Avrameas S. Mouse natural autoantibodies can interfere with murine alpha and beta interferons. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):955–956. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.955-956.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahm M. H., Scott M. G., Shackelford P. G. Expression of human IgG subclasses. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1987 May-Jun;17(3):183–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxelius V. A. Chronic infections in a family with hereditary deficiency of IgG2 and IgG4. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 May;17(1):19–27. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrick D., Wray B. B., Leffell M. S., Harmon J. D., Porubsky E. S. Evaluation of immunocompetency in juvenile laryngeal papillomatosis. Ann Allergy. 1990 Jul;65(1):69–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quesada J. R., Gutterman J. U. Clinical study of recombinant DNA-produced leukocyte interferon (clone A) in a intermittent schedule in cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 Jun;70(6):1041–1046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer M., Taylor-Papadimitriou J., Griffin D., Balkwill F. Monoclonal antibodies that distinguish between subspecies of human interferon-alpha and that detect interferon oligomers. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3096–3101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel R. J., Spicehandler J. R., Jacobs S. L., Oden E. M. Low incidence of serum neutralizing factors in patients receiving recombinant alfa-2b interferon (Intron A). Am J Med. 1986 Feb;80(2):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes A., Mims C. A., Grahame R. Subclass distribution of IgG and IgA responses to rubella virus in man. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Jun;21(4):283–285. doi: 10.1099/00222615-21-4-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurmond L. M., Brand C. M., Leventhal B. G., Finter N. B., Johnston J. M. Antibodies in patients with recurrent respiratory papillomatosis treated with lymphoblastoid interferon. J Lab Clin Med. 1991 Sep;118(3):232–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trown P. W., Kramer M. J., Dennin R. A., Jr, Connell E. V., Palleroni A. V., Quesada J., Gutterman J. U. Antibodies to human leucocyte interferons in cancer patients. Lancet. 1983 Jan 15;1(8316):81–84. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91737-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weck P. K., Leventhal B. G., Brand C., Finter N. B. Detection and incidence of neutralizing antibodies to interferon-alpha-n1. J Interferon Res. 1989 Sep;9 (Suppl 1):S37–S43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedege E., Michaelsen T. E. Human immunoglobulin G subclass immune response to outer membrane antigens in meningococcal group B vaccine. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1349–1353. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1349-1353.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Zee J. S., van Swieten P., Aalberse R. C. Serologic aspects of IgG4 antibodies. II. IgG4 antibodies form small, nonprecipitating immune complexes due to functional monovalency. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 1;137(11):3566–3571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


