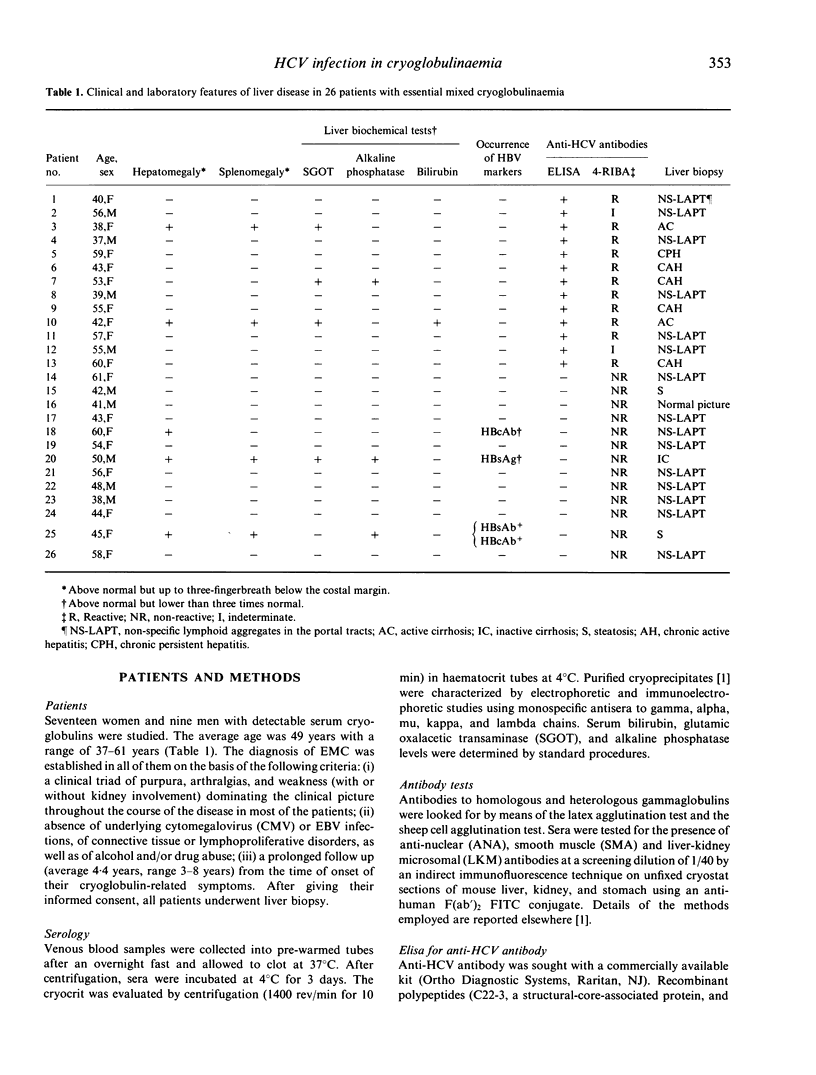
Abstract
Although essential mixed cryoglobulinaemia (EMC) is recognized to be frequently associated with chronic liver disease, aetiology and pathogenesis of liver damage remain unsolved questions. The purpose of this study was to assess the possible causative role of hepatitis C virus (HCV) in the liver impairment occurring in patients with EMC. Twenty-six consecutive EMC patients were evaluated. All patients underwent percutaneous liver biopsy. Anti-HCV antibodies were assayed by ELISA and supported by a recombinant immunoblotting assay (4-RIBA). The prevalence of anti-HCV antibodies in patients with and without chronic active liver disease (CALD) was compared. Anti-HCV antibodies were detected in 13 patients (50%) by ELISA and confirmed in 11 of them (42.3%) by 4-RIBA, the remaining two patients being indeterminate in the supportive assay. CALD correlated significantly with anti-HCV antibodies: indeed, 7/11 (63.6%) anti-HCV+ patients showed histological and clinical pictures of CALD, compared with 1/15 (6.6%) anti-HCV- patients (P less than 0.01). With the exception of the patient who was found to be HBsAg+, no liver tissue expressed hepatitis B virus-related antigens in the hepatocytes. Additional histological findings included discrete lymphoid aggregates in portal tracts, siderosis, fatty changes, hyperplasia of Kupffer cells. It can be concluded that chronic liver damage in EMC is frequently associated with anti-HCV antibodies. Although the cause of EMC remains unknown, this study has obvious implications for clarifying the etiology of associated CALD and further supports the therapeutic use of interferons in this disease.
Full text
PDF

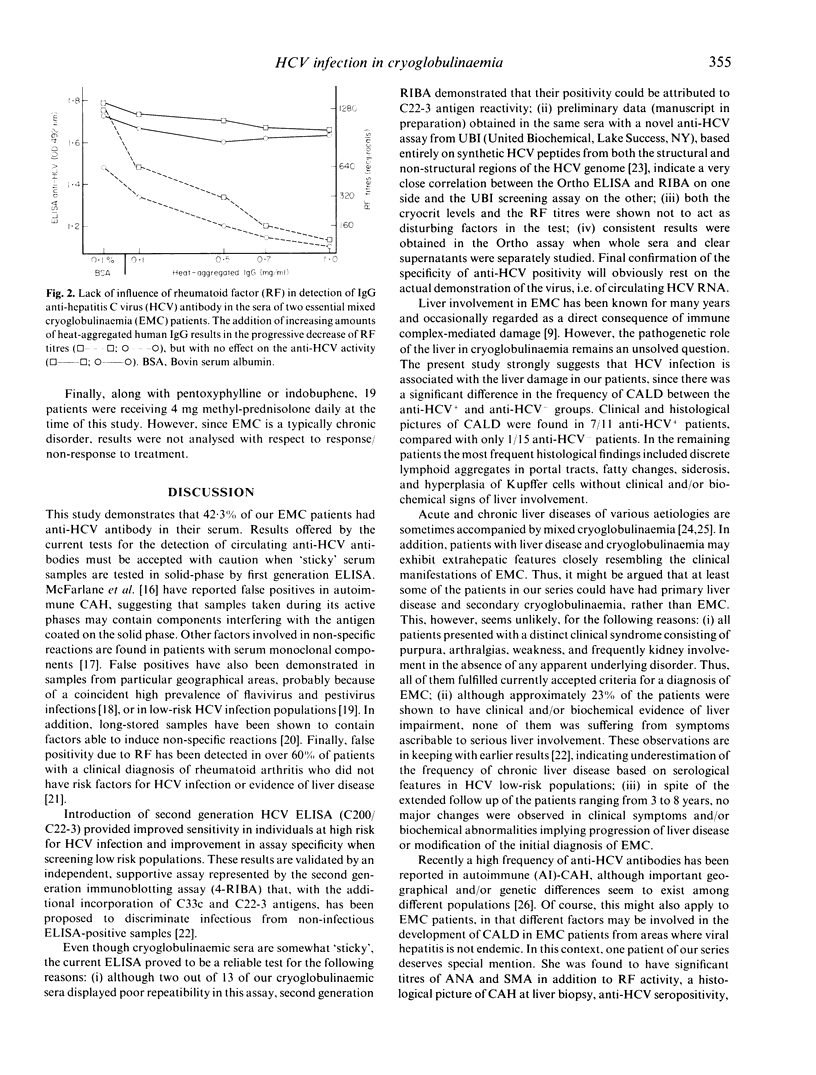

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonomo L., Casato M., Afeltra A., Caccavo D. Treatment of idiopathic mixed cryoglobulinemia with alpha interferon. Am J Med. 1987 Oct;83(4):726–730. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90904-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boudart D., Lucas J. C., Muller J. Y., Le Carrer D., Planchon B., Harousseau J. L. False-positive hepatitis C virus antibody tests in paraproteinaemia. Lancet. 1990 Jul 7;336(8706):63–63. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo Q. L., Kuo G., Weiner A. J., Overby L. R., Bradley D. W., Houghton M. Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):359–362. doi: 10.1126/science.2523562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienstag J. L., Rhodes A. R., Bhan A. K., Dvorak A. M., Mihm M. C., Jr, Wands J. R. Urticaria associated with acute viral hepatitis type B: studies of pathogenesis. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Jul;89(1):34–40. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-1-34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorini G. F., Sinico R. A., Winearls C., Custode P., De Giuli-Morghen C., D'Amico G. Persistent Epstein-Barr virus infection in patients with type II essential mixed cryoglobulinemia. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Jun;47(3):262–269. doi: 10.1016/s0090-1229(88)80004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florin-Christensen A., Roux M. E., Aarana R. M. Cryoglobulins in acute and chronic liver diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Apr;16(4):599–605. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli M., Careddu F., D'Armino A., Monti G., Messina K., Invernizzi F. Hepatitis B virus and essential mixed cryoglobulinaemia. Lancet. 1980 May 17;1(8177):1093–1093. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91541-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorevic P. D., Kassab H. J., Levo Y., Kohn R., Meltzer M., Prose P., Franklin E. C. Mixed cryoglobulinemia: clinical aspects and long-term follow-up of 40 patients. Am J Med. 1980 Aug;69(2):287–308. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90390-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosein B., Fang C. T., Popovsky M. A., Ye J., Zhang M., Wang C. Y. Improved serodiagnosis of hepatitis C virus infection with synthetic peptide antigen from capsid protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3647–3651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idéo G., Bellati G., Pedraglio E., Bottelli R., Donzelli T., Putignano G. Intrafamilial transmission of hepatitis C virus. Lancet. 1990 Feb 10;335(8685):353–353. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90636-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jori G. P., Buonanno G. Chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver in cryoglobulinaemia. Gut. 1972 Aug;13(8):610–613. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.8.610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jori G. P., Buonanno G., D'onofrio F., Tirelli A., Gonnella F., Gentile S. Incidence and immunochemical features of serum cryoglobulin in chronic liver disease. Gut. 1977 Mar;18(3):245–249. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.3.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo G., Choo Q. L., Alter H. J., Gitnick G. L., Redeker A. G., Purcell R. H., Miyamura T., Dienstag J. L., Alter M. J., Stevens C. E. An assay for circulating antibodies to a major etiologic virus of human non-A, non-B hepatitis. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):362–364. doi: 10.1126/science.2496467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenzi M., Johnson P. J., McFarlane I. G., Ballardini G., Smith H. M., McFarlane B. M., Bridger C., Vergani D., Bianchi F. B., Williams R. Antibodies to hepatitis C virus in autoimmune liver disease: evidence for geographical heterogeneity. Lancet. 1991 Aug 3;338(8762):277–280. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90418-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levo Y., Gorevic P. D., Kassab H. J., Tobias H., Franklin E. C. Liver involvement in the syndrome of mixed cryoglobulinemia. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Sep;87(3):287–292. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-87-3-287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levo Y., Gorevic P. D., Kassab H. J., Zucker-Franklin D., Franklin E. C. Association between hepatitis B virus and essential mixed cryoglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jun 30;296(26):1501–1504. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197706302962605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane I. G., Smith H. M., Johnson P. J., Bray G. P., Vergani D., Williams R. Hepatitis C virus antibodies in chronic active hepatitis: pathogenetic factor or false-positive result? Lancet. 1990 Mar 31;335(8692):754–757. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90870-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer M., Franklin E. C., Elias K., McCluskey R. T., Cooper N. Cryoglobulinemia--a clinical and laboratory study. II. Cryoglobulins with rheumatoid factor activity. Am J Med. 1966 Jun;40(6):837–856. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90200-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterlini P., Gerken G., Nakajima E., Terre S., D'Errico A., Grigioni W., Nalpas B., Franco D., Wands J., Kew M. Polymerase chain reaction to detect hepatitis B virus DNA and RNA sequences in primary liver cancers from patients negative for hepatitis B surface antigen. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 12;323(2):80–85. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007123230202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontisso P., Stenico D., Diodati G., Marin G., Caldironi M. V., Giacchino R., Realdi G., Alberti A. HBV-DNA sequences are rarely detected in the liver of patients with HBsAg-negative chronic active liver disease and with hepatocellular carcinoma in Italy. Liver. 1987 Aug;7(4):211–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1987.tb00345.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popp J. W., Jr, Dienstag J. L., Wands J. R., Bloch K. J. Essential mixed cryoglobulinemia without evidence for hepatitis B virus infection. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Mar;92(3):379–383. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-3-379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonno D. E., Detomaso P., Papanice M. A., Fiore G., Bufano G., Manghisi O. G. Correlation between hepatitis B virus deoxyribonucleic acid and receptors for polymerized human albumin in HBV chronic infection. Digestion. 1987;37(4):206–210. doi: 10.1159/000199502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonno D. E., Fiore G., Bufano G., Manghisi O. G. Cytoplasmic localization of hepatitis B core antigen in hepatitis B virus infected livers. J Immunol Methods. 1988 May 9;109(2):245–252. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90249-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theilmann L., Blazek M., Goeser T., Gmelin K., Kommerell B., Fiehn W. False-positive anti-HCV tests in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1990 Jun 2;335(8701):1346–1346. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91229-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Poel C. L., Cuypers H. T., Reesink H. W., Weiner A. J., Quan S., Di Nello R., Van Boven J. J., Winkel I., Mulder-Folkerts D., Exel-Oehlers P. J. Confirmation of hepatitis C virus infection by new four-antigen recombinant immunoblot assay. Lancet. 1991 Feb 9;337(8737):317–319. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90942-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. J., Truett M. A., Rosenblatt J., Han J., Quan S., Polito A. J., Kuo G., Choo Q. L., Houghton M., Agius C. HCV testing in low-risk population. Lancet. 1990 Sep 15;336(8716):695–695. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92194-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong D. C., Diwan A. R., Rosen L., Gerin J. L., Johnson R. G., Polito A., Purcell R. H. Non-specificity of anti-HCV test for seroepidemiological analysis. Lancet. 1990 Sep 22;336(8717):750–751. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92245-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarski J. P., Rougier D., Aubert H., Renversez J. C., Cordonnier D., Stoebner P., Rachail M. Association cryoglobuline et maladie hépatique: fréquence, nature et caractères immuno-chimiques de la cryoglobulinémie. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1984 Nov;8(11):845–850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


