Abstract
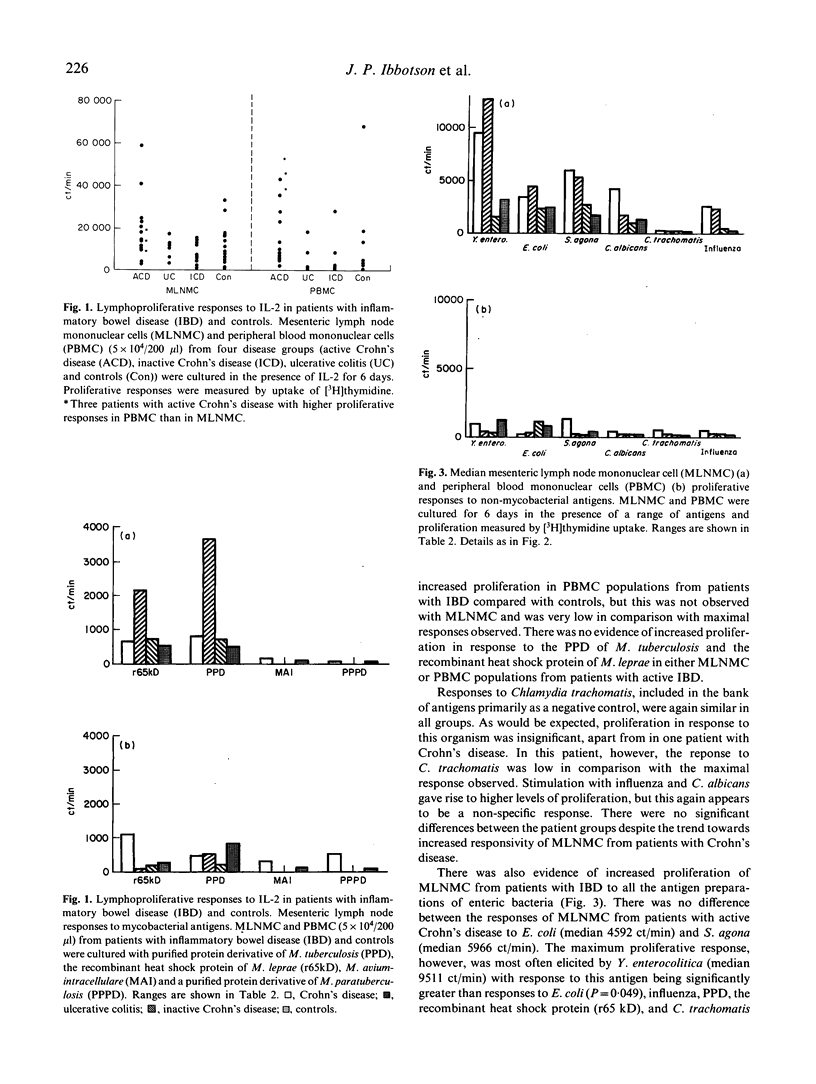
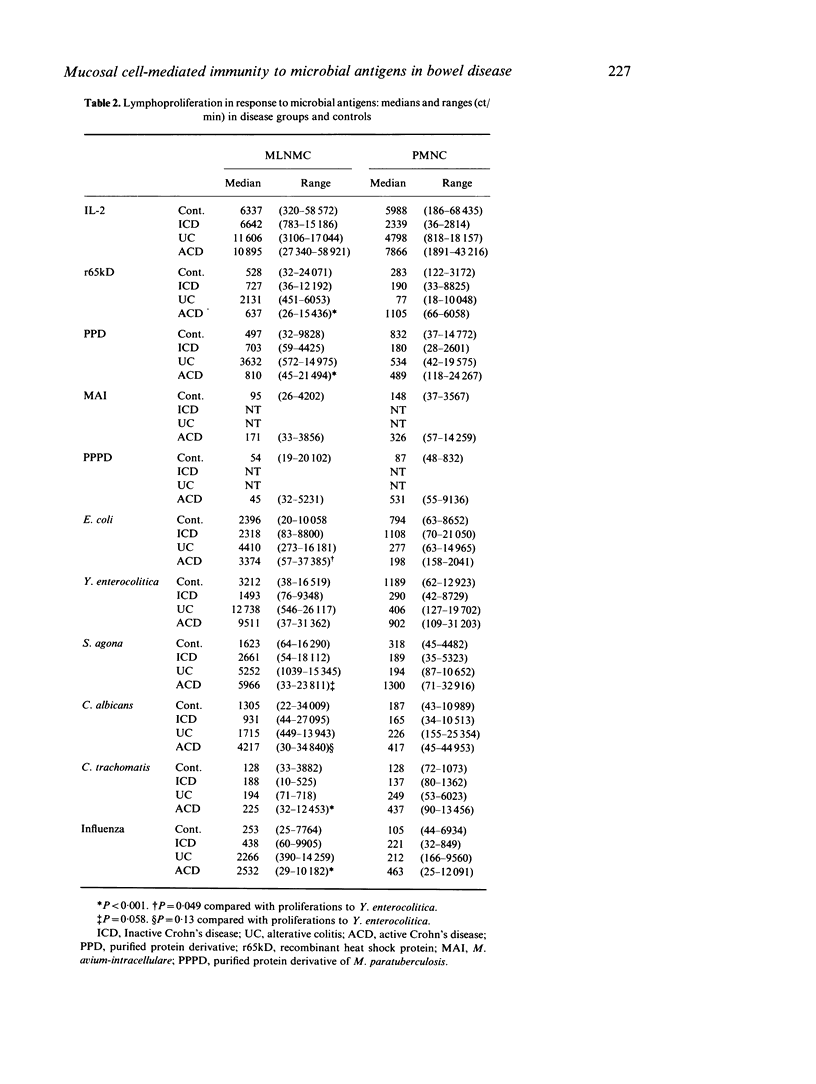
Culture studies have suggested that Mycobacterium paratuberculosis may play a role in the aetiology of Crohn's disease. However, evidence of sensitization to mycobacterial antigens amongst patients with Crohn's disease has not yet been adequately demonstrated. Previous studies of cell-mediated immunity (CMI) in Crohn's disease were restricted to responses of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) to mycobacterial antigens. In this study we have investigated the proliferative responses of both PBMC and mesenteric lymph node mononuclear cells (MLNMC) to a range of mycobacterial and non-mycobacterial antigens. There was no evidence of specific sensitization in the responses of MLNMC and PBMC from patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) to the mycobacterial antigens. However, anergy to M. paratuberculosis could not be excluded. IBD MLNMC responses to most antigens were generally greater than those of PBMC, which were often undetectable. When compared with controls, there was evidence of increased CMI to a range of non-mycobacterial antigens, especially Yersinia enterocolitica, amongst both MLNMC and PBMC from patients with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis (UC). These results do not provide support to the proposed role of mycobacteria in the pathogenesis of Crohn's disease, but indicate that further investigation may determine a role for bacterial-specific T cell-mediated responses in the pathogenesis of IBD.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser M. J., Miller R. A., Lacher J., Singleton J. W. Patients with active Crohn's disease have elevated serum antibodies to antigens of seven enteric bacterial pathogens. Gastroenterology. 1984 Oct;87(4):888–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J. Crohn's disease and the mycobacterioses: a review and comparison of two disease entities. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jan;2(1):90–117. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.1.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J., Van Kruiningen H. J., Thayer W. R., Coutu J. A. Spheroplastic phase of mycobacteria isolated from patients with Crohn's disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Sep;24(3):357–363. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.3.357-363.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J., Van Kruiningen H. J., Thayer W. R., Merkal R. S., Coutu J. A. Possible role of mycobacteria in inflammatory bowel disease. I. An unclassified Mycobacterium species isolated from patients with Crohn's disease. Dig Dis Sci. 1984 Dec;29(12):1073–1079. doi: 10.1007/BF01317078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cover T. L., Aber R. C. Yersinia enterocolitica. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jul 6;321(1):16–24. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198907063210104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos M., Cuvelier C., Mielants H., Veys E., Barbier F., Elewaut A. Ileocolonoscopy in seronegative spondylarthropathy. Gastroenterology. 1989 Feb;96(2 Pt 1):339–344. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91557-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert E. C., Bhatt B. D., Liu S., Das K. M. Induction of suppressor cells by Mycobacterium paratuberculosis antigen in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Feb;83(2):320–325. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05635.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Maraghi N. R., Mair N. S. The histopathology of enteric infection with Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979 Jun;71(6):631–639. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/71.6.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott P. R., Lennard-Jones J. E., Burnham W. R., White S., Stanford J. L. Further data on skin testing with mycobacterial antigens in inflammatory bowel disease. Lancet. 1980 Aug 30;2(8192):483–484. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91922-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiocchi C., Battisto J. R., Farmer R. G. Studies on isolated gut mucosal lymphocytes in inflammatory bowel disease. Detection of activated T cells and enhanced proliferation to Staphylococcus aureus and lipopolysaccharides. Dig Dis Sci. 1981 Aug;26(8):728–736. doi: 10.1007/BF01316863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford D. K., da Roza D., Schulzer M. Lymphocytes from the site of disease but not blood lymphocytes indicate the cause of arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1985 Oct;44(10):701–710. doi: 10.1136/ard.44.10.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston J. S., Life P. F., Granfors K., Merilahti-Palo R., Bailey L., Consalvey S., Toivanen A., Bacon P. A. Synovial T lymphocyte recognition of organisms that trigger reactive arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Jun;76(3):348–353. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holoshitz J., Klajman A., Drucker I., Lapidot Z., Yaretzky A., Frenkel A., van Eden W., Cohen I. R. T lymphocytes of rheumatoid arthritis patients show augmented reactivity to a fraction of mycobacteria cross-reactive with cartilage. Lancet. 1986 Aug 9;2(8502):305–309. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoogkamp-Korstanje J. A., de Koning J., Heesemann J. Persistence of Yersinia enterocolitica in man. Infection. 1988 Mar-Apr;16(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF01644307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibbotson J. P., Pease P. E., Allan R. N. Serological studies in Crohn's disease. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jun;6(3):286–290. doi: 10.1007/BF02017614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi K., Brown W. R., Brennan P. J., Blaser M. J. Serum antibodies to mycobacterial antigens in active Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jun;94(6):1404–1411. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90679-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagercrantz R., Hammarström S., Perlmann P., Gustafsson B. E. Immunological studies in ulcerative colitis. IV. Origin of autoantibodies. J Exp Med. 1968 Dec 1;128(6):1339–1352. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.6.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Life P. F., Viner N. J., Bacon P. A., Gaston J. S. Synovial fluid antigen-presenting cells unmask peripheral blood T cell responses to bacterial antigens in inflammatory arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Feb;79(2):189–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05177.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. P., Lyng K., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydial disease pathogenesis. Ocular hypersensitivity elicited by a genus-specific 57-kD protein. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):663–675. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orda R., Samra Z., Levy Y., Shperber Y., Scapa E. Chlamydia trachomatis and inflammatory bowel disease--a coincidence? J R Soc Med. 1990 Jan;83(1):15–17. doi: 10.1177/014107689008300108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallone F., Fais S., Squarcia O., Biancone L., Pozzilli P., Boirivant M. Activation of peripheral blood and intestinal lamina propria lymphocytes in Crohn's disease. In vivo state of activation and in vitro response to stimulation as defined by the expression of early activation antigens. Gut. 1987 Jun;28(6):745–753. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.6.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent K., Mitchell P. Cell wall-defective variants of pseudomonas-like (group Va) bacteria in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1978 Sep;75(3):368–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson S., Danielsson D., Kjellander J., Wallensten S. Studies on Crohn's disease. 1. The relationship between Yersinia enterocolitica infection and terminal ileitis. Acta Chir Scand. 1976;142(1):84–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purrmann J., Bertrams J., Borchard F., Miller B., Cleveland S., Stolze T., Strohmeyer G. Monozygotic triplets with Crohn's disease of the colon. Gastroenterology. 1986 Dec;91(6):1553–1559. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuller J. L., Piket-van Ulsen J., Veeken I. V., Michel M. F., Stolz E. Antibodies against Chlamydia of lymphogranuloma-venereum type in Crohn's disease. Lancet. 1979 Jan 6;1(8106):19–20. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seldenrijk C. A., Drexhage H. A., Meuwissen S. G., Meijer C. J. T-cellular immune reactions (in macrophage inhibition factor assay) against Mycobacterium paratuberculosis, Mycobacterium kansasii, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium in patients with chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1990 May;31(5):529–535. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.5.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swarbrick E. T., Kingham J. G., Price H. L., Blackshaw A. J., Griffiths P. D., Darougar S., Buckell N. A. Chlamydia, cytomegalovirus, and Yersinia in inflammatory bowel disease. Lancet. 1979 Jul 7;2(8132):11–12. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabaqchali S., O'Donoghue D. P., Bettelheim K. A. Escherichia coli antibodies in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1978 Feb;19(2):108–113. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.2.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer W. R., Jr, Coutu J. A., Chiodini R. J., Van Kruiningen H. J., Merkal R. S. Possible role of mycobacteria in inflammatory bowel disease. II. Mycobacterial antibodies in Crohn's disease. Dig Dis Sci. 1984 Dec;29(12):1080–1085. doi: 10.1007/BF01317079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tysk C., Lindberg E., Järnerot G., Flodérus-Myrhed B. Ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease in an unselected population of monozygotic and dizygotic twins. A study of heritability and the influence of smoking. Gut. 1988 Jul;29(7):990–996. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.7.990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vantrappen G., Ponette E., Geboes K., Bertrand P. Yersinia enteritis and enterocolitis: gastroenterological aspects. Gastroenterology. 1977 Feb;72(2):220–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winblad S., Niléhn B., Sternby N. H. Yersinia enterocolitica (Pasteurella x) in human enteric infections. Br Med J. 1966 Dec 3;2(5526):1363–1366. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5526.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


