Abstract
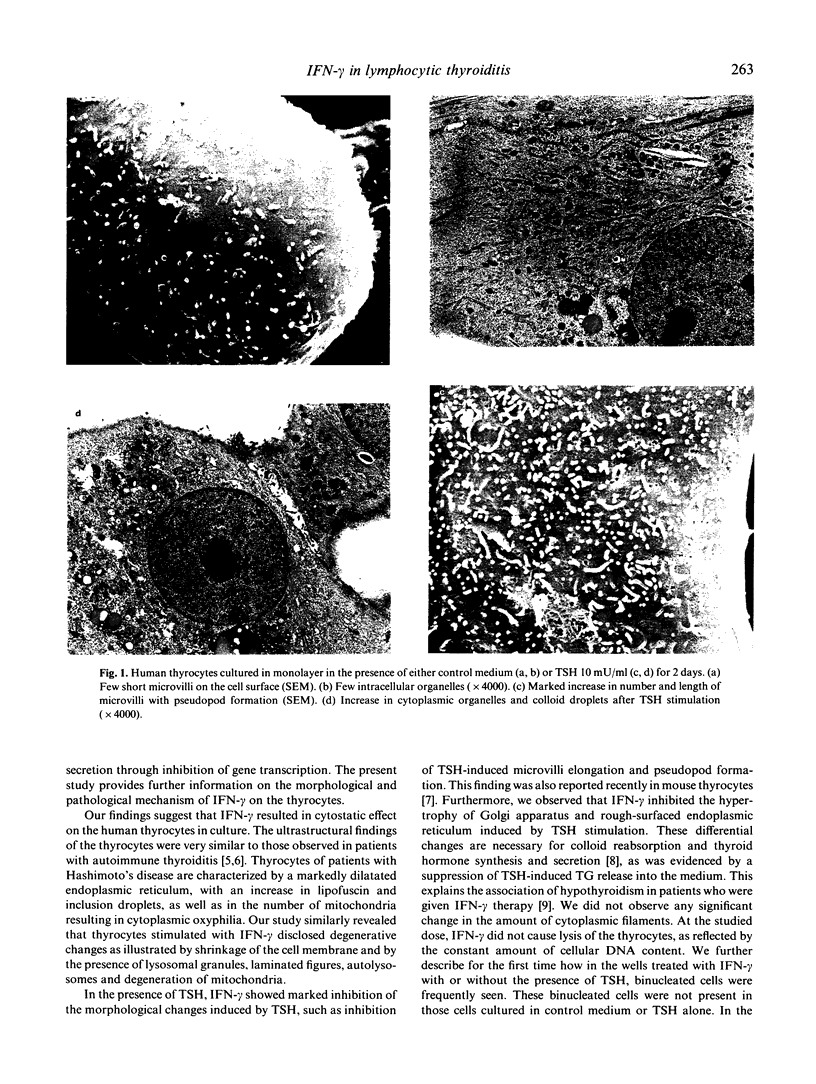
Interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) has been recognized to possess diverse non-immunological effects on epithelial cells such as cellular growth and differentiation. We have previously demonstrated that IFN-gamma suppressed thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)-stimulated thyroglobulin (TG) synthesis in human thyrocytes through inhibition of TG gene transcription. To define the pathological mechanism involved in the action of IFN-gamma, we studied the ultrastructural changes of human thyrocytes cultured in monolayer. Stimulation of the thyrocytes with TSH 10 mU/ml for 2 days resulted in marked increase in TG release into the medium. This was accompanied by elongation of microvilli, increase in follicles and acinar formation, increase in secretory granules and prominence of Golgi apparatus and rough-surfaced endoplasmic reticulum. Addition of IFN-gamma (500 U/ml) resulted in marked degeneration with shrinkage of the cell membrane, vacuolation of cytoplasm, swollen mitochondria and presence of lysosomal granules. Co-culturing the thyrocytes with the IFN-gamma and TSH resulted in suppression of the morphological responsiveness to TSH. There was also suppression of TSH-induced TG secretion. However, at 500 U/ml IFN-gamma did not cause lysis of the thyrocytes as estimated by the cellular DNA content. Furthermore, binucleated cells were frequently encountered in those wells that were treated with IFN-gamma for either 2 or 5 days. The findings suggest that IFN-gamma resulted in de-differentiation and degeneration of the thyrocytes, which subsequently regained the growth potential and showed attempts at regeneration. This may explain why most patients with lymphocytic thyroiditis recover from the acute injury and do not suffer from permanent hypothyroidism.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asakawa H., Miyagawa J., Hanafusa T., Katsura H., Miyazaki A., Otsuka A., Nakagawa C., Yamagata K., Tajima K., Mashita K. Interferon-gamma reduces actin filaments and inhibits thyroid-stimulating hormone-induced formation of microvilli and pseudopods in mouse monolayer thyrocytes. Endocrinology. 1990 Jul;127(1):325–329. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-1-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashizawa K., Yamashita S., Nagayama Y., Kimura H., Hirayu H., Izumi M., Nagataki S. Interferon-gamma inhibits thyrotropin-induced thyroidal peroxidase gene expression in cultured human thyrocytes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Aug;69(2):475–477. doi: 10.1210/jcem-69-2-475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bech K., Nistrup Madsen S. Thyroid adenylate cyclase stimulating immunoglobulins in thyroid diseases. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1979 Jul;11(1):47–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1979.tb03045.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Todd I., Mirakian R., Belfiore A., Pujol-Borrell R. Organ-specific autoimmunity: a 1986 overview. Immunol Rev. 1986 Dec;94:137–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.1986.tb01168.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouty-Boyé D., Tovey M. G. Inhibition by interferon of thymidine uptake in chemostat cultures of L1210 cells. Intervirology. 1978;9(4):243–252. doi: 10.1159/000148942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burman P., Tötterman T. H., Oberg K., Karlsson F. A. Thyroid autoimmunity in patients on long term therapy with leukocyte-derived interferon. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Nov;63(5):1086–1090. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-5-1086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens M. J., McNurlan M. A. Regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation by interferons. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 1;226(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2260345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. E., Roger P. P., Ludgate M. Assays for thyroid growth immunoglobulins and their clinical implications: methods, concepts, and misconceptions. Endocr Rev. 1987 Nov;8(4):448–452. doi: 10.1210/edrv-8-4-448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraiem Z., Sobel E., Sadeh O., Kinarty A., Lahat N. Effects of gamma-interferon on DR antigen expression, growth, 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine secretion, iodide uptake, and cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate accumulation in cultured human thyroid cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Oct;71(4):817–824. doi: 10.1210/jcem-71-4-817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung A. W., Lau K. S. Interferon-gamma inhibits thyrotropin-induced thyroglobulin gene transcription in cultured human thyrocytes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Jun;70(6):1512–1517. doi: 10.1210/jcem-70-6-1512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDSAY S., DAILEY M. E., FRIEDLANDER J., YEE G., SOLEY M. H. Chronic thyroiditis: a clinical and pathologic study of 354 patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1952 Dec;12(12):1578–1600. doi: 10.1210/jcem-12-12-1578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misaki T., Tramontano D., Ingbar S. H. Effects of rat gamma- and non-gamma-interferons on the expression of Ia antigen, growth, and differentiated functions of FRTL5 cells. Endocrinology. 1988 Dec;123(6):2849–2857. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-6-2849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagayama Y., Izumi M., Ashizawa K., Kiriyama T., Yokoyama N., Morita S., Ohtakara S., Fukuda T., Eguchi K., Morimoto I. Inhibitory effect of interferon-gamma on the response of human thyrocytes to thyrotropin (TSH) stimulation: relationship between the response to TSH and the expression of DR antigen. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 May;64(5):949–953. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-5-949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parodi M. T., Cornaglia-Ferraris P., Ponzoni M. Effects of gamma-interferon on the growth, morphology, and membrane and cytoskeletal proteins expression of Lan-1 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Dec;185(2):327–341. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90303-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer L. M., Murphy J. S., Tamm I. Interferon effects on the growth and division of human fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Jun;121(1):111–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90450-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidbord H. E., Fisher E. R. Ultrastructural features of subacute granulomatous thyroiditis and Hashimoto's disease. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 Mar;59(3):327–337. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/59.3.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein A. A., Hernandez I., McClintock J. C. Subacute Granulomatous Thyroiditis: A Clinicopathologic Review. Ann Surg. 1961 Jan;153(1):149–156. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196101000-00018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd I., Pujol-Borrell R., Hammond L. J., McNally J. M., Feldmann M., Bottazzo G. F. Enhancement of thyrocyte HLA class II expression by thyroid stimulating hormone. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Sep;69(3):524–531. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe R. Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Compr Ther. 1977 Nov;3(11):68–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel B. K., Spicer S. S., Wollman S. H. Changes in fine structure and acid phosphatase localization in rat thyroid cells following thyrotropin administration. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jun;25(3):593–618. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.3.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakarija M., Hornicek F. J., Levis S., McKenzie J. M. Effects of gamma-interferon and tumor necrosis factor alpha on thyroid cells: induction of class II antigen and inhibition of growth stimulation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1988 Aug;58(2-3):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(88)90146-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]