Abstract
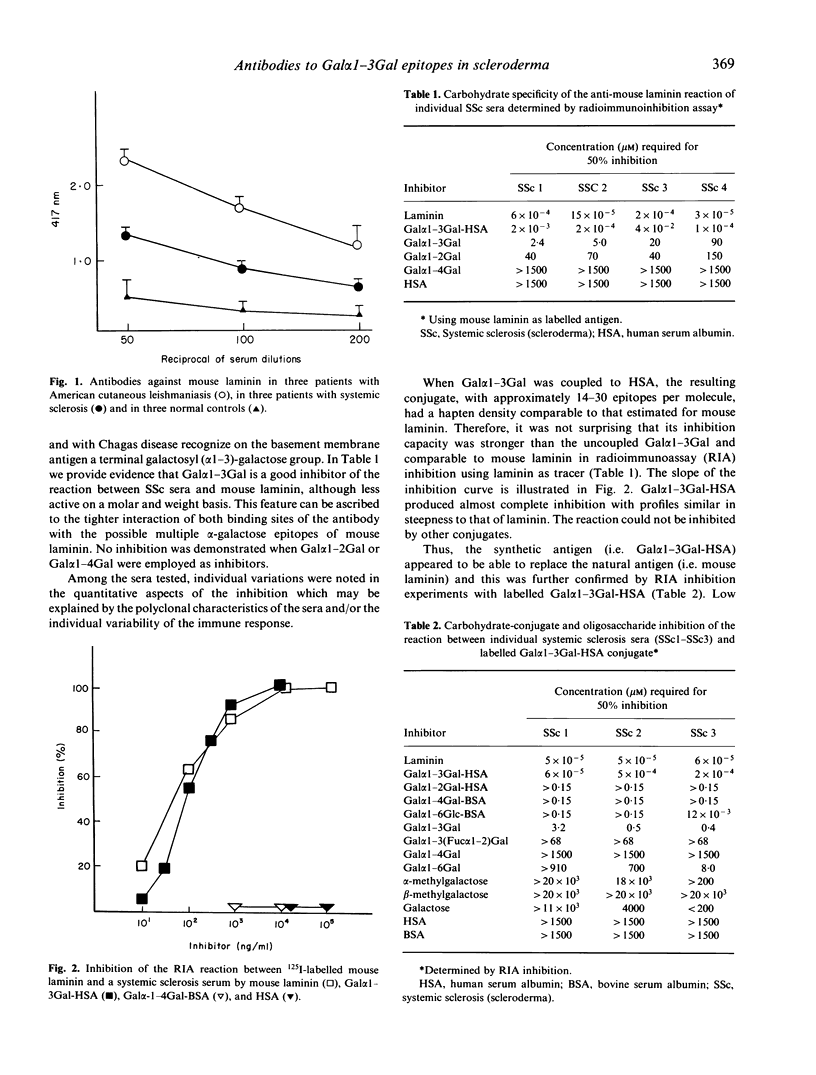
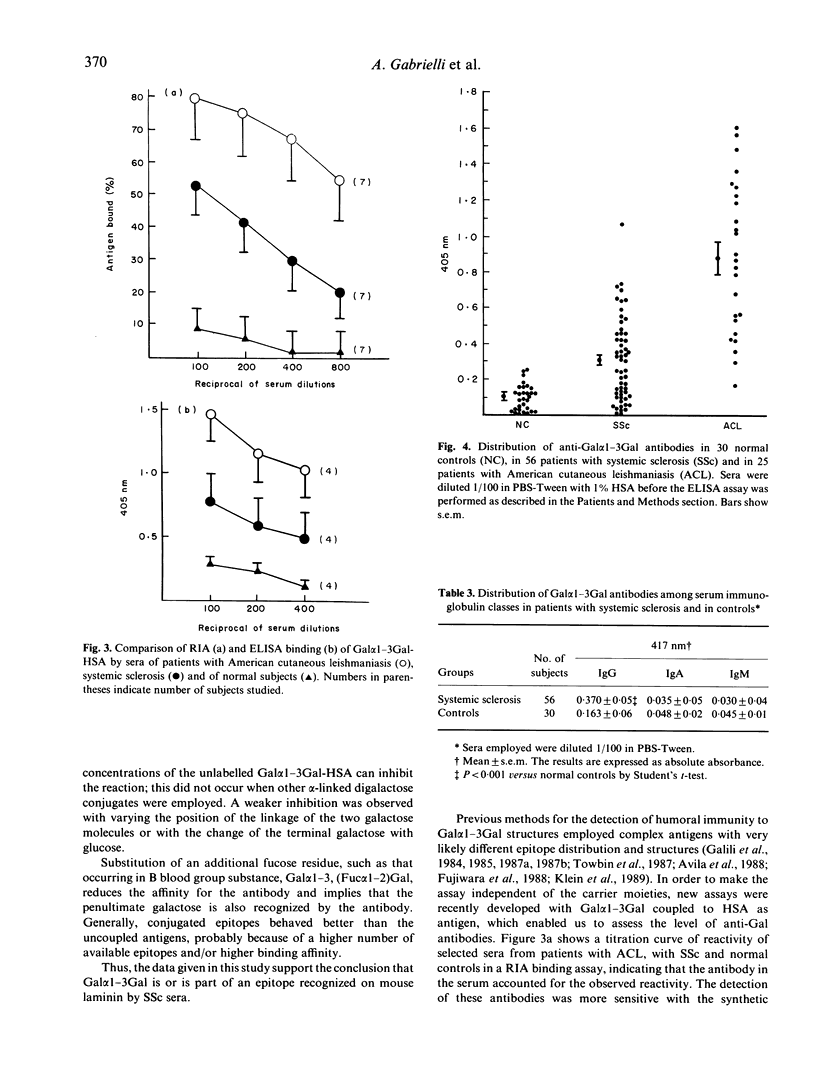
Employing radioimmunoinhibition assays with distinct oligosaccharides as inhibitors, this study demonstrates that the epitope recognized on mouse laminin by sera from patients with systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) is a terminal galactosyl (alpha 1-3)-galactose disaccharide. The reaction with this alpha-digalactose was further confirmed when the sera were tested in radioimmunoassay (RIA) binding assay and in ELISA with synthetic galactose alpha 1-3 galactose coupled to human serum albumin. The circulating antibody appeared restricted to the IgG class and mostly to the subclass IgG3 and IgG4. Antibodies with the same specificity can be found in patients with American cutaneous leishmaniasis and Chagas disease; however, whilst in these diseases the antibody production is triggered by antigenic determinants present on the surface of the parasites, the events eliciting their appearance in systemic sclerosis are unknown.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avila J. L., Rojas M., Galili U. Immunogenic Gal alpha 1----3Gal carbohydrate epitopes are present on pathogenic American Trypanosoma and Leishmania. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 15;142(8):2828–2834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avila J. L., Rojas M., Rieber M. Antibodies to laminin in American cutaneous leishmaniasis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):402–406. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.402-406.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avila J. L., Rojas M., Velazquez-Avila G., von der Mark H., Timpl R. Antibodies to basement membrane protein nidogen in Chagas' disease and American cutaneous leishmaniasis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Nov;24(5):775–778. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.5.775-778.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avila J. L., Rojas M., Velázquez-Avila G., Rieber M. Antibodies to basement membrane proteins nidogen and laminin in sera from streptococcal-related diseases and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Dec;70(3):555–561. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castronovo V., Colin C., Parent B., Foidart J. M., Lambotte R., Mahieu P. Possible role of human natural anti-Gal antibodies in the natural antitumor defense system. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1989 Feb 1;81(3):212–216. doi: 10.1093/jnci/81.3.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Cashman S. J., Walport M. Progressive systemic sclerosis: autoimmune arteriopathy. Lancet. 1987 Feb 28;1(8531):480–482. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92091-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmajer R., Gay S., Meigel W. N., Perlish J. S. Collagen in the cellular and fibrotic stages of scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 May;21(4):418–428. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmajer R., Perlish J. S., Shaw K. V., Pirozzi D. J. Skin capillary changes in early systemic scleroderma. Electron microscopy and "in vitro" autoradiography with tritiated thymidine. Arch Dermatol. 1976 Nov;112(11):1553–1557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmajer R., Perlish J. S., West W. P. Ultrastructure of cutaneous cellular infiltrates in scleroderma. Arch Dermatol. 1977 Dec;113(12):1661–1666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara S., Shinkai H., Deutzmann R., Paulsson M., Timpl R. Structure and distribution of N-linked oligosaccharide chains on various domains of mouse tumour laminin. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 1;252(2):453–461. doi: 10.1042/bj2520453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielli A., Leoni P., Danieli G., Herrmann K., Krieg T., Wieslander J. Antibodies against galactosyl (alpha 1----3) galactose in connective tissue diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Mar;34(3):375–376. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielli A., Montroni M., Rupoli S., Caniglia M. L., DeLustro F., Danieli G. A retrospective study of antibodies against basement membrane antigens (type IV collagen and laminin) in patients with primary and secondary Raynaud's phenomenon. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Nov;31(11):1432–1436. doi: 10.1002/art.1780311114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielli A., Montroni M., Rupoli S., Caniglia M. L., DeLustro F., Danieli G. A retrospective study of antibodies against basement membrane antigens (type IV collagen and laminin) in patients with primary and secondary Raynaud's phenomenon. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Nov;31(11):1432–1436. doi: 10.1002/art.1780311114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U. Abnormal expression of alpha-galactosyl epitopes in man. A trigger for autoimmune processes? Lancet. 1989 Aug 12;2(8659):358–361. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90539-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Buehler J., Shohet S. B., Macher B. A. The human natural anti-Gal IgG. III. The subtlety of immune tolerance in man as demonstrated by crossreactivity between natural anti-Gal and anti-B antibodies. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):693–704. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Clark M. R., Shohet S. B., Buehler J., Macher B. A. Evolutionary relationship between the natural anti-Gal antibody and the Gal alpha 1----3Gal epitope in primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1369–1373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Clark M. R., Shohet S. B. Excessive binding of natural anti-alpha-galactosyl immunoglobin G to sickle erythrocytes may contribute to extravascular cell destruction. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):27–33. doi: 10.1172/JCI112286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Macher B. A., Buehler J., Shohet S. B. Human natural anti-alpha-galactosyl IgG. II. The specific recognition of alpha (1----3)-linked galactose residues. J Exp Med. 1985 Aug 1;162(2):573–582. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.2.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Mandrell R. E., Hamadeh R. M., Shohet S. B., Griffiss J. M. Interaction between human natural anti-alpha-galactosyl immunoglobulin G and bacteria of the human flora. Infect Immun. 1988 Jul;56(7):1730–1737. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.7.1730-1737.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Rachmilewitz E. A., Peleg A., Flechner I. A unique natural human IgG antibody with anti-alpha-galactosyl specificity. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1519–1531. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huffstutter J. E., DeLustro F. A., LeRoy E. C. Cellular immunity to collagen and laminin in scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Jul;28(7):775–780. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Timpl R., Zanetti F. R., Plester D., Berg P. A. High antibody levels against mouse laminin with specificity for galactosyl-(alpha 1-3)galactose in patients with inner ear diseases. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1989 Jul;98(7 Pt 1):537–542. doi: 10.1177/000348948909800708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapenas D., Rodnan G. P., Cavallo T. Immunopathology of the renal vascular lesion of progressive systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Am J Pathol. 1978 May;91(2):243–258. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Simmons D. A., Westphal G. The immunochemistry of Salmonella chemotype VI O-antigens. The structure of oligosaccharides from Salmonella group U (o 43) lipopolysaccharides. Biochem J. 1965 Dec;97(3):820–826. doi: 10.1042/bj0970820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackel A. M., DeLustro F., Harper F. E., LeRoy E. C. Antibodies to collagen in scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 May;25(5):522–531. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penning C. A., Cunningham J., French M. A., Harrison G., Rowell N. R., Hughes P. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity of human vascular endothelium in systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Sep;57(3):548–556. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schur P. H., Monroe M., Rothfield N. The gammaG subclass of antinuclear and antinucleic acid antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Mar-Apr;15(2):174–182. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szarfman A., Terranova V. P., Rennard S. I., Foidart J. M., de Fatima Lima M., Scheinman J. I., Martin G. R. Antibodies to laminin in Chagas' disease. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1161–1171. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R. Antibodies to collagens and procollagens. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):472–498. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Rohde H., Robey P. G., Rennard S. I., Foidart J. M., Martin G. R. Laminin--a glycoprotein from basement membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9933–9937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Rosenfelder G., Wieslander J., Avila J. L., Rojas M., Szarfman A., Esser K., Nowack H., Timpl R. Circulating antibodies to mouse laminin in Chagas disease, American cutaneous leishmaniasis, and normal individuals recognize terminal galactosyl(alpha 1-3)-galactose epitopes. J Exp Med. 1987 Aug 1;166(2):419–432. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.2.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount W. J., Dorner M. M., Kunkel H. G., Kabat E. A. Studies on human antibodies. VI. Selective variations in subgroup composition and genetic markers. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):633–646. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zopf D. A., Smith D. F., Drzeniek Z., Tsai C. M., Ginburg V. Affinity purification of antibodies using oligosaccharide-phenethylamine derivaties coupled to Sepharose. Methods Enzymol. 1978;50:171–175. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(78)50018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


