Abstract
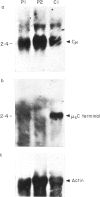
Serum IgM concentrations were low although serum IgG and IgA concentrations were normal in both our patients with Bloom's syndrome. Although the percentages of surface IgM-bearing cells were not reduced, the numbers of IgM-secreting cells were markedly reduced. The membrane-bound mu (microns) and secreted mu (microseconds) mRNAs are produced from transcripts of a single immunoglobulin mu gene by alternative RNA processing pathways. The control of microseconds mRNA synthesis depends on the addition of poly(A) to microseconds C-terminal segment. In both patients, mu mRNA was well detected but microseconds C-terminal mRNA was scarcely detected, suggesting that microns mRNA was well transcribed but microseconds mRNA was not. There was, at least, no mutation or deletion in the microseconds C-terminal coding sequence, the RNA splice site (GG/TAAAC) at the 5' end of microseconds C-terminal segment and the AATAAA poly(A) signal sequence in both patients. Our results suggest that selective IgM deficiency in Bloom's syndrome is due to an abnormality in the maturation of surface IgM-bearing B cells into IgM-secreting cells and a failure of microseconds mRNA synthesis. Moreover, reduced microseconds mRNA synthesis may be due to the defect on developmental regulation of the site at which poly(A) is added to transcripts of the mu gene.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Bothwell A. L., Knapp M., Siden E., Mather E., Koshland M., Baltimore D. Synthesis of secreted and membrane-bound immunoglobulin mu heavy chains is directed by mRNAs that differ at their 3' ends. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):293–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90615-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaganti R. S., Schonberg S., German J. A manyfold increase in sister chromatid exchanges in Bloom's syndrome lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4508–4512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J. Y., Becker F. F., German J., Ray J. H. Altered DNA ligase I activity in Bloom's syndrome cells. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):357–359. doi: 10.1038/325357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Rogers J., Davis M., Calame K., Bond M., Wall R., Hood L. Two mRNAs can be produced from a single immunoglobulin mu gene by alternative RNA processing pathways. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90617-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German J. Bloom's syndrome. I. Genetical and clinical observations in the first twenty-seven patients. Am J Hum Genet. 1969 Mar;21(2):196–227. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German J., Takebe H. Bloom's syndrome. XIV. The disorder in Japan. Clin Genet. 1989 Feb;35(2):93–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1989.tb02913.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hütteroth T. H., Litwin S. D., German J. Abnormal immune responses of Bloom's syndrome lymphocytes in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jul;56(1):1–7. doi: 10.1172/JCI108058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehry M., Ewald S., Douglas R., Sibley C., Raschke W., Fambrough D., Hood L. The immunoglobulin mu chains of membrane-bound and secreted IgM molecules differ in their C-terminal segments. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):393–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90476-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo N., Orii T., Uetake H. Competence of B cells for T-cell help in pokeweed mitogen-induced immunoglobulin production. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Feb;26(2):192–200. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruger G., Welte K., Ciobanu N., Cunningham-Rundles C., Ralph P., Venuta S., Feldman S., Koziner B., Wang C. Y., Moore M. A. Interleukin-2 correction of defective in vitro T-cell mitogenesis in patients with common varied immunodeficiency. J Clin Immunol. 1984 Jul;4(4):295–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00915297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Dhar R., Khoury G. Mapping the spliced and unspliced late lytic SV40 RNAs. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):971–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90351-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muraguchi A., Hirano T., Tang B., Matsuda T., Horii Y., Nakajima K., Kishimoto T. The essential role of B cell stimulatory factor 2 (BSF-2/IL-6) for the terminal differentiation of B cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):332–344. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J. How RNA polymerase II terminates transcription in higher eukaryotes. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Mar;14(3):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Forster A., Milstein C. P. Human immunoglobulin heavy chain genes: evolutionary comparisons of C mu, C delta and C gamma genes and associated switch sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 25;9(18):4509–4524. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.18.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Marcu K. B., Perry R. P. The synthesis and processing of the messenger RNAs specifying heavy and light chain immunoglobulins in MPC-11 cells. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1495–1509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitia R., Alberini C., Biassoni R., Rubartelli A., DeAmbrosis S., Vismara D. The control of membrane and secreted heavy chain biosynthesis varies in different immunoglobulin isotypes produced by a monoclonal B cell lymphoma. Mol Immunol. 1988 Feb;25(2):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(88)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitia R., Neuberger M. S., Milstein C. Regulation of membrane IgM expression in secretory B cells: translational and post-translational events. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3969–3977. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02739.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi N., Mukai M., Nagaoki T., Miyawaki T., Moriya N., Takahashi H., Kondo N. Impaired B-cell differentiation and T-cell regulatory function in four patients with Bloom's syndrome. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 Feb;22(2):247–258. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):575–581. doi: 10.1038/302575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Kerckhove C. W., Ceuppens J. L., Vanderschueren-Lodeweyckx M., Eggermont E., Vertessen S., Stevens E. A. Bloom's syndrome. Clinical features and immunologic abnormalities of four patients. Am J Dis Child. 1988 Oct;142(10):1089–1093. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1988.02150100083032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weemaes C. M., Bakkeren J. A., ter Haar B. G., Hustinx T. W., van Munster P. J. Immune responses in four patients with Bloom syndrome. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 Jan;12(1):12–19. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis A. E., Weksberg R., Tomlinson S., Lindahl T. Structural alterations of DNA ligase I in Bloom syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8016–8020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]