Abstract
Objective:
To assess the effects of sex, joint angle, and the gastrocnemius muscle on passive ankle joint complex stiffness (JCS).
Design and Setting:
A repeated-measures design was employed using sex as a between-subjects factor and joint angle and inclusion of the gastrocnemius muscle as within-subject factors. All testing was conducted in a neuromuscular research laboratory.
Subjects:
Twelve female and 12 male healthy, physically active subjects between the ages of 18 and 30 years volunteered for participation in this study. The dominant leg was used for testing. No subjects had a history of lower extremity musculoskeletal injury or circulatory or neurologic disorders.
Measurements:
We determined passive ankle JCS by measuring resistance to passive dorsiflexion (5°·s−1) from 23° plantar flexion (PF) to 13° dorsiflexion (DF). Angular position and torque data were collected from a dynamometer under 2 conditions designed to include or reduce the contribution of the gastrocnemius muscle. Separate fourth-order polynomial equations relating angular position and torque were constructed for each trial. Stiffness values (Nm·degree−1) were calculated at 10° PF, neutral (NE), and 10° DF using the slope of the line at each respective position.
Results:
Significant condition-by-position and sex-by-position interactions and significant main effects for sex, position, and condition were revealed by a 3-way (sex-by-position, condition-by-position) analysis of variance. Post hoc analyses of the condition-by-position interaction revealed significantly higher stiffness values under the knee-straight condition compared with the knee-bent condition at both ankle NE and 10° DF. Within each condition, stiffness values at each position were significantly higher as the ankle moved into DF. Post hoc analysis of the sex-by-position interaction revealed significantly higher stiffness values at 10° DF in the male subjects. Post hoc analysis of the position main effect revealed that as the ankle moved into dorsiflexion, the stiffness at each position became significantly higher than at the previous position.
Conclusions:
The gastrocnemius contributes significantly to passive ankle JCS, thereby providing a scientific basis for clinicians incorporating stretching regimens into rehabilitation programs. Further research is warranted considering the cause and application of the sex-by-position interaction.
Keywords: muscle, pathology, rehabilitation, range of motion, flexibility
Functional joint stability (FJS), the quality of possessing adequate joint stability to enable normal performance of a joint during functional activity, arises from complementary relationships existing between static and dynamic components.1 Collectively, both components serve to maintain FJS throughout the physiologic range of motion by resisting potentially destabilizing forces.1 An enhanced ability to diffuse destabilizing forces results in augmented FJS.2–4 Stiffness is the mechanical property that determines how effectively external forces delivered to the skeletal system are absorbed or transmitted (or both) by the articular soft tissues.5,6 In contrast to muscle stiffness, which describes the stiffness properties specifically exhibited by the tenomuscular tissues, joint stiffness encompasses contributions from all structures located within and over the joint (muscles, tendons, skin, subcutaneous tissue, fascia, ligaments, joint capsule, and cartilage).1,7,8 Because dynamic restraints are included in addition to static restraints, joint stiffness becomes a function of not only the passive factors (ie, viscoelasticity) associated with each structure but also the level of neural influence over each articular muscle.2,5,6,8–11 Neural influences can be considered to exist intrinsically, represented by the level of muscle activation (number of actin-myosin crossbridges) existing at an instant,2,5,10,12–15 and extrinsically, represented by the arrival of a reflexive activation in response to a sensory stimuli.2,10,16 Superimposed on these neural influences are the factors of single muscle fibers (ie, sarcomere length-tension and force-velocity relationships) as well as whole muscles (ie, arrangement of muscle fibers within a muscle and precise location of insertional sites).9
From an engineering perspective, stiffness may be defined in terms of elasticity, viscosity, friction, inertia, and plasticity.7,8 In normal finger and knee joints measured with passive arthrography, elastic stiffness has been credited as the largest stiffness component (more than half).8 Comprising ligaments, tendons, and muscle are varying concentrations of collagen, proteoglycans, water, and elastin.17–20 These structural components determine each tissue's characteristic viscoelastic behavior during passive lengthening15,21 and the elastic and viscous stiffness properties.
A joint stability perspective suggests that increased joint stiffness is a desirable characteristic. Stiffer joints, arising from increased muscle stiffness, are theorized to have a heightened ability to absorb energy contained in destabilizing forces.2–4,22,23 Although destabilizing forces may not be countered entirely, many could potentially be lessened in magnitude, thereby reducing the incidence of joint subluxation or dislocation. In contrast, stiffer joints are also theorized to increase the risk for injuries5,23 or exacerbate the signs and symptoms associated with antagonistic muscle syndromes.24,25 For example, increased extensor muscular stiffness requires higher contractile forces to be developed by the flexor muscles for a given movement. Secondary to the requirement for higher force production are increased stresses to the bone-tendon interfaces and abnormal muscle hypertrophy. Over time, these alterations may potentially increase the predisposition for development of insertional tendinitis and compartment syndromes, respectively.
Quantifying the influence of the gastrocnemius on passive ankle joint complex stiffness (JCS) would provide practitioners with a scientific rationale for selecting clinically advocated rehabilitation and intervention strategies. Such strategies include common clinical techniques such as stretching and strengthening the lower leg musculature. In the one study conducted on the influence of the gastrocnemius muscle on passive ankle JCS,25 researchers focused solely on sedentary women older than 21 years. Additionally, while sex differences in stiffness have been shown at the knee and elbow joints,7,26–28 no investigators have considered the existence of sex differences relative to passive ankle JCS. Therefore, our purpose was to determine the effects of sex, ankle and knee joint angles, and the gastrocnemius muscle on passive ankle JCS.
METHODS
Subjects
Twenty-four physically active subjects participated in this investigation (Table 1). The dominant leg, defined as the preferred leg for kicking a ball, was used for all data collection. Physically active was operationally defined as participation in physical activity for a minimum of 20 minutes, 3 times per week. None of the subjects had sustained a lower extremity musculoskeletal injury in their dominant leg or had a history of circulatory or neurologic disorders that could have potentially affected their JCS. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects in accordance with the university's institutional review board, which also approved the study.
Table 1.
Subject Demographics (Mean ± SD)*

Procedures
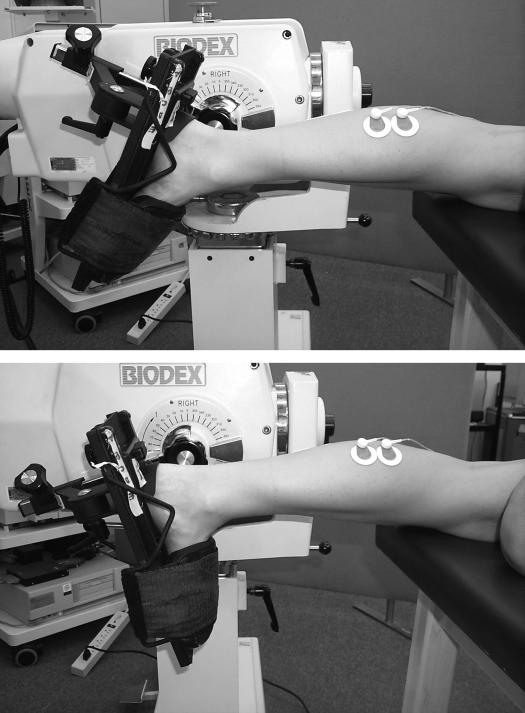
We determined passive ankle JCS by measuring the resistance to passive movement7,8,21,24,25,28–30 from 23° plantar flexion (PF) into 13° dorsiflexion (DF) (Figure 1). Passive movements at an angular velocity of 5°·s−1 were delivered14,21 using the Biodex System 2 Isokinetic Dynameter (Biodex Inc, Shirley, NY) in a passive mode. The extra 3° ensured that constant velocity was achieved and maintained throughout the target range of 20° PF to 10° DF, thereby eliminating confounding changes in inertia. We used 2 straps (forefoot and midfoot) to fix the foot to the footplate once the axis of rotation was aligned with the lateral malleolus. During all testing, the ambient air temperature was maintained between 20.6°C and 21.7°C.
Figure 1.
During each trial, the ankle was moved from a starting position of 23° plantar flexion (top) to an ending position of 13° dorsiflexion (bottom).
Trials were completed under 2 conditions designed to include or reduce the contribution of the gastrocnemius muscle. The first condition involved the subject in a prone position with the knee at 0° flexion, while the second condition involved the subject's maintaining a kneeling position with the knee held at 90° flexion. The order of the conditions was counterbalanced among subjects. During testing, we instructed subjects to relax all muscles in the lower leg and to not interfere with the passive movements. Before data collection, we gave each subject several familiarization trials under each condition. In addition to allowing the subjects to become familiar with the testing procedures, the familiarization trials decreased thixotropy31 and the stress relaxation phenomena described by Taylor et al.32
Analogue data concerning angular position and torque from the potentiometer and load cell contained within the dynamometer head were collected at 100 Hz via an analogue-to-digital converter (Keithley Metrabyte DAS1402, Keithley Instruments Inc, Tauton, MA) and stored on a personal computer for later analysis. Additionally, to ensure that reflexive or voluntary muscle activity was not being elicited during the passive movements, we monitored the activity of the soleus, medial and lateral heads of the gastrocnemius, and medial and lateral hamstring muscles using the Noraxon Telemyo Electromyography System (Noraxon USA Inc, Scottsdale, AZ). Signals from the muscles were collected using self-adhesive silver-silver chloride bipolar surface electrodes (Multi Bio Sensors Inc, El Paso, TX) and passed through a single-ended amplifier (gain 500) to an 8-channel FM transmitter worn by the subject. A receiver then filtered and further amplified the signals (gain 500, Butterworth 15-Hz low-pass and 500-Hz high-pass filters, common mode-rejection ratio of 130 db) before conveying the data to the analogue-to-digital card.
Data Reduction
Although 6 trials of data were recorded under each experimental condition, only the first 3 trials that matched the selection criteria were used in the subsequent analyses. The selection criteria included no muscle activity or alterations in the torque curves through visual inspection of the raw data. We developed customized software to complete all data reduction procedures. First, torque and angular position data were smoothed using a median 5 filter. Gravity corrections for each torque data point were then completed using the corresponding angular position. Factored into the gravity corrections were the mass of the footplate, mass of the foot,33 and lever arm length. Separate fourth-order polynomial equations relating angular position and torque were then constructed for each trial (Y = ax4 + bx3 + cx2 + dx + e, where Y is the gravity corrected torque, x is the angular position, and a through e are constants). Stiffness values were calculated at 10° PF, neutral (NE), and 10° DF by using the first derivative (slope) of the equation (dy/dx = 4ax3 + 3bx2 + 2c2 + d, where dy/dx is the stiffness) at each of the respective positions. This method of stiffness measurement, using the slope of the line relating torque and angular position during passive movement, has been previously described30 and used.24,25,29 The stiffness represented by taking the slope of the line has been attributed to elastic stiffness at that point in the range of motion.25,34
Reliability
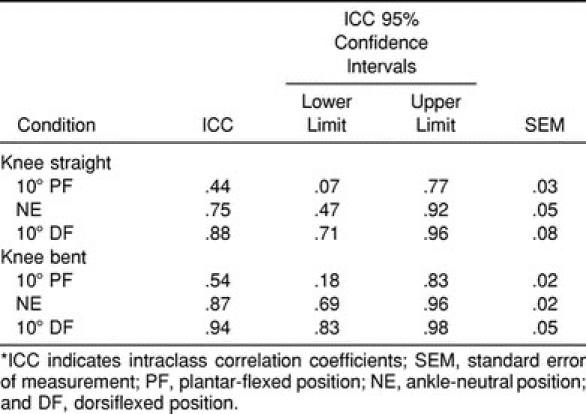
We conducted a pilot study in conjunction with the current study to establish the reliability for our exact methods. Twelve subjects (8 men, 4 women, mean height = 176.6 cm, mean weight = 80.2 kg) participated in 3 repeated testing sessions. Twelve subjects were chosen based on an a priori power analysis.35 All subjects conformed to the previously discussed inclusion and exclusion criteria. Intraclass correlation coefficients36 (ICC) (2, K) ranged from .44 to .93 (Table 2). In addition, we established the confidence intervals and standard error of measurement associated with each ICC. Standard error of measurement ranged from .02 to .08, supporting the absolute reliability of the methods. These results are comparable with those previously reported using similar methods at the ankle.37
Table 2.
Reliability Analyses*
Data Analysis
The stiffness values across the 3 trials under each condition were averaged and analyzed using a 3-factor, repeated-measures analysis of variance with sex as a between-subjects factor and condition and position as within-subjects factors. Statistical significance of P < .05 was set a priori for all analyses.
In an attempt to probe the cause of the significant sex effects, we conducted several post facto analyses. First, we performed Pearson bivariate correlational analyses between the stiffness values (each position and condition) and subject height, weight, and ponderal index (calculated by dividing height by the cube root of weight38) across all subjects. Additionally, independent t tests were conducted on the height, weight, and ponderal index variables between the sexes. To reduce the Type I error rate, statistical significance for the t tests was adjusted to α < .01. Last, we repeated the 3-factor analysis of variance using any of the demographic variables (height, weight, ponderal index) determined to be significantly related to stiffness and significantly different between the sexes as a covariate.
RESULTS
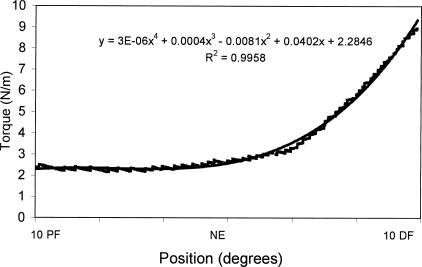
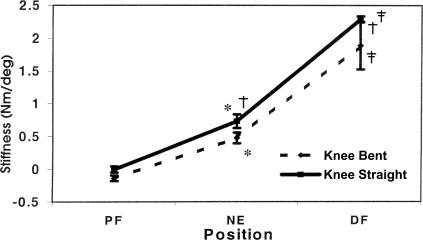
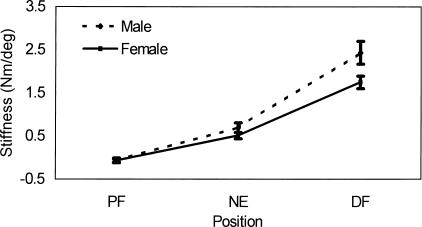
The data of 1 subject had to be disregarded for technical reasons. An example of the torque versus position data from 1 acceptable trial, as well as the constructed equation, is presented in Figure 2. Means and standard deviations are provided in Table 3. The results of the statistical analysis on the remaining subjects revealed significant condition-by-position (F2,42 = 6.39, P = .004) and sex-by-position (F2,42 = 7.40, P = .002) interactions, as well as significant main effects for sex (F1,21 = 6.22, P = .021), position (F2,42 = 288.00, P < .000), and condition (F1,21=73.90, P < .000). Tukey post hoc analyses of the condition-by-position interaction revealed significantly higher stiffness values under the knee-straight condition compared with the knee-bent condition at both ankle NE and 10° DF (Figure 3). Within each condition, stiffness values across positions were significantly higher as the ankle moved into DF (10° PF < NE < 10° DF). Tukey post hoc analysis of the sex-by-position interaction revealed significantly higher stiffness values at 10° DF in men (Figure 4). Lastly, Tukey post hoc analysis of the position main effect revealed that, as the ankle moved into dorsiflexion, the stiffness at each position became significantly higher than at the previous position (10° PF < NE < 10° DF).
Figure 2.
Separate fourth-order polynomial equations were constructed relating the angular position and torque data for each trial. Pictured are the original data (rough line) and line of the equation (solid).
Table 3.
Stiffness Values (degrees) by Sex (Mean ± SD)*
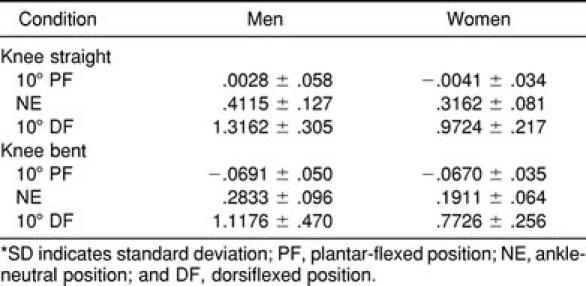
Figure 3.
Position stiffness mean (±SD) for each condition illustrating the condition-by position interaction.
Figure 4.
Position stiffness mean (±SD) for each sex illustrating the sex-by-position interaction.
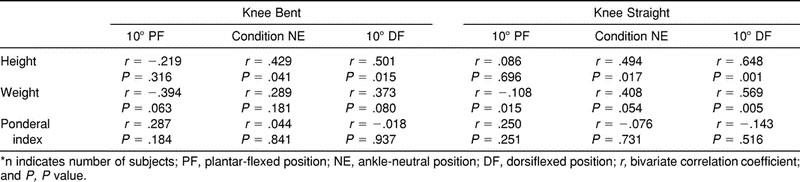
Results of the post facto correlational analyses revealed significant relationships (P < .05) between height and the stiffness values at the NE and DF positions under both conditions (Table 4). The independent t tests revealed only height to be statistically different between the sexes (t21 = 4.01, P = .00). The results of the analysis of covariance using height as the covariate were identical to the analysis of variance except that the main effect for sex was nonsignificant.
Table 4.
Correlational Analyses Among Demographic Variables and Stiffness Values (n = 23)*
DISCUSSION
The purpose of our investigation was to determine the effects of sex, joint angle, and the gastrocnemius muscle on passive ankle JCS. The most significant aspect of our study was the quantification of the gastrocnemius' influence on passive ankle JCS. Collapsed across sex, our results suggest that the gastrocnemius significantly increased passive ankle JCS moving into DF as early as ankle NE. Clinically, this implies that the contribution of the gastrocnemius represents an important consideration during rehabilitation programs involving the lower extremity. Additionally, collapsed across condition, our results demonstrate significant sex differences in stiffness at 10° DF. The clinical significance and cause of this result warrant further investigation.
The speed with which we induced the passive displacements, 5°·s−1, was chosen to avoid eliciting stretch reflexes.14 Further, resistance to passive ankle displacement at this speed has been demonstrated as unchanged under ischemic conditions that block the Ia afferent fibers from the muscle spindles.14 By asking subjects to not intervene with the passive movements,5,6,10,21,23,27,29 we took advantage of the ability to abolish muscle activity through conscious relaxation,39 thereby eliminating conscious muscle activation as a confounding factor. The relatively few trials in which increased electric activity occurred in our study, coupled with the ability to easily identify and eliminate these instances, support this presumption. Thus, it is reasonable to attribute the resistance measured in response to passive ankle joint displacement into DF to the intrinsic mechanical properties of the joint complex. The potential contributory sources, in addition to the gastrocnemius, include any of the structures spanning the joint: skin, ligaments, joint capsule, and anterior and posterior surrounding compartment muscles. After sequential resections of the tissues crossing the wrist joint, Johns and Wright40 reported that resistance to passive movement arose primarily from the joint capsule (47%) and the muscles (41%). The remainder of the resistance was provided by tendons (10%) and skin (2%). With respect to the elbow joint, Chleboun et al28 noted that muscle volume accounted for 84% of the variance in elbow stiffness. Considered collectively, these studies suggest that the degree of contribution from each articular structure may be unique to a particular joint.7 We were unable to find similar studies comparing contributions of the various articular structures at the ankle joint, leaving some of the etiologic interpretation of our results to limited degrees of speculation.
Our experimental design took advantage of the biarticular span of the gastrocnemius muscle. Because the proximal attachment of the gastrocnemius resides above the posterior femoral condyles, flexing the knee to 90° shortens the distance between the distal and proximal attachment sites, thereby decreasing the potential passive resistance. A similar method has been used to determine the contribution of the gastrocnemius to maximal voluntary ankle torque production.41 Thus, comparing the stiffness values attained during the knee-bent condition with those attained during the knee-straight condition provided a means by which we could determine the relative influence of the gastrocnemius. Although changes in the tension offered by skin and associated connective tissues could have accompanied the change in knee position, we feel that it is reasonable to disregard such effects as minimal in light of the paper by Johns and Wright.40
Both testing conditions included the resistance offered by the uniarticular muscles crossing the axis of the ankle joint, posterior ankle joint capsule, and ligaments. Measurement of ankle ligament force values in various degrees of DF and PF using isolated cadaveric specimens has been conducted.42 The anterior talofibular ligament comes under tension as the ankle moves into PF, while the calcaneofibular ligament comes under maximal tension in 15° of PF and DF. The deltoid ligament displays a pattern similar to that of the anterior talofibular ligament, coming under increased tension as the ankle moves into plantar flexion. The relevance of these results in resisting passive motion in vivo, with other articular structures intact, remains unknown. With respect to individual uniarticular muscle contributions, Gareis et al,43 in establishing the active length-tension curves and passive force characteristics of 9 lower extremity muscles, demonstrated that the passive tension provided throughout the full range of elongation by the soleus muscle was more pronounced than that of the peroneus longus, tibialis posterior, and flexor digitorum longus muscles.
Our results of a significant condition-by-position interaction and a significant main effect for condition demonstrate that the gastrocnemius has substantial influence on passive ankle JCS. These results are in contrast with those reported by Chesworth and Vandervoort.25,37 We find this discrepancy quite surprising and difficult to explain considering the identical methods in the 2 studies. The largest difference between the 2 studies involved the subjects. While we studied physically active men and women between 18 and 30 years old, Chesworth and Vandervoort25,37 studied only women between 21 and 80 years old.
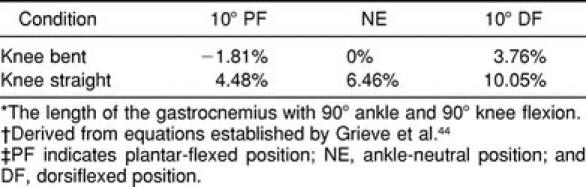
Several studies considering the effects of ankle and knee joint angle on the gastrocnemius support our significant condition results. Grieve et al44 established a technique to estimate the length of the gastrocnemius muscle from knee and ankle angular measurements. Using the equations provided by their report, the knee-straight condition would have increased the length of the gastrocnemius in our subjects by approximately 6.5% in comparison with the reference length (the length of the gastrocnemius with 90° ankle and 90° knee flexion) at each of the respective ankle angular positions (Table 5). Sale et al41 confirmed through a radiologic series that femoral condyle rotation accompanying knee extension causes considerable lengthening of the gastrocnemius independent of foot position. Although length and stiffness are not synonymous terms, temporarily increasing the length of the muscle-tendon unit with changes in joint position shifts the passive resistance-position curve to the left, resulting in increased stiffness at each ankle angle.
Table 5.
Gastrocnemius Muscle Length Relative to Reference Position Length* Associated with the Knee And Ankle Angular Positions†‡
The post hoc analysis of the condition-by-position interaction revealed significant differences between conditions, beginning at the ankle neutral position. Further research should focus on further isolating the angular position where the significant difference begins. Given the differences in the passive length-force curves between the lateral and medial gastrocnemius43 and differences in recruitment patterns,15 we recommend further research to consider the influence of each head independently.
In light of several other studies reporting sex differences in stiffness,7,26–28 our results of a significant sex-by-position interaction and significant main effect for sex are not surprising. The lack of significant sex-by-condition and sex-by-condition-by-position interactions, however, suggests that there was no difference in the stiffness of the gastrocnemius muscle between the sexes. The origin of the significant differences revealed could be related to dissimilarities in structural or physical characteristics. Potential structural characteristics include such factors as tissue elastic and collagen content variations. Komi and Karlsson45,46 suggested the lower rates of force development and elastic energy storage exhibited by women could be related to differences in elastic tissue content within the muscle. Resistance to passive motion in the absence of muscle activation has been attributed to the parallel elastic components of muscle.45,47,48 Different concentrations of elastic tissue between the sexes, as Komi and Karlsson45,46 suggested, could therefore potentially explain the revealed sex differences in stiffness.
Pertinent physical characteristics include such factors as tissue cross-sectional areas, flexibility, and mechanical advantage differences. Several studies have demonstrated differences in muscle mass between the sexes.28,49,50 Additionally, relationships have been shown to exist between cross-sectional areas and stiffness.26,28,29 Thus, it could be that differences in muscle mass existed within our subjects between sexes, thereby accounting for the significant sex differences. However, within the limits of the relationships existing among muscle mass, body weight and ponderal index, this does not appear to be a factor in our study. The number of nonsignificant relationships revealed among stiffness, body weight, and ponderal index provides support for this statement. Interestingly, Chleboun et al28 failed to reveal a significant relationship between muscle size and elbow stiffness at the end-range position, the location in the range where we revealed significant sex differences.
Much to our surprise were the significant, moderate-magnitude relationships revealed between the stiffness values and height. The results of the analysis of covariance, using height as the covariant, demonstrated that height could account for some of the previously revealed sex differences. This provides support for the ideas of structural or mechanical advantage (or both) differences existing between the sexes. Further research is needed to quantify the mechanism by which height influences stiffness.
We are not unique in finding significant position differences in stiffness at the ankle.11,13,14,16,25,34 Toft et al34 suggested that as the joint reaches end range, more parallel tissue elements become loaded, giving rise to the exponential increases in resistive forces required to passively move the ankle into further DF. The curves presented by Gareis et al43 illustrate the exponential increases in passive tension resulting from muscle lengthening. The technique provided by Grieve et al44 provides us with a method of quantifying the approximate length changes the gastrocnemius undergoes as the ankle moves into DF under each condition (Table 4).
It is also interesting to note the negative mean stiffness values at the 10° PF position under the knee-bent condition (both sexes) and under the knee-straight condition (women). We are not the first authors to report negative stiffness values.51–53 Such expression, however, does not comply with the traditional concept of the physical characteristic stiffness. As Latash and Zatsiorsky51 described, stiffness assessments reflect both features of the system and the method of testing. Because negative stiffness of biological tissues and structures is a clear impossibility, the negative stiffness values can be attributed to our particular assessment approach. Our method involved measuring the stiffness of the entire ankle joint complex under a passive state with respect to movement into dorsiflexion. During our measurements, throughout the entire range of motion, all components acting on the ankle joint, both anterior and posterior to the ankle joint axis, imposed their respective influences on our measurements. The negative stiffness value indicates that the net resistance measured while moving into DF from the 10° PF position was acting in the opposite direction (pulling the ankle into DF). In other words, in the plantar-flexed position, the posterior musculoskeletal structures did not impose sufficient passive torque to overcome the passive torque being imposed by the anterior musculoskeletal structures, so negative values resulted. These negative values indicate the opposite of stiffness, or compliance, in the direction associated with the measurement (dorsiflexion). The anterior muscles (tibialis anterior, extensor digitorium longus, extensor hallicus longus) were most likely the major contributors to this phenomenon, with contributions also arising from the anterior joint capsule and anterior talofibular and deltoid ligaments.42 Thus, the negative stiffness is simply a result of conducting the passive torque measurements on both sides of the equilibrium point of the ankle joint.7 A similar phenomenon can be observed at the knee joint, as presented by Allison et al.24
Clinically, our results suggest that the stiffness of the gastrocnemius represents an important consideration in the management of lower leg conditions. Examples include antagonistic muscle syndromes such as anterior compartment syndrome and insertional tendinitis. Activities of daily living, including normal gait,54,55 involve the ankle's moving repetitively into flexion positions greater than neutral by action of the anterior ankle muscles. If either of the previously mentioned antagonistic muscle syndromes is present, our results suggest that the work performed by the anterior muscles could be lessened through a reduction in the stiffness of the gastrocnemius. In other words, this investigation provides scientific rationale for addressing the gastrocnemius during clinical management strategies involving the lower limb. Further research should address the acute and chronic effectiveness of various intervention strategies on altering the passive stiffness of the ankle.
Most often, only flexibility (length) is taken into account during clinical assessments. Although stiffness and flexibility are interrelated,6 they are largely separate physical characteristics. Flexibility is best defined as the angle beyond which no further displacement is possible,34 providing limited information regarding the behavior of muscle-tendon units in response to stretch,21,56 especially at muscle lengths used during daily activities.34 In contrast, stiffness represents the amount of deformation proportional to the load applied.21 Thus, from a clinical perspective, measuring passive stiffness to imposed dorsiflexion may provide additional insight into the cause of such pathologic conditions.
CONCLUSIONS
The results of this investigation are applicable to all clinicians treating lower extremity conditions and provide a scientific basis for clinicians incorporating gastrocnemius-stretching regimens into rehabilitation programs. The cause and application of the significant sex-by-position interaction requires further study. Further research is also warranted regarding the influence of the gastrocnemius during various levels of muscle activation and knee positions. The effectiveness of short-term and long-term intervention strategies in altering passive ankle JCS remains largely unknown.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Elaine N. Rubinstein, PhD, for her assistance with the statistical analysis.
REFERENCES
- 1.Riemann BL, Lephart SM. Anatomical and physiologic basis for the sensorimotor system. J Athl Train. In press [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Johansson H, Sjolander P. The neurophysiology of joints. In: Wright V, Radin EL, editors. Mechanics of Joints: Physiology, Pathophysiology and Treatment. New York, NY: Marcel Dekker; 1993. pp. 243–290. [Google Scholar]
- 3.McNair PJ, Wood GA, Marshall RN. Stiffness of the hamstring muscles and its relationship to function in anterior cruciate ligament deficient individuals. Clin Biomech. 1991;7:131–137. doi: 10.1016/0268-0033(92)90027-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Louie JK, Mote CD., Jr Contribution of the musculature to rotatory laxity and torsional stiffness at the knee. J Biomech. 1987;20:281–300. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(87)90295-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Blanpied P, Smidt GL. Human plantarflexor stiffness to multiple single-stretch trials. J Biomech. 1992;25:29–39. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(92)90243-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wilson GJ, Wood GA, Elliott BC. The relationship between stiffness of the musculature and static flexibility: an alternative explanation for the occurance of muscular injury. Int J Sports Med. 1991;12:403–407. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1024702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Helliwell PS. Joint stiffness. In: Wright V, Radin EL, editors. Mechanics of Joints: Physiology, Pathophysiology and Treatment. New York, NY: Marcel Dekker; 1993. pp. 203–218. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wright V. Stiffness: a review of its measurement and physiological importance. Physiotherapy. 1973;59:107–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lieber RL, Friden J. Neuromuscular stabilization of the shoulder girdle. In: Matsen FA, Fu FH, Hawkins R, editors. The Shoulder: A Balance of Mobility and Stability. Rosemont, IL: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons; 1993. pp. 91–105. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sinkjaer T, Toft E, Andreassen S, Hornemann BC. Muscle stiffness in human ankle dorsiflexors: instrinsic and reflex components. J Neurophysiol. 1988;60:1110–1121. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.60.3.1110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Weiss PL, Hunter IW, Kearney RE. Human ankle joint stiffness over the full range of muscle activation levels. J Biomech. 1988;21:539–544. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(88)90217-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Morgan DL. Separation of active and passive components of short-range stiffness of muscle. Am J Physiol. 1977;232:C45–C49. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1977.232.1.C45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Weiss PL, Kearney RE, Hunter IW. Position dependence of ankle joint dynamics, I: passive mechanics. J Biomech. 1986;19:727–735. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(86)90196-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hufschmidt A, Mauritz KH. Chronic transformation of muscle in spasticity: a peripheral contribution to increased tone. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1985;48:676–685. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.48.7.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gregor RJ. Skeletal muscle mechanics and movement. In: Grabiner M, editor. Current Issues in Biomechanics. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics; 1993. pp. 171–211. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gottlieb GL, Agarwal GC. Dependence of human ankle compliance on joint ankle. J Biomech. 1978;11:177–181. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(78)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gelberman R, Goldberg V, Kai-Nan A, Banes A. Tendon. In: Woo SL, Buckwalter J, editors. Injury and Repair of the Musculoskeletal Soft Tissues. Park Ridge, IL: American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons; 1988. pp. 5–40. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Caplan A, Carlson B, Faulkner J, Fischman D, Garrett W. Skeletal muscle. In: Woo SL, Buckwalter J, editors. Injury and Repair of the Musculoskeletal Soft Tissues. Park Ridge, IL: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons; 1988. pp. 213–291. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Frank C, Woo S, Andriacchi T, et al. Normal ligament: structure, function and composition. In: Woo SL, Buckwalter J, editors. Injury and Repair of the Musculoskeletal Soft Tissues. Park Ridge, IL: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons; 1988. pp. 45–101. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hawkins D. Ligament biomechanics. In: Grabiner M, editor. Current Issues in Biomechanics. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics; 1993. pp. 123–150. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Magnusson SP, Simonsen EB, Aagaard P, Kjaer M. Biomechanical responses to repeated stretches in human hamstring muscle in vivo. Am J Sports Med. 1996;24:622–628. doi: 10.1177/036354659602400510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Grillner S. The role of muscle stiffness in meeting the changing postural and locomotor requirements for force development by the ankle extensors. Acta Physiol Scand. 1972;86:92–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1972.tb00227.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Blanpied P, Smidt GL. The difference in stiffness of the active plantarflexors between young and elderly human females. J Gerontol. 1993;48:M58–M63. doi: 10.1093/geronj/48.2.m58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Allison GT, Weston R, Shaw R, et al. The reliability of quadriceps muscle stiffness in individuals with Osgood-Schlatter disease. J Sport Rehabil. 1998;7:258–266. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chesworth BM, Vandervoort AA. Age and passive ankle stiffness in healthy women. Phys Ther. 1989;69:217–224. doi: 10.1093/ptj/69.3.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Howe A, Thompson D, Wright V. Reference values for metacarpophalangeal joint stiffness in normals. Ann Rheum Dis. 1985;44:469–476. doi: 10.1136/ard.44.7.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Oatis CA. The use of a mechanical model to describe the stiffness and damping characteristics of the knee joint in healthy adults. Phys Ther. 1993;73:740–749. doi: 10.1093/ptj/73.11.740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Chleboun GS, Howell JN, Conatser RR, Giesey JJ. The relationship between elbow flexor volume and angular stiffness at the elbow. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 1997;12:383–392. doi: 10.1016/s0268-0033(97)00027-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wiegner AW, Watts RL. Elastic properties of muscles measured at the elbow in man, I: normal controls. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986;49:1171–1176. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.49.10.1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Enoka RM. Neuromechanical Basis of Kinesiology. 2nd ed. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics; 1994. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lakie M, Robson LG. Thixotropic changes in human muscle fatigue stiffness and the effects of fatigue. Quart J Exper Physiol. 1988;73:487–500. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1988.sp003169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Taylor DC, Dalton JD, Searber AV, Garrett WE., Jr Viscoeleastic properties of muscle-tendon units: the biomechanical effects of stretching. Am J Sports Med. 1990;18:300–309. doi: 10.1177/036354659001800314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Winter DA. Biomechanics and Motor Control of Human Movement. 2nd ed. New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons Inc; 1990. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Toft E, Espersen GT, Kalund S, Sinkjaer T, Hornemann BC. Passive tension of the ankle before and after stretching. Am J Sports Med. 1989;17:489–494. doi: 10.1177/036354658901700407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Donner A, Eliasziw M. Sample size requirements for reliability studies. Stat Med. 1987;6:441–448. doi: 10.1002/sim.4780060404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Shrout PE, Fleiss JL. Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull. 1979;86:420–428. doi: 10.1037//0033-2909.86.2.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Chesworth BM, Vandervoort AA. Reliability of a torque motor system for measurement of passive ankle joint stiffness in control subjects. Physiother Can. 1988;40:300–303. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ryan AJ, Allman FL. Sports Medicine. New York, NY: Academic Press; 1974. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Basmajian JV, DeLuca CJ. Muscles Alive: Their Functions Revealed by Electromyography. 5th ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams & Wilkins; 1985. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Johns RJ, Wright V. Relative importance of various tissues in joint stiffness. J Appl Physiol. 1962;17:824–828. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Sale D, Quinlan J, Marsh E, McComas AJ, Belanger AY. Influence of joint position on ankle plantar flexion in humans. J Appl Physiol. 1982;52:1636–1642. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.52.6.1636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Nigg BM, Skarvan G, Frank CB, Yeadon MR. Elongation and forces of ankle ligaments in physiological range of motion. Foot Ankle. 1990;11:30–40. doi: 10.1177/107110079001100107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Gareis H, Solomonow M, Baratta R, Best R, D'Ambrosia R. The isometric length-force models of nine different skeletal muscles. J Biomech. 1992;25:903–916. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(92)90230-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Grieve DW, Pheasant S, Cavanagh PR. Prediction of gastrocnemius length from knee and ankle posture. In: Asmussen E, Jorensen K, editors. Biomechanics VI-A. Baltimore, MD: University Park Press; 1978. pp. 405–412. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Komi PV. Physiological and biomechanical correlates of muscle function: effects of muscle structure and stretch-shortening cycle on force and speed. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 1984;12:81–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Komi PV, Karlsson J. Skeletal muscle fibre types, enzyme activities and physical performance in young males and females. Acta Physiol Scand. 1978;103:210–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1978.tb06208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Shorten MR. Muscle elasticity and human performance. Med Sport Sci. 1987;25:1–18. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Winters JM. Hill-based muscle models: a systems engineering perspective. In: Winters J, Woo SLY, editors. Biomechanics and Movement Organization. New York, NY: Springer-Verlag; 1990. pp. 68–93. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Evetovich TK, Housh TJ, Johnson GO, Smith DB, Ebersole KT, Perry SR. Gender comparisons of the mechanomyographic responses to maximal concentric and eccentric isokinetic muscle actions. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1998;30:1697–1702. doi: 10.1097/00005768-199812000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Lynch NA, Metter EJ, Lindle RS, et al. Muscle quality, I: age associated differences between arm and leg muscle groups. J Appl Physiol. 1999;86:188–194. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1999.86.1.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Latash ML, Zatsiorsky VM. Joint stiffness: myth or reality? Hum Mov Sci. 1993;12:653–692. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Akazawa K, Okuno R. Negative and positive stiffness of elbow flexors with constant muscle activation in isovelocity movements. Paper presented at: 13th Congress of International Society of Electrophysiology and Kinesiology; June 25–28, 2000; Sapporo, Japan. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Dyhre-Poulsen P, Simonsen EB, Voigt M. Dynamic control of muscle stiffness and H reflex modulation during hopping and jumping in man. J Physiol. 1991;437:287–304. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Murray MP. Gait as a total pattern of movement. Am J Phys Med. 1967;46:290–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Apkarian J, Naumann S, Cairns B. A three-dimensional kinematic and dynamic model of the lower limb. J Biomech. 1989;22:143–155. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(89)90037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.McNair PJ, Stanley SN. Effect of passive stretching and jogging on the series elastic muscle stiffness and range of motion of the ankle joint. Br J Sports Med. 1996;30:313–318. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.30.4.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]