Abstract
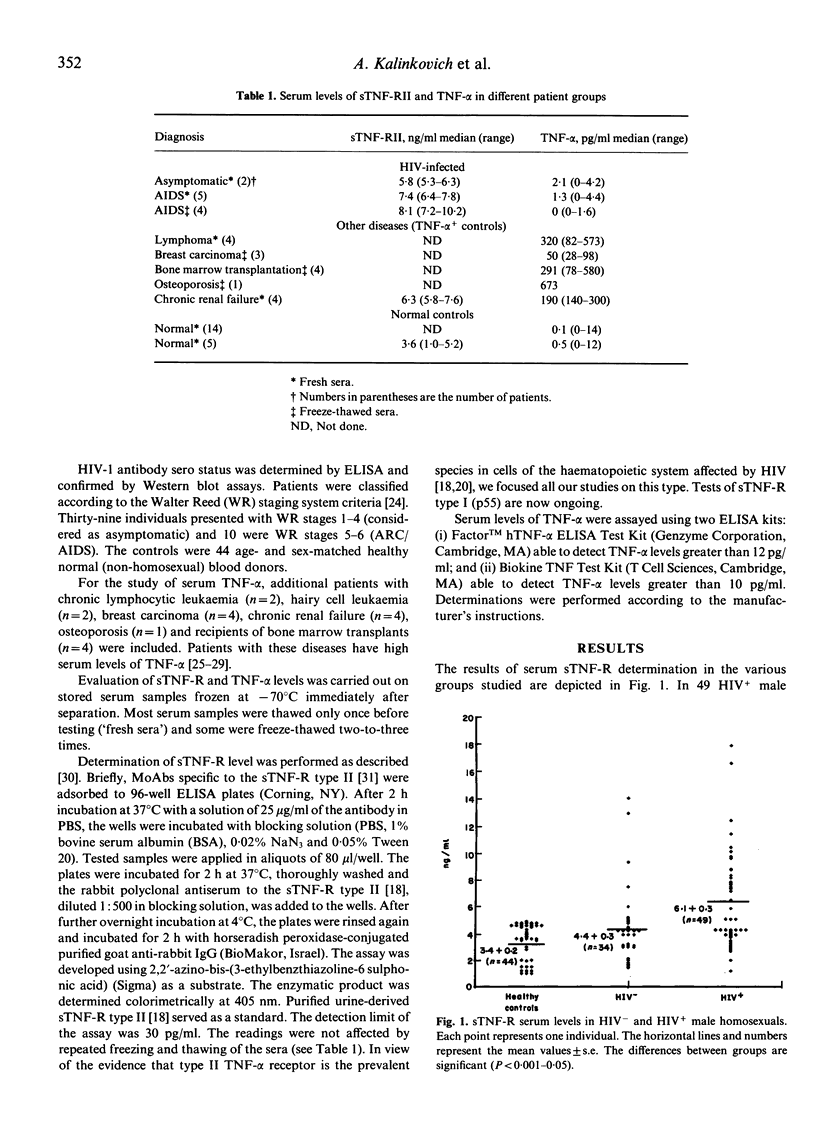
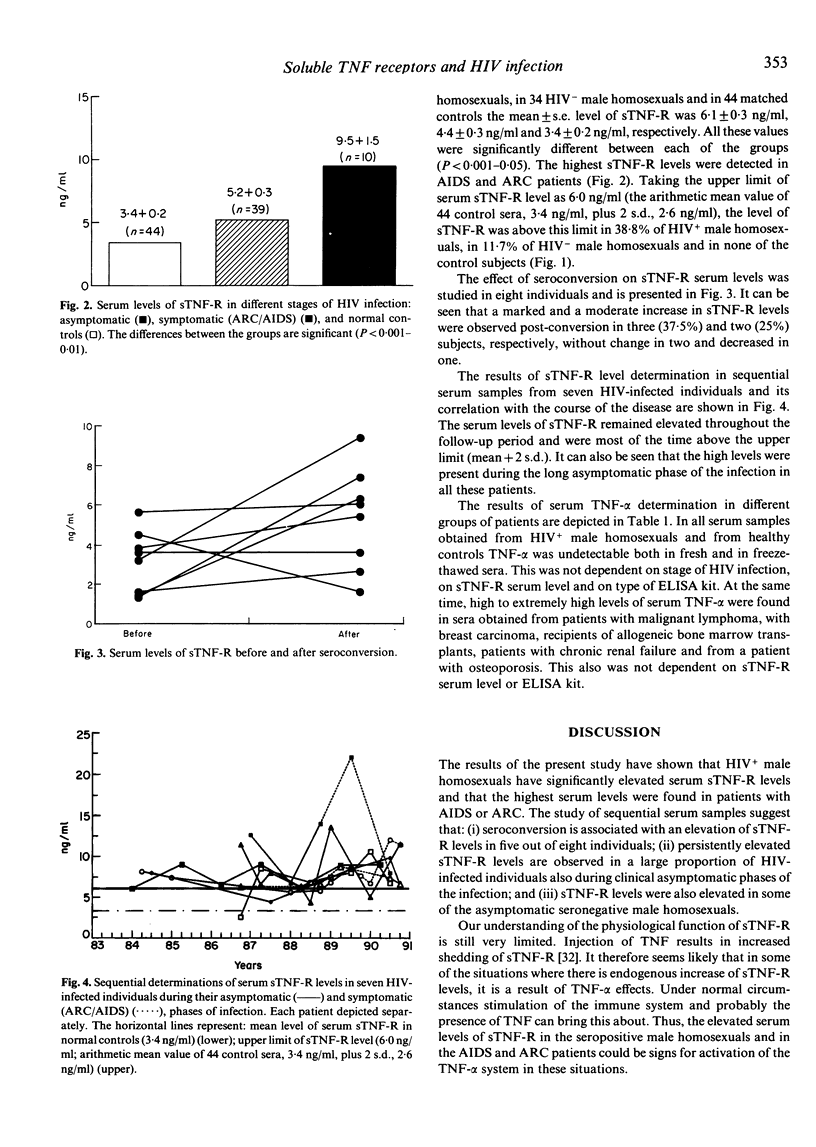
Serum levels of the soluble form of tumour necrosis factor receptor type II (p75) (sTNF-R) were determined in HIV-infected individuals and risk groups and were then correlated with the course of infection and prognosis. sTNF-R levels were determined by an ELISA with MoAbs and polyclonal antibodies to urine-derived sTNF-R proteins. The mean +/- s.e. levels of sTNF-R in the sera of 49 HIV+ male homosexuals, 34 HIV- male homosexuals and 44 matched controls were 6.1 +/- 0.3 ng/ml, 4.4 +/- 0.3 ng/ml and 3.4 +/- 0.2 ng/ml, respectively. All these values were significantly different between each of the groups (P less than 0.001-0.05). Sequential studies of sTNF-R revealed higher levels following seroconversion in 5/8 individuals, remained persistently high during the asymptomatic phase of the infection and became even more elevated in some ARC and AIDS patients. At the same time TNF-alpha was undetectable in sera obtained from HIV+ male homosexuals and from healthy controls. This was independent of stage of HIV infection, serum sTNF-R level and type of ELISA kit used. These findings suggest that TNF-alpha/TNF-R system is turned on before and during HIV infection and raise the possibility that sTNF-R, the natural inhibitor of TNF, may be of importance in determining the course and probably prognosis of the disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderka D., Englemann H., Hornik V., Skornick Y., Levo Y., Wallach D., Kushtai G. Increased serum levels of soluble receptors for tumor necrosis factor in cancer patients. Cancer Res. 1991 Oct 15;51(20):5602–5607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arditi M., Kabat W., Yogev R. Serum tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1-beta, p24 antigen concentrations and CD4+ cells at various stages of human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1991 Jun;10(6):450–455. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199106000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balkwill F., Osborne R., Burke F., Naylor S., Talbot D., Durbin H., Tavernier J., Fiers W. Evidence for tumour necrosis factor/cachectin production in cancer. Lancet. 1987 Nov 28;2(8570):1229–1232. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91850-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Tumor necrosis, cachexia, shock, and inflammation: a common mediator. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:505–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockhaus M., Schoenfeld H. J., Schlaeger E. J., Hunziker W., Lesslauer W., Loetscher H. Identification of two types of tumor necrosis factor receptors on human cell lines by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3127–3131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew W. L., Mintz L., Miner R. C., Sands M., Ketterer B. Prevalence of cytomegalovirus infection in homosexual men. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):188–192. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelmann H., Aderka D., Rubinstein M., Rotman D., Wallach D. A tumor necrosis factor-binding protein purified to homogeneity from human urine protects cells from tumor necrosis factor toxicity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11974–11980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelmann H., Holtmann H., Brakebusch C., Avni Y. S., Sarov I., Nophar Y., Hadas E., Leitner O., Wallach D. Antibodies to a soluble form of a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor have TNF-like activity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14497–14504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelmann H., Novick D., Wallach D. Two tumor necrosis factor-binding proteins purified from human urine. Evidence for immunological cross-reactivity with cell surface tumor necrosis factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1531–1536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S. Cytokine regulation of HIV expression. Lymphokine Res. 1990 Winter;9(4):527–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foa R., Massaia M., Cardona S., Tos A. G., Bianchi A., Attisano C., Guarini A., di Celle P. F., Fierro M. T. Production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha by B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells: a possible regulatory role of TNF in the progression of the disease. Blood. 1990 Jul 15;76(2):393–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foley N., Lambert C., McNicol M., Johnson N., Rook G. A. An inhibitor of the toxicity of tumour necrosis factor in the serum of patients with sarcoidosis, tuberculosis and Crohn's disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Jun;80(3):395–399. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb03299.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folks T. M., Clouse K. A., Justement J., Rabson A., Duh E., Kehrl J. H., Fauci A. S. Tumor necrosis factor alpha induces expression of human immunodeficiency virus in a chronically infected T-cell clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2365–2368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatanaga T., Hwang C. D., Kohr W., Cappuccini F., Lucci J. A., 3rd, Jeffes E. W., Lentz R., Tomich J., Yamamoto R. S., Granger G. A. Purification and characterization of an inhibitor (soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor) for tumor necrosis factor and lymphotoxin obtained from the serum ultrafiltrates of human cancer patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8781–8784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi L. M., Martino G. V., Franciotta D. M., Brustia R., Castagna A., Pristerà R., Lazzarin A. Elevated alpha-tumor necrosis factor levels in spinal fluid from HIV-1-infected patients with central nervous system involvement. Ann Neurol. 1991 Jan;29(1):21–25. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn T., Schattner A., Handzel Z. T., Levin S., Bentwich Z. Possible role of natural cytotoxic activity in the pathogenesis of AIDS. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Jan;50(1 Pt 1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90221-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann W., Hitzler H., Schlickenrieder J. H., Zapf J., Heit W., Gaedicke G., Vetter U. Heterogeneity of insulin and insulin-like growth factor I binding in a human Burkitt type ALL cell line during the cell cycle and in three Burkitt type ALL sublines. Leukemia. 1988 Apr;2(4):241–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward M., Fiedler-Nagy C. Mechanisms of bone loss: rheumatoid arthritis, periodontal disease and osteoporosis. Agents Actions. 1987 Dec;22(3-4):251–254. doi: 10.1007/BF02009053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbelin A., Nguyen A. T., Zingraff J., Ureña P., Descamps-Latscha B. Influence of uremia and hemodialysis on circulating interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha. Kidney Int. 1990 Jan;37(1):116–125. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hober D., Haque A., Wattre P., Beaucaire G., Mouton Y., Capron A. Production of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-1 (IL-1) in patients with AIDS. Enhanced level of TNF-alpha is related to a higher cytotoxic activity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Dec;78(3):329–333. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hober D., Lucas B., Wattre P., Capron A., Haque A. TNF-alpha production by U937 promonocytes is enhanced by factors released from HIV-infected T4 lymphocytes: TNF-alpha is one of the mediators causing lysis of HIV-infected T4 cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1992 Feb;62(2):168–175. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(92)90069-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holler E., Kolb H. J., Möller A., Kempeni J., Liesenfeld S., Pechumer H., Lehmacher W., Ruckdeschel G., Gleixner B., Riedner C. Increased serum levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha precede major complications of bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1990 Feb 15;75(4):1011–1016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël N., Hazan U., Alcami J., Munier A., Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Bachelerie F., Israël A., Virelizier J. L. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates transcription of HIV-1 in human T lymphocytes, independently and synergistically with mitogens. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):3956–3960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M., Baba M., Mori S., Hirabayashi K., Sato A., Shigeta S., De Clercq E. Tumor necrosis factor antagonizes inhibitory effect of azidothymidine on human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) replication in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Feb 14;166(3):1095–1101. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90979-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Hamamoto Y., Kobayashi N., Yamamoto N. Serum level of TNF alpha in HIV-infected individuals. AIDS. 1990 Feb;4(2):169–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantz M., Gullberg U., Nilsson E., Olsson I. Characterization in vitro of a human tumor necrosis factor-binding protein. A soluble form of a tumor necrosis factor receptor. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1396–1402. doi: 10.1172/JCI114853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantz M., Malik S., Slevin M. L., Olsson I. Infusion of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) causes an increase in circulating TNF-binding protein in humans. Cytokine. 1990 Nov;2(6):402–406. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(90)90048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau A. S., Livesey J. F. Endotoxin induction of tumor necrosis factor is enhanced by acid-labile interferon-alpha in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1989 Sep;84(3):738–743. doi: 10.1172/JCI114231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loetscher H., Steinmetz M., Lesslauer W. Tumor necrosis factor: receptors and inhibitors. Cancer Cells. 1991 Jun;3(6):221–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lähdevirta J., Maury C. P., Teppo A. M., Repo H. Elevated levels of circulating cachectin/tumor necrosis factor in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1988 Sep;85(3):289–291. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90576-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Hamamoto Y., Soma G., Mizuno D., Yamamoto N., Kobayashi N. Cytocidal effect of tumor necrosis factor on cells chronically infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV): enhancement of HIV replication. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2504–2509. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2504-2509.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Kobayashi N., Yamamoto N. Cytokines and HIV infection: is AIDS a tumor necrosis factor disease? AIDS. 1991 Dec;5(12):1405–1417. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199112000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellors J. W., Griffith B. P., Ortiz M. A., Landry M. L., Ryan J. L. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha/cachectin enhances human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication in primary macrophages. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jan;163(1):78–82. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.1.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz M., Rapaport R., Oleske J. M., Connor E. M., Koenigsberger M. R., Denny T., Epstein L. G. Elevated serum levels of tumor necrosis factor are associated with progressive encephalopathy in children with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Dis Child. 1989 Jul;143(7):771–774. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1989.02150190021012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noronha I. L., Daniel V., Schimpf K., Opelz G. Soluble IL-2 receptor and tumour necrosis factor-alpha in plasma of haemophilia patients infected with HIV. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Feb;87(2):287–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb02989.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odeh M. The role of tumour necrosis factor-alpha in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Intern Med. 1990 Dec;228(6):549–556. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.1990.tb00278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson I., Lantz M., Nilsson E., Peetre C., Thysell H., Grubb A., Adolf G. Isolation and characterization of a tumor necrosis factor binding protein from urine. Eur J Haematol. 1989 Mar;42(3):270–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1989.tb00111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porteu F., Nathan C. Shedding of tumor necrosis factor receptors by activated human neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1990 Aug 1;172(2):599–607. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.2.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purtilo D. T., Kipscomb H., Krueger G., Sonnabend J., Casareale D., Volsky D. J. Role of Epstein-Barr virus in acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1985;187:53–65. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9430-7_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rautonen J., Rautonen N., Martin N. L., Philip R., Wara D. W. Serum interleukin-6 concentrations are elevated and associated with elevated tumor necrosis factor-alpha and immunoglobulin G and A concentrations in children with HIV infection. AIDS. 1991 Nov;5(11):1319–1325. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199111000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfield R. R., Wright D. C., Tramont E. C. The Walter Reed staging classification for HTLV-III/LAV infection. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jan 9;314(2):131–132. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198601093140232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux-Lombard P., Modoux C., Cruchaud A., Dayer J. M. Purified blood monocytes from HIV 1-infected patients produce high levels of TNF alpha and IL-1. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Mar;50(3):374–384. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schattner A., Hanuka N., Sarov B., Sarov I., Handzel Z., Bentwich Z. Sequential serological studies of homosexual men with and without HIV infection. Epstein-Barr virus activation preceding and following HIV seroconversion. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Aug;85(2):209–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05706.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott-Algara D., Vuillier F., Marasescu M., de Saint Martin J., Dighiero G. Serum levels of IL-2, IL-1 alpha, TNF-alpha, and soluble receptor of IL-2 in HIV-1-infected patients. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Apr;7(4):381–386. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Isaaz S., Dayer J. M. Purification and biologic characterization of a specific tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11966–11973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Cerami A. The role of cachectin/tumor necrosis factor in AIDS. Cancer Cells. 1989 Oct;1(2):62–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. C., Jewett A., Mitsuyasu R., Bonavida B. Spontaneous cytotoxicity and tumor necrosis factor production by peripheral blood monocytes from AIDS patients. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):99–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Sydow M., Sönnerborg A., Gaines H., Strannegård O. Interferon-alpha and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in serum of patients in various stages of HIV-1 infection. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Apr;7(4):375–380. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



