Abstract
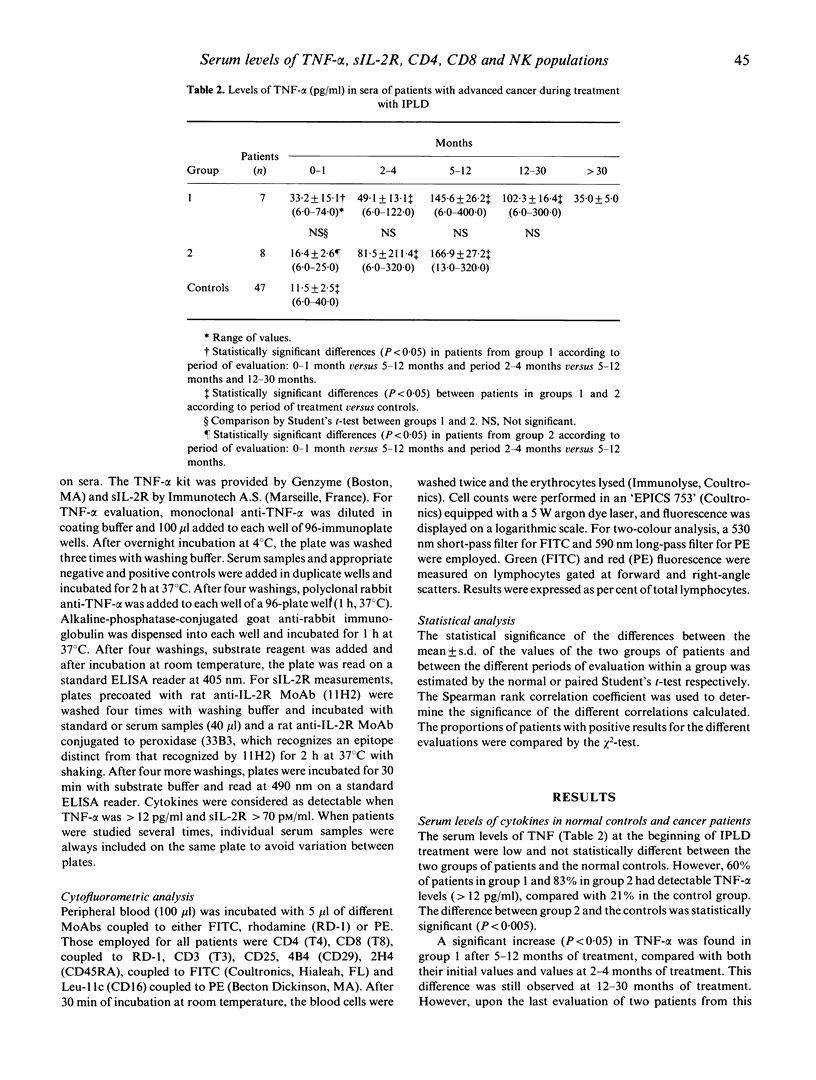
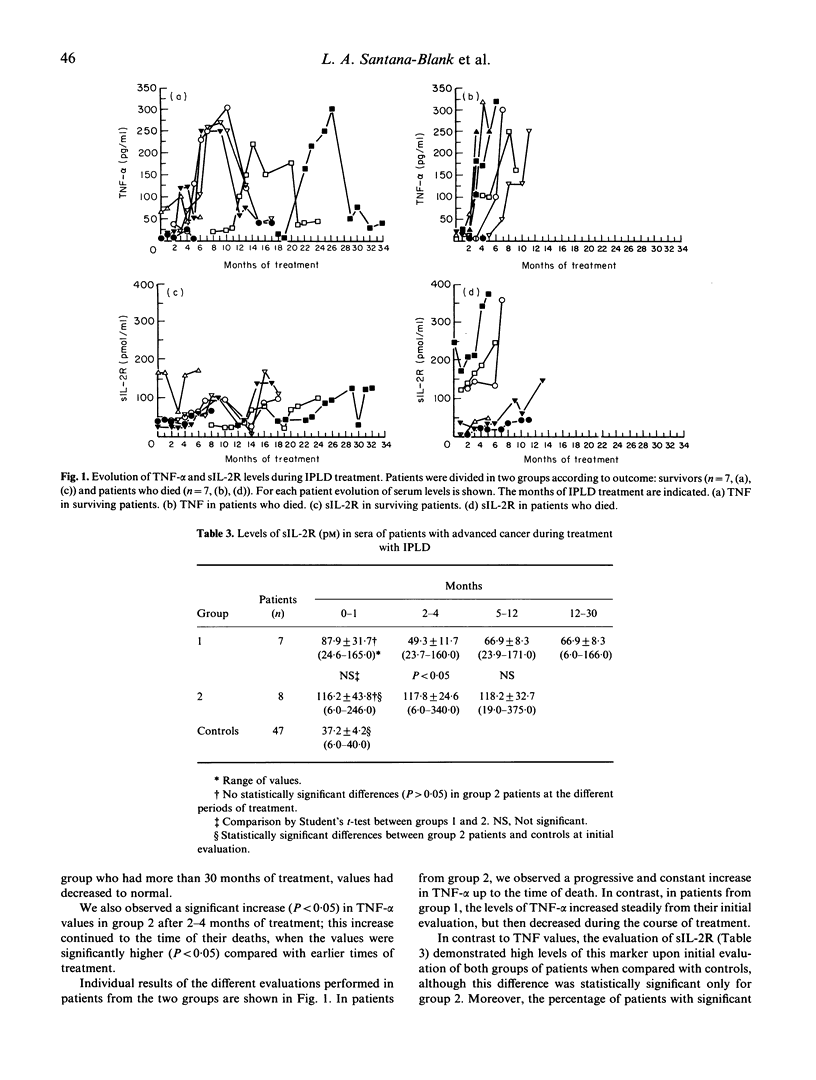
The purpose of this study was to evaluate serum levels of TNF-alpha, sIL-2R and distribution of peripheral leucocyte subsets in patients with advanced neoplastic disease undergoing IPLD treatment. Fifteen cancer patients with evidence of persistent disease were further divided in two groups according to outcome at the end of the period of clinical evaluation: group 1 patients were still alive and group 2 patients had died. Our results show: (i) an increase in the initial level of TNF-alpha in both groups; (ii) a decrease in TNF-alpha levels during the follow up of group 1 patients; (iii) a significant increase in serum levels of sIL-2R in patients in group 2 compared with those in group 1; (iv) a progressive and constant increase in TNF-alpha levels in group 2; (v) a decrease in CD4+CD45RA+ subpopulation in both groups; (vi) an increase in CD25+ cells; (vii) an increase in CD4+, CD4+CD45RA+ and CD25+ cells during the follow up of group 2 patients. The data generated here form the basis for further investigations on the use of IPLD as a single agent and in combination with other biological response modifiers in cancer patients.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balkwill F., Osborne R., Burke F., Naylor S., Talbot D., Durbin H., Tavernier J., Fiers W. Evidence for tumour necrosis factor/cachectin production in cancer. Lancet. 1987 Nov 28;2(8570):1229–1232. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91850-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belkin M., Schwartz M. New biological phenomena associated with laser radiation. Health Phys. 1989 May;56(5):687–690. doi: 10.1097/00004032-198905000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillman R. O., Koziol J. A., Zavanelli M. I., Beauregard J. C., Halliburton B. L., Glassy M. C., Royston I. Immunoincompetence in cancer patients. Assessment by in vitro stimulation tests and quantification of lymphocyte subpopulations. Cancer. 1984 Apr 1;53(7):1484–1491. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19840401)53:7<1484::aid-cncr2820530710>3.0.co;2-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karu T. Photobiology of low-power laser effects. Health Phys. 1989 May;56(5):691–704. doi: 10.1097/00004032-198905000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloster B. E., John P. A., Miller L. E., Rubin L. A., Nelson D. L., Blair D. C., Tomar R. H. Soluble interleukin 2 receptors are elevated in patients with AIDS or at risk of developing AIDS. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Dec;45(3):440–446. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(87)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp W., Rieber P., Dörken B., Schmidt R. E., Stein H., vd Borne A. E. Towards a better definition of human leucocyte surface molecules. Immunol Today. 1989 Aug;10(8):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90135-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komp D. M., McNamara J., Buckley P. Elevated soluble interleukin-2 receptor in childhood hemophagocytic histiocytic syndromes. Blood. 1989 Jun;73(8):2128–2132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lissoni P., Barni S., Rovelli F., Rescaldani R., Rizzo V., Biondi A., Tancini G. Correlation of serum interleukin-2 levels, soluble interleukin-2 receptors and T lymphocyte subsets in cancer patients. Tumori. 1990 Feb 28;76(1):14–17. doi: 10.1177/030089169007600103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkovský M., Sondel P. M., Strober W., Dalgleish A. G. The interleukins in acquired disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Nov;74(2):151–161. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor M. S., Stamp G. W., Balkwill F. R. Investigation of cytokine gene expression in human colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 1990 Jul 15;50(14):4436–4440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Nedwin G. E., Hayflick J. S., Seeburg P. H., Derynck R., Palladino M. A., Kohr W. J., Aggarwal B. B., Goeddel D. V. Human tumour necrosis factor: precursor structure, expression and homology to lymphotoxin. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):724–729. doi: 10.1038/312724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillai R., Balaram P., Nair B. S., Hareendran N. K., Padmanabhan T. K., Nair M. K. Lymphocyte subset distribution after radiation therapy for cancer of the uterine cervix. Possible prognostic implications and correlation with disease course. Cancer. 1991 Apr 15;67(8):2071–2078. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19910415)67:8<2071::aid-cncr2820670811>3.0.co;2-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. A., Jay G., Nelson D. L. The released interleukin 2 receptor binds interleukin 2 efficiently. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 15;137(12):3841–3844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. A., Kurman C. C., Fritz M. E., Biddison W. E., Boutin B., Yarchoan R., Nelson D. L. Soluble interleukin 2 receptors are released from activated human lymphoid cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3172–3177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. A., Nelson D. L. The soluble interleukin-2 receptor: biology, function, and clinical application. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Oct 15;113(8):619–627. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-113-8-619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saarinen U. M., Koskelo E. K., Teppo A. M., Siimes M. A. Tumor necrosis factor in children with malignancies. Cancer Res. 1990 Feb 1;50(3):592–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato N., Goto T., Haranaka K., Satomi N., Nariuchi H., Mano-Hirano Y., Sawasaki Y. Actions of tumor necrosis factor on cultured vascular endothelial cells: morphologic modulation, growth inhibition, and cytotoxicity. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Jun;76(6):1113–1121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S., Saha K., Shinghal R. N., Malik G. B. Serum soluble interleukin-2 (IL-2) receptor levels in women with breast carcinoma and its correlation with IL-2 receptor expression on blood lymphocytes and lymphocytic infiltration within the tumour. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1991;33(3):198–202. doi: 10.1007/BF01756142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman B. J., Aggarwal B. B., Hass P. E., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Shepard H. M. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha: effects on proliferation of normal and transformed cells in vitro. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):943–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3933111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Roenn J., Harris J. E., Braun D. P. Suppressor cell function in solid tumor cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 1987 Jan;5(1):150–159. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1987.5.1.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


