Abstract
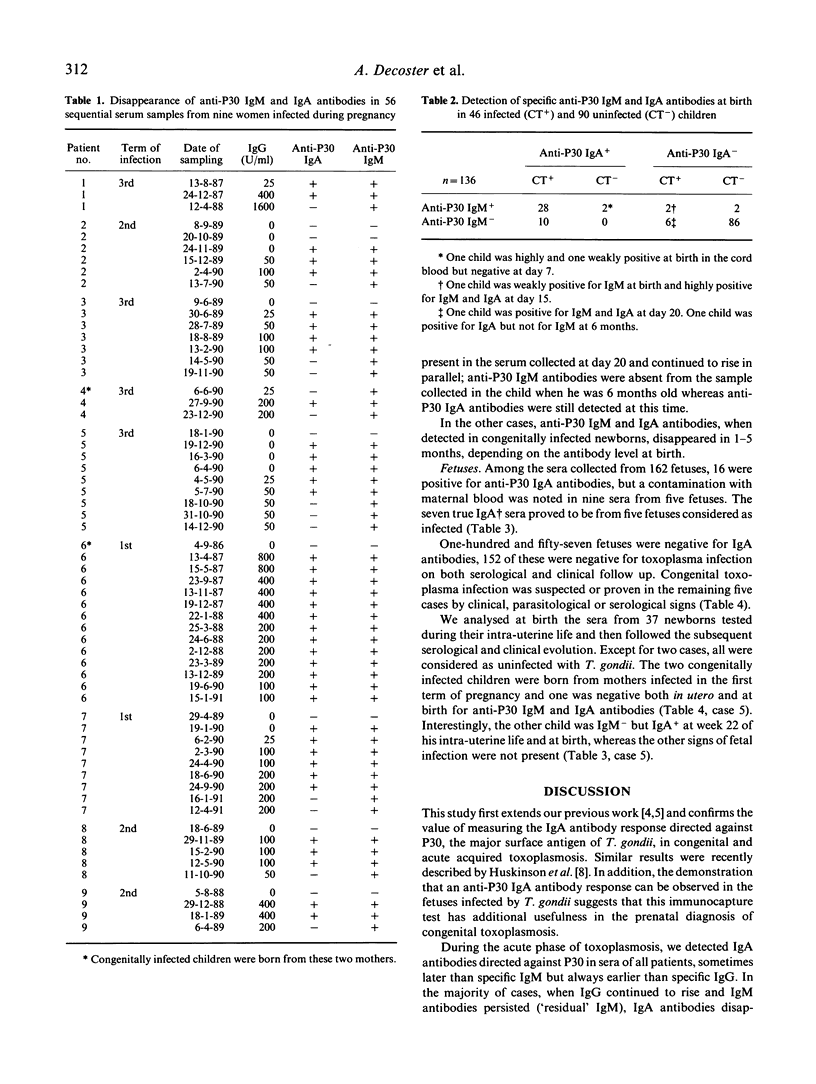
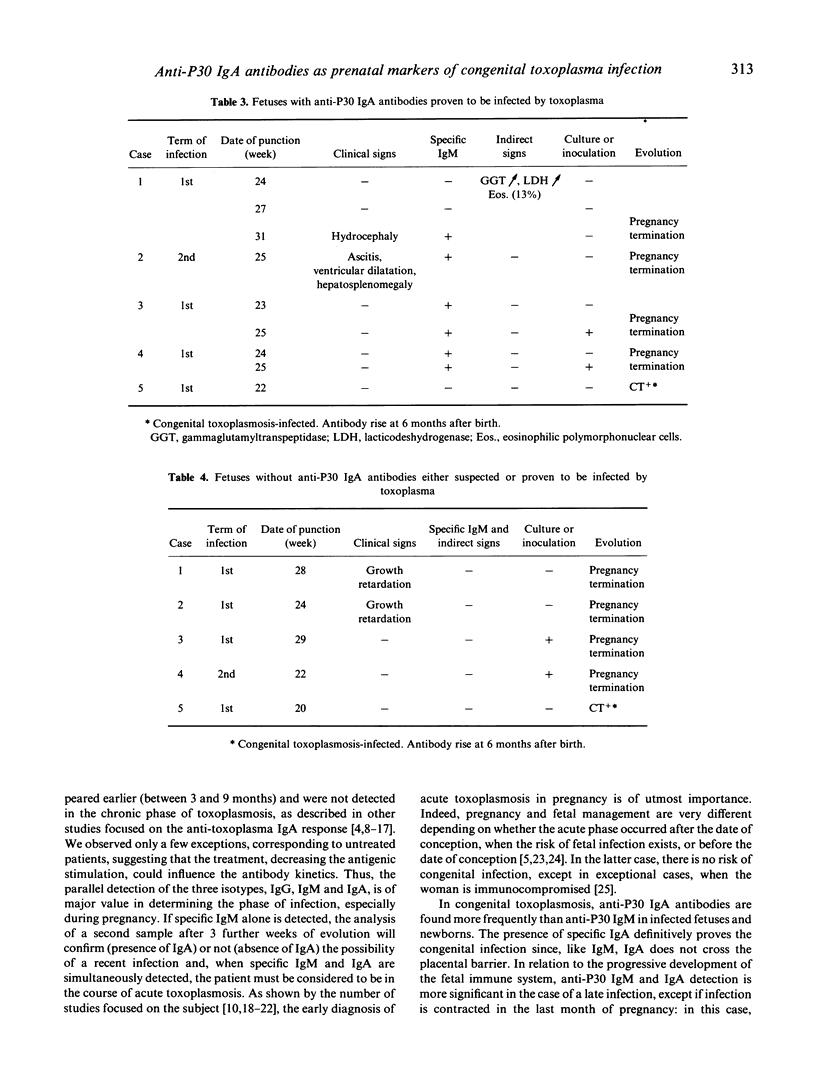
This study extends a previous study and confirms that the detection of anti-P30 IgA antibodies is very helpful in the diagnosis of acute acquired or congenital toxoplasmosis. Moreover, we demonstrate that an anti-P30 IgA response can be mounted in the fetuses infected by Toxoplasma gondii during their intra-uterine life as early as week 23 of gestation. A double-sandwich ELISA described in our previous work was used to detect anti-P30 IgA antibodies in 1378 human serum samples collected from 551 patients, including 162 fetuses whose mothers had been infected by T. gondii during pregnancy, 46 congenitally infected and 90 uninfected newborns and 253 women suspected of having been infected during pregnancy, including the mothers of fetuses and newborns previously described. Anti-P30 IgA antibodies were detected in all cases of acute toxoplasmosis but in no case of chronic toxoplasmosis: in the majority of cases, the IgA antibody titre fell below cut-off in 3-9 months. Among the 46 congenitally infected newborns, anti-P30 IgA antibodies were detected in sera of 41 infected newborns (38 at birth, two in the first months of life, one in the seventh month of life), while anti-P30 IgM antibodies were detected in only 30 cases at birth and in one case during the first month of life. Among 162 fetuses, anti-P30 IgA response was observed in five infected fetuses, but was not detected in either 152 uninfected fetuses or in five fetuses considered as infected. The absence or presence of anti-P30 IgA antibodies in the fetus is discussed in relation to the date of maternal infection and collection of the fetal blood. It clearly appears from our study that the combined testing of both IgM and IgA in the fetus and the newborn is essential for a more efficient diagnosis of infection.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cederqvist L. L., Kimball A. C., Ewool L. C., Litwin S. D. Fetal immune response following congenital toxoplasmosis. Obstet Gynecol. 1977 Aug;50(2):200–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesbron J. Y., Caron A., Santoro F., Wattre P., Ovlaque G., Pierce R. J., Delagneau J. P., Capron A. Une nouvelle méthode ELISA pour le diagnostic de la toxoplasmose. Dosage des IgM sériques par immunocapture avec un anticorps monoclonal anti-Toxoplasma gondii. Presse Med. 1986 Apr 19;15(16):737–740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couvreur J., Desmonts G., Thulliez P. Prophylaxis of congenital toxoplasmosis. Effects of spiramycin on placental infection. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Jul;22 (Suppl B):193–200. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.supplement_b.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daffos F., Capella-Pavlovsky M., Forestier F. Fetal blood sampling during pregnancy with use of a needle guided by ultrasound: a study of 606 consecutive cases. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1985 Nov 15;153(6):655–660. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(85)80254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daffos F., Forestier F., Capella-Pavlovsky M., Thulliez P., Aufrant C., Valenti D., Cox W. L. Prenatal management of 746 pregnancies at risk for congenital toxoplasmosis. N Engl J Med. 1988 Feb 4;318(5):271–275. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198802043180502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dannemann B. R., Vaughan W. C., Thulliez P., Remington J. S. Differential agglutination test for diagnosis of recently acquired infection with Toxoplasma gondii. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):1928–1933. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.1928-1933.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decoster A., Darcy F., Capron A. Recognition of Toxoplasma gondii excreted and secreted antigens by human sera from acquired and congenital toxoplasmosis: identification of markers of acute and chronic infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Sep;73(3):376–382. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decoster A., Darcy F., Caron A., Capron A. IgA antibodies against P30 as markers of congenital and acute toxoplasmosis. Lancet. 1988 Nov 12;2(8620):1104–1107. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90523-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derouin F., Thulliez P., Candolfi E., Daffos F., Forestier F. Early prenatal diagnosis of congenital toxoplasmosis using amniotic fluid samples and tissue culture. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Jun;7(3):423–425. doi: 10.1007/BF01962355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmonts G., Couvreur J. L'isolement du parasite dans la toxoplasmose congénitale: intérêt pratique et théorique. Arch Fr Pediatr. 1974 Feb-Mar;31(2):157–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmonts G., Daffos F., Forestier F., Capella-Pavlovsky M., Thulliez P., Chartier M. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital toxoplasmosis. Lancet. 1985 Mar 2;1(8427):500–504. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durandy A., Fischer A., Griscelli C. Active suppression of B lymphocyte maturation by two different newborn T lymphocyte subsets. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2644–2650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forestier F., Daffos F., Capella Pavlovsky M. Intérêts du prélèvement de sang foetal dans le diagnostic prénatal, la foetologie et la thérapeutique in utero. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1985;43(4):535–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco E. L., Walls K. W., Sulzer A. J. Reverse enzyme immunoassay for detection of specific anti-Toxoplasma immunoglobulin M antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 May;13(5):859–864. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.5.859-864.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward A. R., Lawton A. R. Induction of plasma cell differentiation of human fetal lymphocytes: evidence for functional immaturity of T and B cells. J Immunol. 1977 Oct;119(4):1213–1217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedman K., Lappalainen M., Seppäiä I., Mäkelä O. Recent primary toxoplasma infection indicated by a low avidity of specific IgG. J Infect Dis. 1989 Apr;159(4):736–740. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.4.736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huskinson J., Stepick-Biek P. N., Araujo F. G., Thulliez P., Suzuki Y., Remington J. S. Toxoplasma antigens recognized by immunoglobulin G subclasses during acute and chronic infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):2031–2038. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.2031-2038.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huskinson J., Thulliez P., Remington J. S. Toxoplasma antigens recognized by human immunoglobulin A antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Dec;28(12):2632–2636. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.12.2632-2636.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Fichoux Y., Marty P., Chan H. Les IgA sériques spécifiques dans le diagnostic de la toxoplasmose. Ann Pediatr (Paris) 1987 May;34(5):375–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx-Chemla C., Puygauthier-Toubas D., Foudrinier F., Dorangeon P. H., Leulier J., Quereux C., Leroux B., Pinon J. M. La surveillance immunologique d'une femme enceinte séronégative pour la toxoplasmose doit-elle s'arrêter à l'accouchement? Presse Med. 1990 Mar 3;19(8):367–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partanen P., Turunen H. J., Paasivuo R. T., Leinikki P. O. Immunoblot analysis of Toxoplasma gondii antigens by human immunoglobulins G, M, and A antibodies at different stages of infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):133–135. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.133-135.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinon J. M., Thoannes H., Pouletty P. H., Poirriez J., Damiens J., Pelletier P. Detection of IgA specific for toxoplasmosis in serum and cerebrospinal fluid using a non-enzymatic IgA-capture assay. Diagn Immunol. 1986;4(5):223–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro F., Afchain D., Pierce R., Cesbron J. Y., Ovlaque G., Capron A. Serodiagnosis of toxoplasma infection using a purified parasite protein (P30). Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Nov;62(2):262–269. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stepick-Biek P., Thulliez P., Araujo F. G., Remington J. S. IgA antibodies for diagnosis of acute congenital and acquired toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):270–273. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turunen H., Vuorio K. A., Leinikki P. O. Determination of IgG, IgM and IgA antibody responses in human toxoplasmosis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Scand J Infect Dis. 1983;15(3):307–311. doi: 10.3109/inf.1983.15.issue-3.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loon A. M., van der Logt J. T., Heessen F. W., van der Veen J. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay that uses labeled antigen for detection of immunoglobulin M and A antibodies in toxoplasmosis: comparison with indirect immunofluorescence and double-sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):997–1004. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.997-1004.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



