Abstract
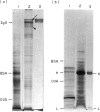
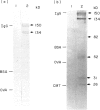
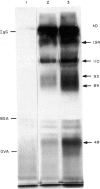
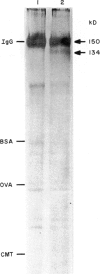
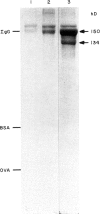
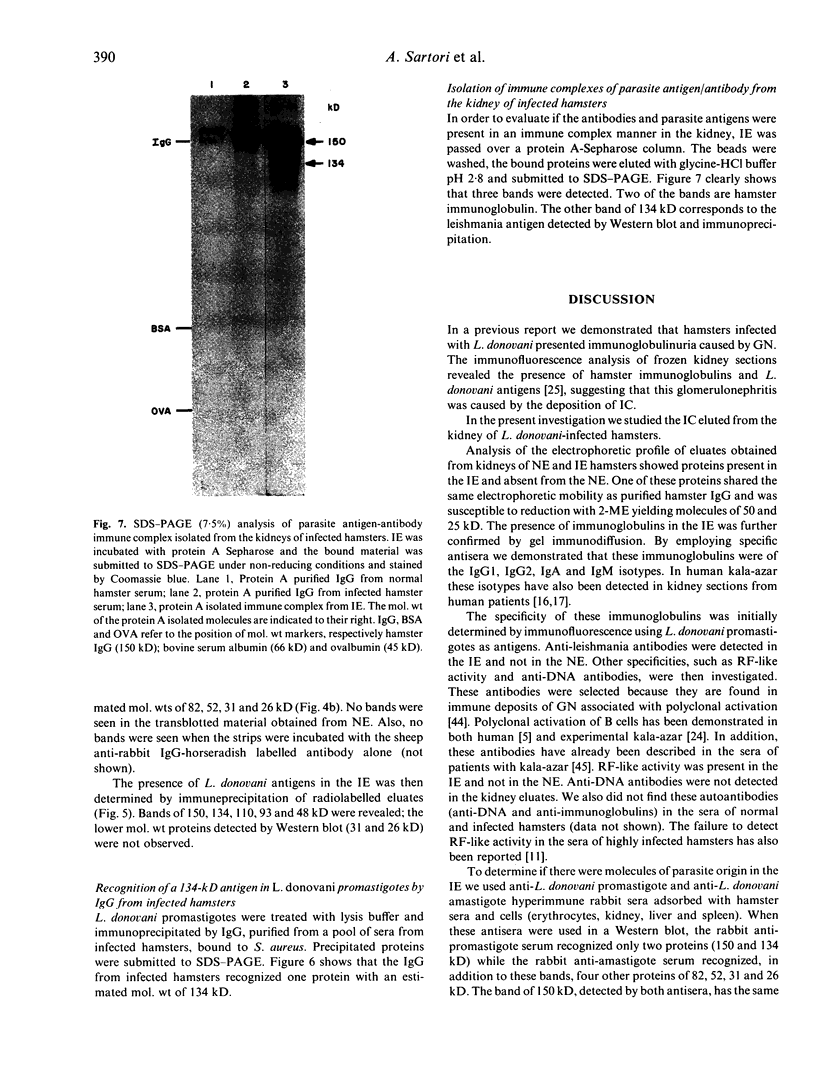
In a previous report analysing kidney sections by immunofluorescence we showed that hamsters infected with L. donovani develop a glomerulonephritis (GN) associated with deposition of hamster immunoglobulins and parasite antigens in the glomeruli. In this study we characterize these immune components eluted from the kidneys. The eluted immunoglobulins showed specificity for L. donovani antigens and hamster immunoglobulins (rheumatoid factor-like activity). The four isotypes IgG1, IgG2, IgA and IgM were detected. Several L. donovani antigens were detected in the renal eluates by Western blot and immunoprecipitation using 125I-labelled eluates. Proteins with mol. wt of 134, 82, 52, 31, and 26 kD were detected by Western blot and proteins with 134, 110, 93, 89 and 48 kD were detected by immunoprecipitation. With the exception of the 134 kD protein which was recognized by both rabbit anti-promastigote and rabbit anti-amastigote sera all the others were recognized only by the anti-amastigote serum. The 134 kD protein was the only one isolated from the kidneys of infected hamster immunocomplexed with IgG and was the only one detected in a promastigote lysate using IgG from L. donovani-infected hamsters.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler S., Couser W. Immunologic mechanisms of renal disease. Am J Med Sci. 1985 Feb;289(2):55–60. doi: 10.1097/00000441-198502000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agu W. E., Farrell J. P., Soulsby E. J. Pathogenesis of anaemia in hamsters infected with Leishmania donovani. Z Parasitenkd. 1982;68(1):27–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00926654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agu W. E., Farrell J. P., Soulsby E. J. Proliferative glomerulonephritis in experimental Leishmania donovani infection of the golden hamster. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1981;4(3-4):353–368. doi: 10.1016/0147-9571(81)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade Z. A., Iabuki K. A nefropatía do calazar. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1972 Jan-Feb;14(1):51–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates P. A., Kurtz M. K., Gottlieb M., Dwyer D. M. Leishmania donovani: generation of monospecific antibody reagents to soluble acid phosphatase. Exp Parasitol. 1987 Oct;64(2):157–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(87)90139-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boonpucknavig V., Sitprija V. Renal disease in acute Plasmodium falciparum infection in man. Kidney Int. 1979 Jul;16(1):44–52. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Border W. A., Kamil E. S., Ward H. J., Cohen A. H. Antigenic changes as a determinant of immune complex localization in the rat glomerulus. Lab Invest. 1981 Nov;45(5):442–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn-Moreno M. M., Madeira E. D., Miller K., Menezes J. A., Campos-Neto A. Hypergammaglobulinaemia in Leishmania donovani infected hamsters: possible association with a polyclonal activator of B cells and with suppression of T cell function. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Feb;59(2):427–434. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos-Neto A., Bunn-Moreno M. M. Polyclonal B cell activation in hamsters infected with parasites of the genus Leishmania. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):871–876. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.871-876.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho E. M., Andrews B. S., Martinelli R., Dutra M., Rocha H. Circulating immune complexes and rheumatoid factor in schistosomiasis and visceral leishmaniasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983 Jan;32(1):61–68. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1983.32.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho E. M., Teixeira R. S., Johnson W. D., Jr Cell-mediated immunity in American visceral leishmaniasis: reversible immunosuppression during acute infection. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):498–500. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.498-500.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casali P., Lambert P. H. Purification of soluble immune complexes from serum using polymethylmetacrylate beads coated with conglutinin or C1q. Application to the analysis of the components of in vitro formed immune complexes and of immune complexes occurring in vivo during leishmaniasis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Aug;37(2):295–309. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavas J., Guimarães Ferri R. Immunoglobulins in visceral leishmaniasis. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1966 Sep-Oct;8(5):225–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coe J. E. The immune response in the hamster. I. Definition of two 7 S globulin classes: 7 S-gamma-1 and 7 S-gamma-2. J Immunol. 1968 Mar;100(3):507–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coe J. E. The immune response in the hamster. II. Studies on IgM. Immunology. 1970 Feb;18(2):223–236. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. S., Monteiro R. C., Lehuen A., Joskowicz M., Noël L. H., Droz D. Immune complex-mediated glomerulopathy in experimental Chagas' disease. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Jan;58(1):102–114. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(91)90152-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE Brito T., Hoshino-Shimizu S., Neto V. A., Duarte I. S., Penna D. O. Glomerular involvement in human kala-azar. A light, immunofluorescent, and electron microscopic study based on kidney biopsies. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1975 Jan;24(1):9–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Blas A. L., Cherwinski H. M. Detection of antigens on nitrocellulose paper immunoblots with monoclonal antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1983 Aug;133(1):214–219. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90245-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T. G., Pearson R. D. Identification of leishmanial antigens in the sera of patients with American visceral leishmaniasis. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3139–3144. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3139-3144.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T. Development of monoclonal antibodies to assay for circulating antigen in visceral leishmaniasis. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 1988 Nov;83 (Suppl 1):471–475. doi: 10.1590/s0074-02761988000500050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo G. R., Caulin-Glaser T., Emancipator S. N., Lamm M. E. Nephritogenicity and differential distribution of glomerular immune complexes related to immunogen charge. Lab Invest. 1983 Mar;48(3):353–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galvão-Castro B., Sá Ferreira J. A., Marzochi K. F., Marzochi M. C., Coutinho S. G., Lambert P. H. Polyclonal B cell activation, circulating immune complexes and autoimmunity in human american visceral leishmaniasis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Apr;56(1):58–66. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M., Baran D., Druet P. Polyclonal activation and experimental nephropathies. Kidney Int. 1988 Aug;34(2):141–150. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb M., Dwyer D. M. Leishmania donovani: surface membrane acid phosphatase activity of promastigotes. Exp Parasitol. 1981 Aug;52(1):117–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(81)90067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haakenstad A. O., Coe J. E. The immune response in the hamster. IV. Studies on IgA. J Immunol. 1971 Apr;106(4):1026–1034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman B. The immune complex: possible ways of regulating the antibody response. Immunol Today. 1990 Sep;11(9):310–313. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90126-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu X. S., Liu Q., Lin F. Q., Yi T. L., Wang Y. J., Qin Z., Luo P., Wang L. Kala-azar infected serum circulating antigens and their characteristics detected by monoclonal antibody. Chin Med J (Engl) 1988 Jan;101(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovelace J. K., Dwyer D. M., Gottlieb M. Purification and characterization of the extracellular acid phosphatase of Leishmania donovani. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986 Sep;20(3):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(86)90105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovelace J. K., Gottlieb M. Comparison of extracellular acid phosphatases from various isolates of Leishmania. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Nov;35(6):1121–1128. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickol A. D., Bonventre P. F. Immunosuppression associated with visceral leishmaniasis of hamsters. Parasite Immunol. 1985 Jul;7(4):439–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1985.tb00089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira A. V., Roque-Barreira M. C., Sartori A., Campos-Neto A., Rossi M. A. Mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis associated with progressive amyloid deposition in hamsters experimentally infected with Leishmania donovani. Am J Pathol. 1985 Aug;120(2):256–262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira A. V., Rossi M. A., Rogue-Barreira M. C., Sartori A., Campos-Neto A. The potential role of Leishmania antigens and immunoglobulins in the pathogenesis of glomerular lesions of hamsters infected with Leishmania donovani. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1985 Oct;79(5):539–543. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1985.11811960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., de Alencar J. E., Romito R., Naidu T. G., Young A. C., Davis J. S., 4th Circulating immune complexes and rheumatoid factors in visceral leishmaniasis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jun;147(6):1102–1102. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.6.1102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remaley A. T., Das S., Campbell P. I., LaRocca G. M., Pope M. T., Glew R. H. Characterization of Leishmania donovani acid phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):880–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAUBER L. A., OCHS J. Q., COY N. H. Electrophoretic patterns of the serum proteins of chinchillas and hamsters infected with Leishmania donovani. Exp Parasitol. 1954 Jul;3(4):325–335. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(54)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartori A., De Oliveira A. V., Roque-Barreira M. C., Rossi M. A., Campos-Neto A. Immune complex glomerulonephritis in experimental kala-azar. Parasite Immunol. 1987 Jan;9(1):93–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1987.tb00491.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal S., Aikat B. K., Pathania A. G. Immune complexes in Indian kala-azar. Bull World Health Organ. 1982;60(6):945–950. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobh M. A., Moustafa F. E., el-Housseini F., Basta M. T., Deelder A. M., Ghoniem M. A. Schistosomal specific nephropathy leading to end-stage renal failure. Kidney Int. 1987 Apr;31(4):1006–1011. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solling J., Olsen S. Circulating immune complexes in glomerulonephritis. Clin Nephrol. 1981 Aug;16(2):63–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisinger J. R., Pinto A., Velazquez G. A., Bronstein I., Dessene J. J., Duque J. F., Montenegro J., Tapanes F., de Rousse A. R. Clinical and histological kidney involvement in human kala-azar. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Mar;27(2 Pt 1):357–359. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wener M. H., Mannik M. Mechanisms of immune deposit formation in renal glomeruli. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1986;9(2-3):219–235. doi: 10.1007/BF02099023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolga J. I., Stahl J. P., Gaillat J., Daniel Ribeiro C., Micoud M. Manifestations immunes et autoimmunes au cours d'une leishmaniose viscérale autochtone avec atteinte hépatique, rénale et vasculaire. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1983 Aug-Oct;76(4):369–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. C., Hudson L., Hindmarsh P. J. Immune precipitation and immunoblotting for the detection of Trypanosoma cruzi antigens. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1986;80(2):275–281. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(86)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodroffe A. J., Wilson C. B. An evaluation of elution techniques in the study of immune complex glomerulonephritis. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1788–1794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]