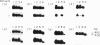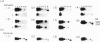Abstract
The synovial tissue and fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) contain activated T cells that probably have a central role in the disease process which leads to joint destruction. A subset of T cells, gamma delta T cells detected at the site of inflammation, may be important in the pathogenesis of the disease. This study investigated variable (V) gene usage of gamma delta T cell receptors (TcRs) expressed in synovia and peripheral blood of patients with RA by using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to amplify TcR gamma- and delta-chain transcripts. Most patients showed no restriction in V gamma gene usage since synovial mononuclear cells (SMC) expressed TcR gamma-chain transcripts which used the same set of V gamma genes as peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). In contrast, the majority of patients expressed a restricted SMC V delta-chain repertoire biased towards V delta 1, but V delta 2 mRNA transcripts were also detected, albeit at low levels in some patients. The TcR delta-chain repertoires of PBMC from healthy control subjects were also characterized. There was variation in the TcR delta-chain repertoires of PBMC from patients when compared with controls, particularly with respect to expression of V delta 4. V delta 4 mRNA transcripts were expressed in PBMC of only two of seven RA patients in contrast with eight of the nine controls (P = 0.03). These findings are compatible with reports that gamma delta T cells in the rheumatoid synovium are reactive to Mycobacterium tuberculosis and that response to M. tuberculosis is restricted to V gamma 9/V delta 2-bearing T cells, if a superantigen is involved in the pathogenesis of RA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguas A., Esaguy N., Sunkel C. E., Silva M. T. Cross-reactivity and sequence homology between the 65-kilodalton mycobacterial heat shock protein and human lactoferrin, transferrin, and DR beta subsets of major histocompatibility complex class II molecules. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1461–1470. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1461-1470.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison J. P., Havran W. L. The immunobiology of T cells with invariant gamma delta antigen receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:679–705. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.003335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison J. P., Lanier L. L. Structure, function, and serology of the T-cell antigen receptor complex. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:503–540. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.002443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmester G. R., Jahn B., Gramatzki M., Zacher J., Kalden J. R. Activated T cells in vivo and in vitro: divergence in expression of Tac and Ia antigens in the nonblastoid small T cells of inflammation and normal T cells activated in vitro. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1230–1234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. W., Kotzin B., Herron L., Callahan J., Marrack P., Kappler J. Interaction of Staphylococcus aureus toxin "superantigens" with human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8941–8945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dembić Z., Haas W., Weiss S., McCubrey J., Kiefer H., von Boehmer H., Steinmetz M. Transfer of specificity by murine alpha and beta T-cell receptor genes. Nature. 1986 Mar 20;320(6059):232–238. doi: 10.1038/320232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deusch K., Lüling F., Reich K., Classen M., Wagner H., Pfeffer K. A major fraction of human intraepithelial lymphocytes simultaneously expresses the gamma/delta T cell receptor, the CD8 accessory molecule and preferentially uses the V delta 1 gene segment. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Apr;21(4):1053–1059. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groh V., Porcelli S., Fabbi M., Lanier L. L., Picker L. J., Anderson T., Warnke R. A., Bhan A. K., Strominger J. L., Brenner M. B. Human lymphocytes bearing T cell receptor gamma/delta are phenotypically diverse and evenly distributed throughout the lymphoid system. J Exp Med. 1989 Apr 1;169(4):1277–1294. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.4.1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haregewoin A., Soman G., Hom R. C., Finberg R. W. Human gamma delta+ T cells respond to mycobacterial heat-shock protein. Nature. 1989 Jul 27;340(6231):309–312. doi: 10.1038/340309a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman A., Kappler J. W., Marrack P., Pullen A. M. Superantigens: mechanism of T-cell stimulation and role in immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:745–772. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.003525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holoshitz J., Klajman A., Drucker I., Lapidot Z., Yaretzky A., Frenkel A., van Eden W., Cohen I. R. T lymphocytes of rheumatoid arthritis patients show augmented reactivity to a fraction of mycobacteria cross-reactive with cartilage. Lancet. 1986 Aug 9;2(8502):305–309. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holoshitz J., Koning F., Coligan J. E., De Bruyn J., Strober S. Isolation of CD4- CD8- mycobacteria-reactive T lymphocyte clones from rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):226–229. doi: 10.1038/339226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabelitz D., Bender A., Prospero T., Wesselborg S., Janssen O., Pechhold K. The primary response of human gamma/delta + T cells to Mycobacterium tuberculosis is restricted to V gamma 9-bearing cells. J Exp Med. 1991 Jun 1;173(6):1331–1338. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.6.1331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabelitz D., Bender A., Schondelmaier S., Schoel B., Kaufmann S. H. A large fraction of human peripheral blood gamma/delta + T cells is activated by Mycobacterium tuberculosis but not by its 65-kD heat shock protein. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):667–679. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J. W., Staerz U., White J., Marrack P. C. Self-tolerance eliminates T cells specific for Mls-modified products of the major histocompatibility complex. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):35–40. doi: 10.1038/332035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe Y., Ochi A. Programmed cell death and extrathymic reduction of Vbeta8+ CD4+ T cells in mice tolerant to Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):245–248. doi: 10.1038/349245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keystone E. C., Rittershaus C., Wood N., Snow K. M., Flatow J., Purvis J. C., Poplonski L., Kung P. C. Elevation of a gamma delta T cell subset in peripheral blood and synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Apr;84(1):78–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldsen-Kragh J., Quayle A., Kalvenes C., Førre O., Sørskaar D., Vinje O., Thoen J., Natvig J. B. T gamma delta cells in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. In the juvenile rheumatoid arthritis synovium the T gamma delta cells express activation antigens and are predominantly V delta 1+, and a significant proportion of these patients have elevated percentages of T gamma delta cells. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Dec;32(6):651–659. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb03207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFranc M. P., Forster A., Baer R., Stinson M. A., Rabbitts T. H. Diversity and rearrangement of the human T cell rearranging gamma genes: nine germ-line variable genes belonging to two subgroups. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):237–246. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90388-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefranc M. P., Chuchana P., Dariavach P., Nguyen C., Huck S., Brockly F., Jordan B., Lefranc G. Molecular mapping of the human T cell receptor gamma (TRG) genes and linkage of the variable and constant regions. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jun;19(6):989–994. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matis L. A., Fry A. M., Cron R. Q., Cotterman M. M., Dick R. F., Bluestone J. A. Structure and specificity of a class II MHC alloreactive gamma delta T cell receptor heterodimer. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):746–749. doi: 10.1126/science.2528206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepom G. T., Byers P., Seyfried C., Healey L. A., Wilske K. R., Stage D., Nepom B. S. HLA genes associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Identification of susceptibility alleles using specific oligonucleotide probes. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Jan;32(1):15–21. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive C., Gatenby P. A., Serjeantson S. W. Analysis of T cell receptor V alpha and V beta gene usage in synovia of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;69(Pt 5):349–354. doi: 10.1038/icb.1991.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paliard X., West S. G., Lafferty J. A., Clements J. R., Kappler J. W., Marrack P., Kotzin B. L. Evidence for the effects of a superantigen in rheumatoid arthritis. Science. 1991 Jul 19;253(5017):325–329. doi: 10.1126/science.1857971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer K., Schoel B., Gulle H., Kaufmann S. H., Wagner H. Primary responses of human T cells to mycobacteria: a frequent set of gamma/delta T cells are stimulated by protease-resistant ligands. Eur J Immunol. 1990 May;20(5):1175–1179. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raulet D. H. Immunology. Antigens for gamma/delta T cells. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):342–343. doi: 10.1038/339342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raulet D. H. The structure, function, and molecular genetics of the gamma/delta T cell receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:175–207. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. D., Bröker B., Moretta L., Ciccone E., Grossi C. E., Edwards J. C., Yüksel F., Colaco B., Worman C., Mackenzie L. T gamma delta cells and their subsets in blood and synovial tissue from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Dec;32(6):585–593. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb03200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottini A., Imberti L., Gorla R., Cattaneo R., Primi D. Restricted expression of T cell receptor V beta but not V alpha genes in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Feb;21(2):461–466. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takihara Y., Champagne E., Griesser H., Kimura N., Tkachuk D., Reimann J., Okada A., Alt F. W., Chess L., Minden M. Sequence and organization of the human T cell delta chain gene. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Feb;18(2):283–287. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takihara Y., Reimann J., Michalopoulos E., Ciccone E., Moretta L., Mak T. W. Diversity and structure of human T cell receptor delta chain genes in peripheral blood gamma/delta-bearing T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1989 Feb 1;169(2):393–405. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.2.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triebel F., Faure F., Mami-Chouaib F., Jitsukawa S., Griscelli A., Genevée C., Roman-Roman S., Hercend T. A novel human V delta gene expressed predominantly in the Ti gamma A fraction of gamma/delta+ peripheral lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Dec;18(12):2021–2027. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Boxel J. A., Paget S. A. Predominantly T-cell infiltrate in rheumatoid synovial membranes. N Engl J Med. 1975 Sep 11;293(11):517–520. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197509112931101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Herman A., Pullen A. M., Kubo R., Kappler J. W., Marrack P. The V beta-specific superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B: stimulation of mature T cells and clonal deletion in neonatal mice. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90980-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wordsworth B. P., Lanchbury J. S., Sakkas L. I., Welsh K. I., Panayi G. S., Bell J. I. HLA-DR4 subtype frequencies in rheumatoid arthritis indicate that DRB1 is the major susceptibility locus within the HLA class II region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10049–10053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagüe J., White J., Coleclough C., Kappler J., Palmer E., Marrack P. The T cell receptor: the alpha and beta chains define idiotype, and antigen and MHC specificity. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikai Y., Toyonaga B., Koga Y., Kimura N., Griesser H., Mak T. W. Repertoire of the human T cell gamma genes: high frequency of nonfunctional transcripts in thymus and mature T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Jan;17(1):119–126. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaller D. M., Osman G., Kanagawa O., Hood L. Prevention and treatment of murine experimental allergic encephalomyelitis with T cell receptor V beta-specific antibodies. J Exp Med. 1990 Jun 1;171(6):1943–1955. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.6.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]