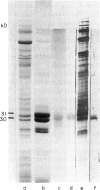
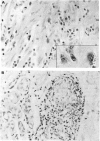
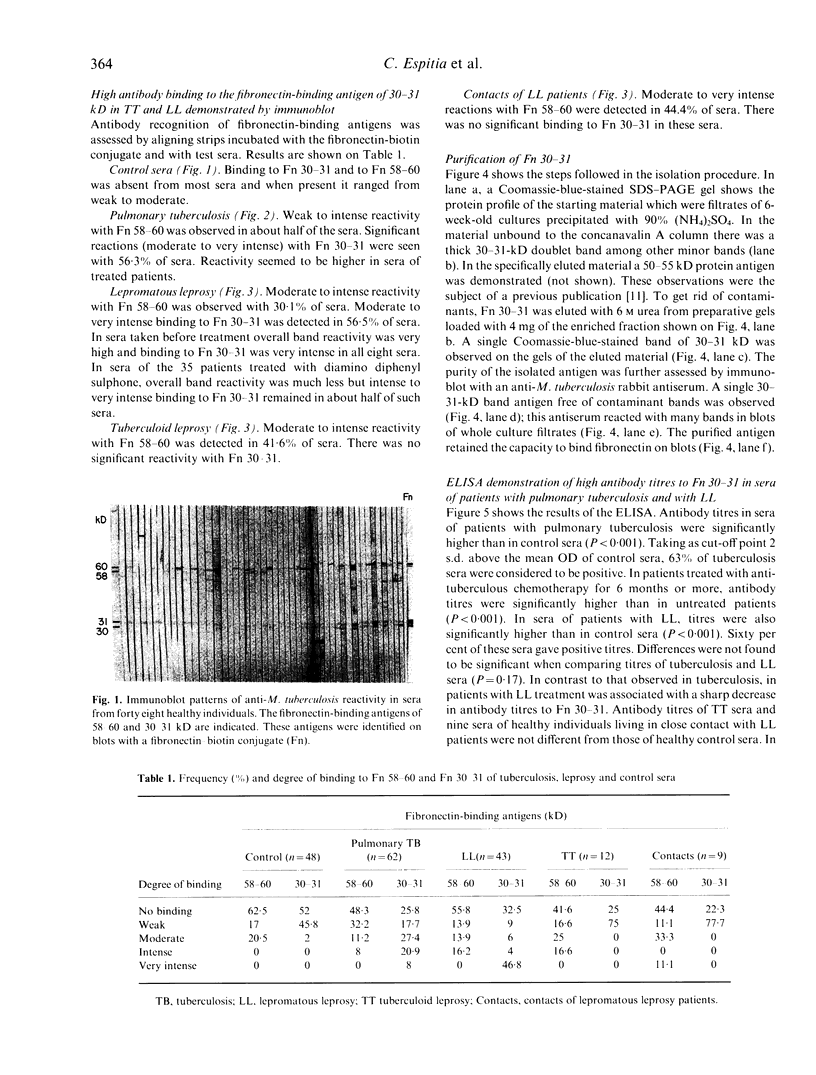
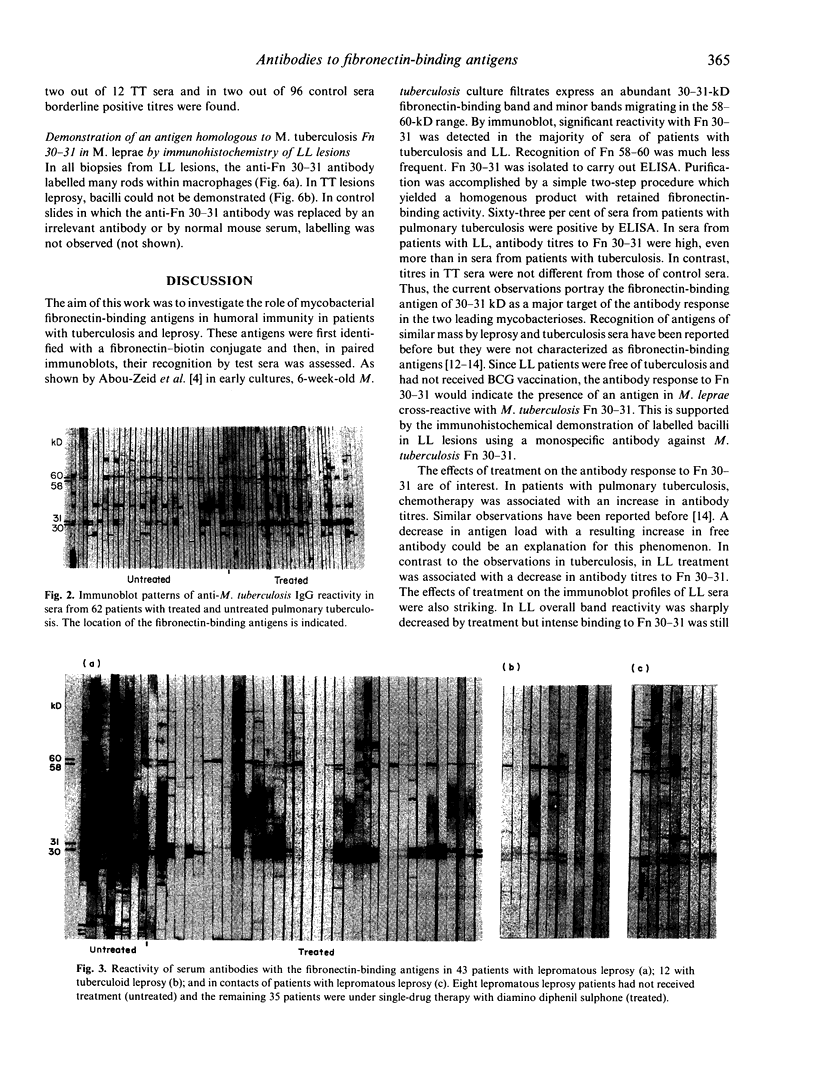
Abstract
Immunoblot assays showed that mycobacterial fibronectin-binding antigens are important targets of the humoral immune response in tuberculosis and leprosy. Using culture filtrate antigens of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, strong reactivity with the fibronectin-binding of 30-31 kD (Fn 30-31) was demonstrated in 55.9% of tuberculosis sera and in 56.5% of lepromatous leprosy sera. Sera from patients with tuberculoid leprosy and control sera gave very weak binding. Reactivity of tuberculosis and lepromatous leprosy sera with the fibronectin-binding antigen of 58-60 kD (Fn 58-60) was less conspicuous. The ability to react with fibronectin of the antigens of 58-60 and 30-31 kD was demonstrated by parallel labelling with a fibronectin-biotin conjugate. Fn 30-31 was purified to homogeneity by a two-step procedure and used for ELISA. Positive titres were found in 63% out of 65 tuberculosis sera and in 60.5% out of 43 lepromatous leprosy sera. Antibody titres in lepromatous leprosy sera were higher than in tuberculosis sera. Our observations indicate indirectly that M. leprae possess a highly immunogenic molecule homologous to M. tuberculosis Fn 30-31, which elicits a high antibody response in lepromatous leprosy but not in tuberculoid leprosy. In this investigation, direct evidence for the presence of this antigen in M. leprae was obtained by immunochemistry of lepromatous leprosy lesions with a monospecific antibody raised against M. tuberculosis Fn 30-31.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abou-Zeid C., Filley E., Steele J., Rook G. A. A simple new method for using antigens separated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to stimulate lymphocytes in vitro after converting bands cut from Western blots into antigen-bearing particles. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Apr 2;98(1):5–10. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90429-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abou-Zeid C., Ratliff T. L., Wiker H. G., Harboe M., Bennedsen J., Rook G. A. Characterization of fibronectin-binding antigens released by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3046–3051. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3046-3051.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen A. B., Hansen E. B. Structure and mapping of antigenic domains of protein antigen b, a 38,000-molecular-weight protein of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2481–2488. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2481-2488.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen A. B., Yuan Z. L., Hasløv K., Vergmann B., Bennedsen J. Interspecies reactivity of five monoclonal antibodies to Mycobacterium tuberculosis as examined by immunoblotting and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):446–451. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.446-451.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aslanzadeh J., Brown E. J., Quillin S. P., Ritchey J. K., Ratliff T. L. Characterization of soluble fibronectin binding to Bacille Calmette-Guérin. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Oct;135(10):2735–2741. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-10-2735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Closs O., Harboe M., Axelsen N. H., Bunch-Christensen K., Magnusson M. The antigens of Mycobacterium bovis, strain BCG, studied by crossed immunoelectrophoresis: a reference system. Scand J Immunol. 1980;12(3):249–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bruyn J., Bosmans R., Nyabenda J., Van Vooren J. P. Effect of zinc deficiency on the appearance of two immunodominant protein antigens (32 kDa and 65 kDa) in culture filtrates of mycobacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Jan;135(1):79–84. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-1-79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espitia C., Mancilla R. Identification, isolation and partial characterization of Mycobacterium tuberculosis glycoprotein antigens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Sep;77(3):378–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oftung F., Mustafa A. S., Shinnick T. M., Houghten R. A., Kvalheim G., Degre M., Lundin K. E., Godal T. Epitopes of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis 65-kilodalton protein antigen as recognized by human T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 15;141(8):2749–2754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor R. A. Fibronectin: a brief overview of its structure, function, and physiology. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jul-Aug;9 (Suppl 4):S317–S321. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.supplement_4.s317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratliff T. L., McGarr J. A., Abou-Zeid C., Rook G. A., Stanford J. L., Aslanzadeh J., Brown E. J. Attachment of mycobacteria to fibronectin-coated surfaces. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 May;134(5):1307–1313. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-5-1307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley D. S., Jopling W. H. Classification of leprosy according to immunity. A five-group system. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1966 Jul-Sep;34(3):255–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumschlag H. S., Shinnick T. M., Cohen M. L. Serological responses of patients with lepromatous and tuberculoid leprosy to 30-, 31-, and 32-kilodalton antigens of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2200–2202. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2200-2202.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Hayman E. G., Pierschbacher M., Engvall E. Fibronectin: purification, immunochemical properties, and biological activities. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):803–831. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turneer M., Van Vooren J. P., De Bruyn J., Serruys E., Dierckx P., Yernault J. C. Humoral immune response in human tuberculosis: immunoglobulins G, A, and M directed against the purified P32 protein antigen of Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1714–1719. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1714-1719.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vega-Lopez F., Stoker N. G., Locniskar M. F., Dockrell H. M., Grant K. A., McAdam K. P. Recognition of mycobacterial antigens by sera from patients with leprosy. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2474–2479. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2474-2479.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiker H. G., Harboe M., Nagai S., Bennedsen J. Quantitative and qualitative studies on the major extracellular antigen of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv and Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Apr;141(4 Pt 1):830–838. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.4_Pt_1.830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Bloom B. R., Grosskinsky C. M., Ivanyi J., Thomas D., Davis R. W. Dissection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens using recombinant DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2583–2587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]