Abstract
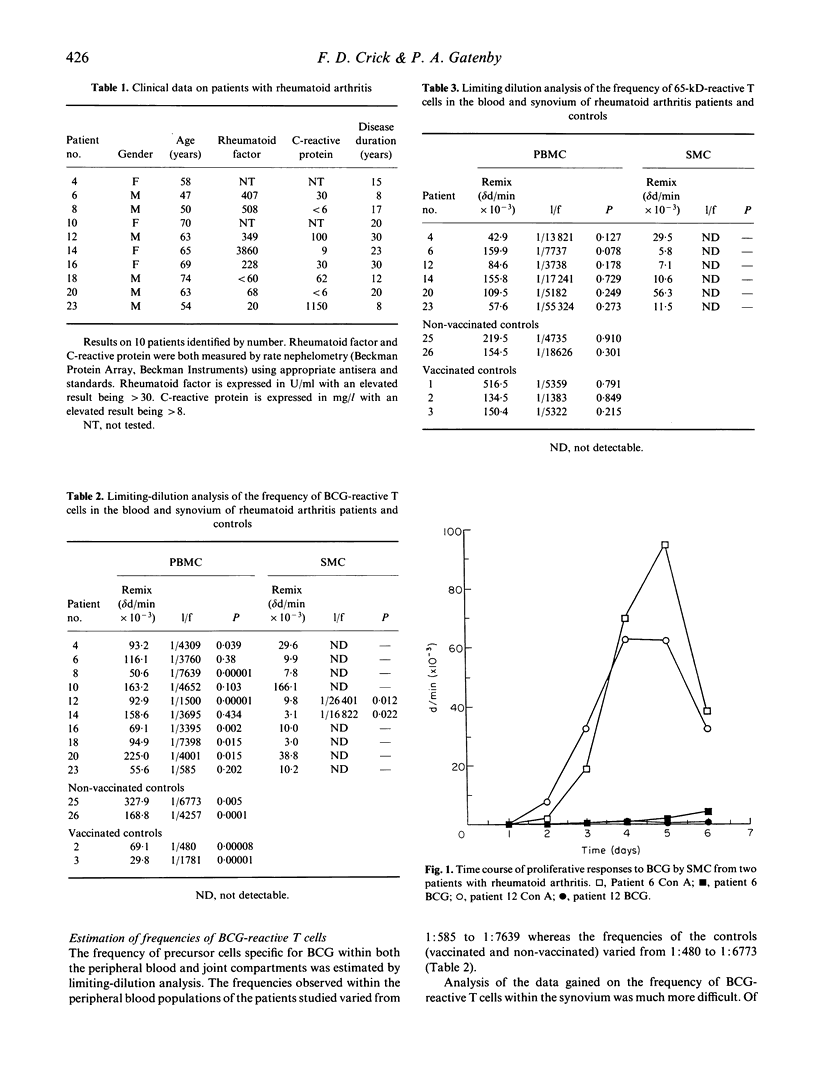
Limiting-dilution analysis (LDA) was used to quantify the frequency of Mycobacterium bovis BCG- and 65-kD-reactive T cells in paired samples of peripheral blood and synovial tissue from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The frequency of BCG-reactive T cells detected in the peripheral blood of patients ranged from 1/585 to 1/7639 versus a control frequency range of 1/480 to 1/6773. The frequency of such cells in the synovium was found to be much lower than it was in peripheral blood; in fact, in 80% of patients synovial BCG-reactive T cells were not detected. The frequency of 65-kD-reactive cells in the peripheral blood of each individual was lower than the frequency of BCG-reactive cells (range 1/3738 to 1/55,324), as would be expected. However, no synovial 65-kD-reactive cells were detected from any of the patients studied. The LDA assay for the 65-kD antigen was consistent with the single hit model, that for BCG was not. The relatively high proportion of mycobacterial-reactive precursors seen in the peripheral blood of non-vaccinated individuals may reflect a population of cells induced either by natural environmental exposure to mycobacteria or, given the highly conserved nature of heat shock proteins across phylogeny, by some other infection. The results also suggest that the frequent finding of reactivity to proteins such as the 65-kD heat shock protein contained within BCG may not be a generalized phenomenon in rheumatoid synovium.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton W. J., Hellqvist L., Basten A., Raison R. L. Mycobacterium leprae antigens involved in human immune responses. I. Identification of four antigens by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4171–4177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmester G. R., Jahn B., Hain N., Strobel G., Kalden J. R. T cell regulation and T cell clones in relation to synovial inflammation. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1989;11(3):259–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00197306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cush J. J., Lipsky P. E. Phenotypic analysis of synovial tissue and peripheral blood lymphocytes isolated from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Oct;31(10):1230–1238. doi: 10.1002/art.1780311003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Graeff-Meeder E. R., van der Zee R., Rijkers G. T., Schuurman H. J., Kuis W., Bijlsma J. W., Zegers B. J., van Eden W. Recognition of human 60 kD heat shock protein by mononuclear cells from patients with juvenile chronic arthritis. Lancet. 1991 Jun 8;337(8754):1368–1372. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)93057-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann M., Londei M., Leech Z., Brennan F., Savill C., Maini R. N. Analysis of T cell clones in rheumatoid arthritis. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1988;10(2-3):157–167. doi: 10.1007/BF01857221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston J. S., Life P. F., Jenner P. J., Colston M. J., Bacon P. A. Recognition of a mycobacteria-specific epitope in the 65-kD heat-shock protein by synovial fluid-derived T cell clones. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):831–841. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holoshitz J., Klajman A., Drucker I., Lapidot Z., Yaretzky A., Frenkel A., van Eden W., Cohen I. R. T lymphocytes of rheumatoid arthritis patients show augmented reactivity to a fraction of mycobacteria cross-reactive with cartilage. Lancet. 1986 Aug 9;2(8502):305–309. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holoshitz J., Koning F., Coligan J. E., De Bruyn J., Strober S. Isolation of CD4- CD8- mycobacteria-reactive T lymphocyte clones from rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):226–229. doi: 10.1038/339226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H. Heat shock proteins and the immune response. Immunol Today. 1990 Apr;11(4):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90050-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. R., Bal V., Mendez-Samperio P., Mehlert A., So A., Rothbard J., Jindal S., Young R. A., Young D. B. Stress proteins may provide a link between the immune response to infection and autoimmunity. Int Immunol. 1989;1(2):191–196. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.2.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Life P. F., Viner N. J., Bacon P. A., Gaston J. S. Synovial fluid antigen-presenting cells unmask peripheral blood T cell responses to bacterial antigens in inflammatory arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Feb;79(2):189–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05177.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahanonda R., Seymour G. J., Powell L. W., Good M. F., Halliday J. W. Limit dilution analysis of peripheral blood T lymphocytes specific to periodontopathic bacteria. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Feb;75(2):245–251. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munk M. E., Schoel B., Modrow S., Karr R. W., Young R. A., Kaufmann S. H. T lymphocytes from healthy individuals with specificity to self-epitopes shared by the mycobacterial and human 65-kilodalton heat shock protein. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):2844–2849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope R. M., Pahlavani M. A., LaCour E., Sambol S., Desai B. V. Antigenic specificity of rheumatoid synovial fluid lymphocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Nov;32(11):1371–1380. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780321105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quayle A., Kjeldsen-Kragh J., Førre O., Waalen K., Sioud M., Kalvenes C., Natvig J. B. Immunoregulatory T cell subsets and T cell activation in rheumatoid arthritis. A need for analysis on the clonal and molecular level. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1989;11(3):273–287. doi: 10.1007/BF00197307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees A., Scoging A., Mehlert A., Young D. B., Ivanyi J. Specificity of proliferative response of human CD8 clones to mycobacterial antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Dec;18(12):1881–1887. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Res P. C., Schaar C. G., Breedveld F. C., van Eden W., van Embden J. D., Cohen I. R., de Vries R. R. Synovial fluid T cell reactivity against 65 kD heat shock protein of mycobacteria in early chronic arthritis. Lancet. 1988 Aug 27;2(8609):478–480. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90123-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxon A., Feldhaus J., Robins R. A. Single step separation of human T and B cells using AET treated srbc rosettes. J Immunol Methods. 1976;12(3-4):285–288. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoenfeld Y., Isenberg D. A. Mycobacteria and autoimmunity. Immunol Today. 1988 Jun;9(6):178–182. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91294-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taswell C. Limiting dilution assays for the determination of immunocompetent cell frequencies. I. Data analysis. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1614–1619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermann J., Pabst R. Lymphocyte subsets in the blood: a diagnostic window on the lymphoid system? Immunol Today. 1990 Nov;11(11):406–410. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90160-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield J. B. Stress proteins, arthritis, and autoimmunity. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Dec;32(12):1497–1504. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780321202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Bloom B. R., Grosskinsky C. M., Ivanyi J., Thomas D., Davis R. W. Dissection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens using recombinant DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2583–2587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eden W., Hogervorst E. J., Hensen E. J., van der Zee R., van Embden J. D., Cohen I. R. A cartilage-mimicking T-cell epitope on a 65K mycobacterial heat-shock protein: adjuvant arthritis as a model for human rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;145:27–43. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74594-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eden W., Holoshitz J., Nevo Z., Frenkel A., Klajman A., Cohen I. R. Arthritis induced by a T-lymphocyte clone that responds to Mycobacterium tuberculosis and to cartilage proteoglycans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5117–5120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eden W., Thole J. E., van der Zee R., Noordzij A., van Embden J. D., Hensen E. J., Cohen I. R. Cloning of the mycobacterial epitope recognized by T lymphocytes in adjuvant arthritis. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):171–173. doi: 10.1038/331171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


