Abstract
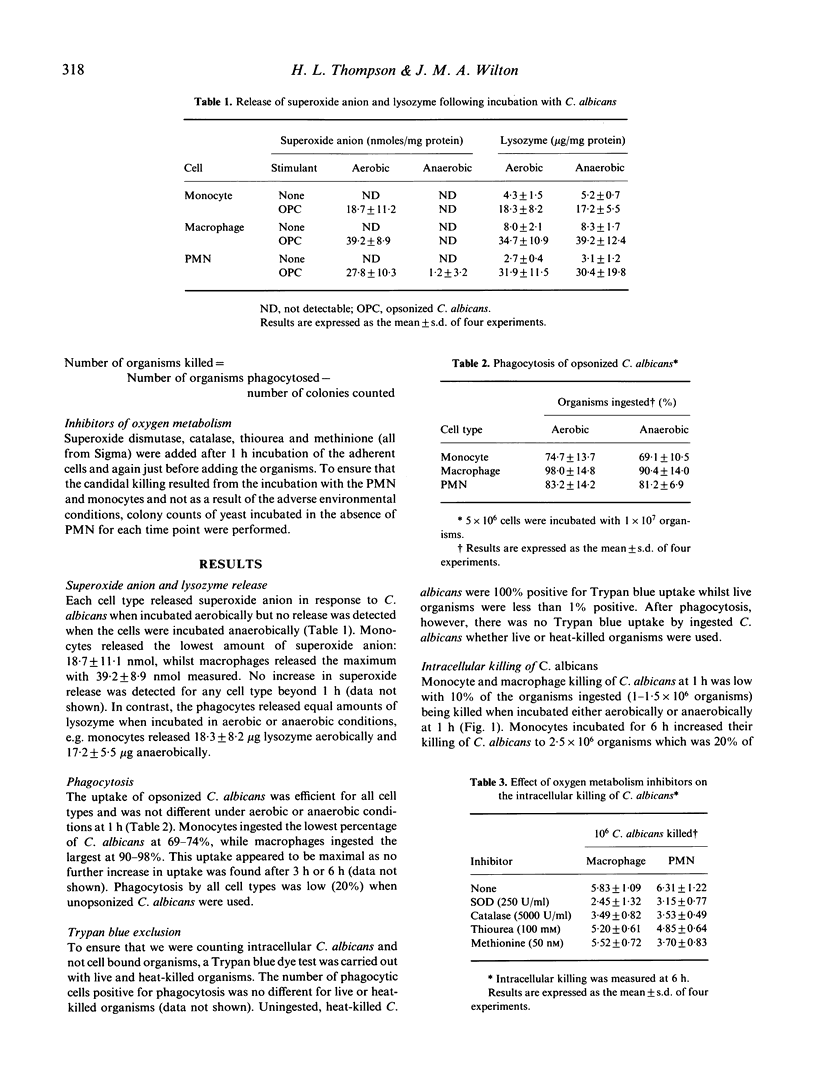
Polymorphonuclear leucocytes (PMN), monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages were capable of interacting with opsonized C. albicans in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Superoxide anion release by these cells was inhibited in anaerobic conditions while lysozyme release and phagocytosis were equally efficient in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. All cell types tested were capable of intracellular killing of C. albicans and this appeared to be maximum at 6 h for monocytes and macrophages and 24 h for PMN. Monocytes killed the lowest number of organisms, 1 x 10(6), and the killing was similar for aerobic and anaerobic conditions. In contrast, PMN and macrophages demonstrated greater killing of C. albicans in aerobic conditions compared with anaerobic conditions; PMN killed 1.9 x 10(6) organisms and macrophages 3 x 10(6) when incubated anaerobically. Inhibitors of oxygen metabolism decreased intracellular killing of C. albicans by macrophages and PMN in aerobic but not anaerobic conditions. The oxygen reaction products involved in the killing of C. albicans appeared to be different however: macrophage killing was decreased by superoxide anion and hydrogen peroxide inhibitors. PMN killing was decreased by superoxide anion, hydrogen peroxide, hypochlorous acid and hydroxyl radical inhibitors. The present study shows that although monocytes, macrophages and PMN function similarly in their interaction with C. albicans, they appear to use different oxygen reactive products for the intracellular killing of C. albicans.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach M. C., Sahyoun A., Adler J. L., Schlesinger R. M., Breman J., Madras P., P'eng F., Monaco A. P. High incidence of fungus infections in renal transplantation patients treated with antilymphocyte and conventional immunosuppression. Transplant Proc. 1973 Mar;5(1):549–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brummer E., Stevens D. A. Fungicidal mechanisms of activated macrophages: evidence for nonoxidative mechanisms for killing of Blastomyces dermatitidis. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3221–3224. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3221-3224.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brune K., Schmid L., Glatt M., Minder B. Correlation between antimicrobial activity and peroxidase content of leukocytes. Nature. 1973 Sep 28;245(5422):209–210. doi: 10.1038/245209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderon R. A., Shennan G. I. Susceptibility of Trichophyton quinckeanum and Trichophyton rubrum to products of oxidative metabolism. Immunology. 1987 Jul;61(3):283–288. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daimond R. D., Krzesicki R. Mechanisms of attachment of neutrophils to Candida albicans pseudohyphae in the absence of serum, and of subsequent damage to pseudohyphae by microbicidal processes of neutrophils in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):360–369. doi: 10.1172/JCI108946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. E., Jr, Lehrer R. I., Stiehm E. R., Fischer T. J., Young L. S. Severe candidal infections: clinical perspective, immune defense mechanisms, and current concepts of therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Jul;89(1):91–106. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromtling R. A., Shadomy H. J. An overview of macrophage-fungal interactions. Mycopathologia. 1986 Feb;93(2):77–93. doi: 10.1007/BF00437738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabay J. E. Microbicidal mechanisms of phagocytes. Curr Opin Immunol. 1988 Sep-Oct;1(1):36–40. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(88)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand J. A., Hurley D. L., Fauci A. S., Frank M. M. Role of complement in host defense against experimental disseminated candidiasis. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jul;138(1):9–16. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore B. J., Retsinas E. M., Lorenz J. S., Hostetter M. K. An iC3b receptor on Candida albicans: structure, function, and correlates for pathogenicity. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):38–46. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Myeloperoxidase-halide-hydrogen peroxide antibacterial system. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2131–2138. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2131-2138.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. J., Watanakunakorn C. Hospital-acquired fungemia. Its natural course and clinical significance. Am J Med. 1979 Jul;67(1):51–58. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90073-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. S., Harris C. A., Small C. B., Moll B., Lesser M., Friedland G. H. Oral candidiasis in high-risk patients as the initial manifestation of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1984 Aug 9;311(6):354–358. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198408093110602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Cline M. J. Leukocyte myeloperoxidase deficiency and disseminated candidiasis: the role of myeloperoxidase in resistance to Candida infection. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1478–1488. doi: 10.1172/JCI106114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I. The fungicidal mechanisms of human monocytes. I. Evidence for myeloperoxidase-linked and myeloperoxidase-independent candidacidal mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1975 Feb;55(2):338–346. doi: 10.1172/JCI107937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijh P. C., van den Barselaar M. T., van Furth R. Kinetics of phagocytosis and intracellular killing of Candida albicans by human granulocytes and monocytes. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):313–318. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.313-318.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Rubin B. Y., Carriero S. M., Harris A. M., Jaffee E. A. Human mononuclear phagocyte antiprotozoal mechanisms: oxygen-dependent vs oxygen-independent activity against intracellular Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1982–1988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osserman E. F., Lawlor D. P. Serum and urinary lysozyme (muramidase) in monocytic and monomyelocytic leukemia. J Exp Med. 1966 Nov 1;124(5):921–952. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.5.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick E., Mizel D. Rapid microassays for the measurement of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide production by macrophages in culture using an automatic enzyme immunoassay reader. J Immunol Methods. 1981;46(2):211–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos D., Loos J. A. Changes in the carbohydrate metabolism of mitogenically stimulated human peripheral lymphocytes. I. Stimulation by phytohaemagglutinin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 29;222(3):565–582. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90182-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Rosenthal A. S., Balestra D. J. Abnormal bactericidal, metabolic, and lysosomal functions of Chediak-Higashi Syndrome leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1972 Mar;51(3):649–665. doi: 10.1172/JCI106854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. D., Cain J. A., Lachmann P. J. Membrane complement receptor type three (CR3) has lectin-like properties analogous to bovine conglutinin as functions as a receptor for zymosan and rabbit erythrocytes as well as a receptor for iC3b. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3307–3315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasada M., Johnston R. B., Jr Macrophage microbicidal activity. Correlation between phagocytosis-associated oxidative metabolism and the killing of Candida by macrophages. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):85–98. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitznagel J. K. Nonoxidative antimicrobial reactions of leukocytes. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1984;14:283–343. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-4862-8_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steigbigel R. T., Lambert L. H., Jr, Remington J. S. Phagocytic and bacterial properties of normal human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):131–142. doi: 10.1172/JCI107531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., Peters R., Peterson P. K., Verhoef J. Phagocytosis and killing of staphylococci by human polymorphonuclear and mononuclear leucocytes. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jun;31(6):539–545. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.6.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. K., Collins-Lech C., Sohnle P. G. Inhibition of neutrophil killing of Candida albicans pseudohyphae by substances which quench hypochlorous acid and chloramines. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):731–735. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.731-735.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde C. G., Griffith J. E., Marra M. N., Snable J. L., Scott R. W. Purification and characterization of human neutrophil peptide 4, a novel member of the defensin family. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11200–11203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Saito H., Tomioka H., Jidoi J. Relationship between the susceptibility of various bacteria to active oxygen species and to intracellular killing by macrophages. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Aug;133(8):2015–2021. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-8-2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van 't Wout J. W., Linde I., Leijh P. C., van Furth R. Contribution of granulocytes and monocytes to resistance against experimental disseminated Candida albicans infection. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;7(6):736–741. doi: 10.1007/BF01975039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



