Abstract
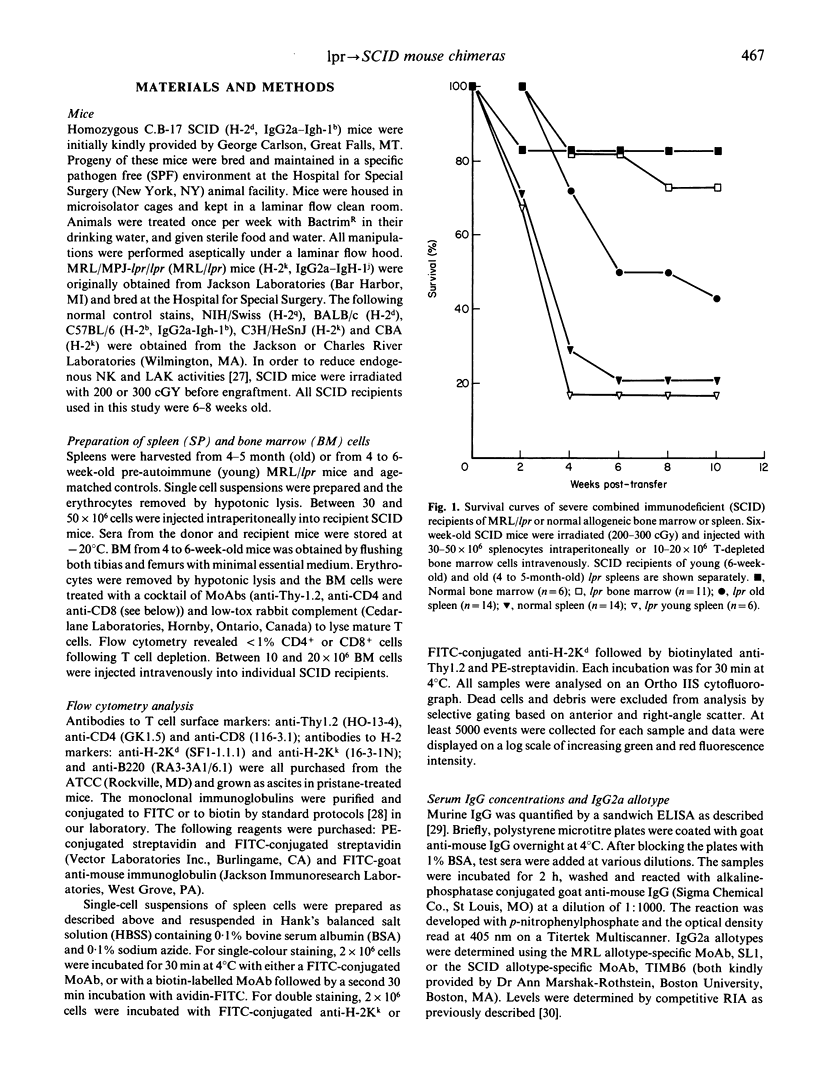
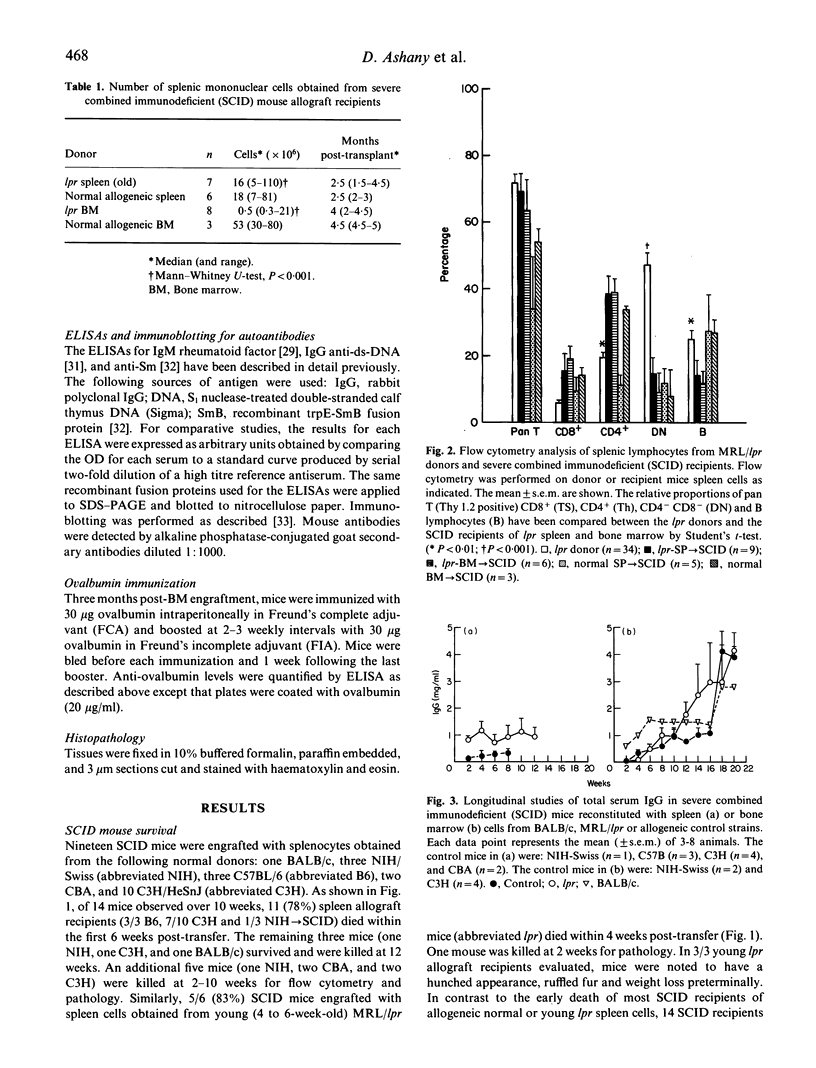
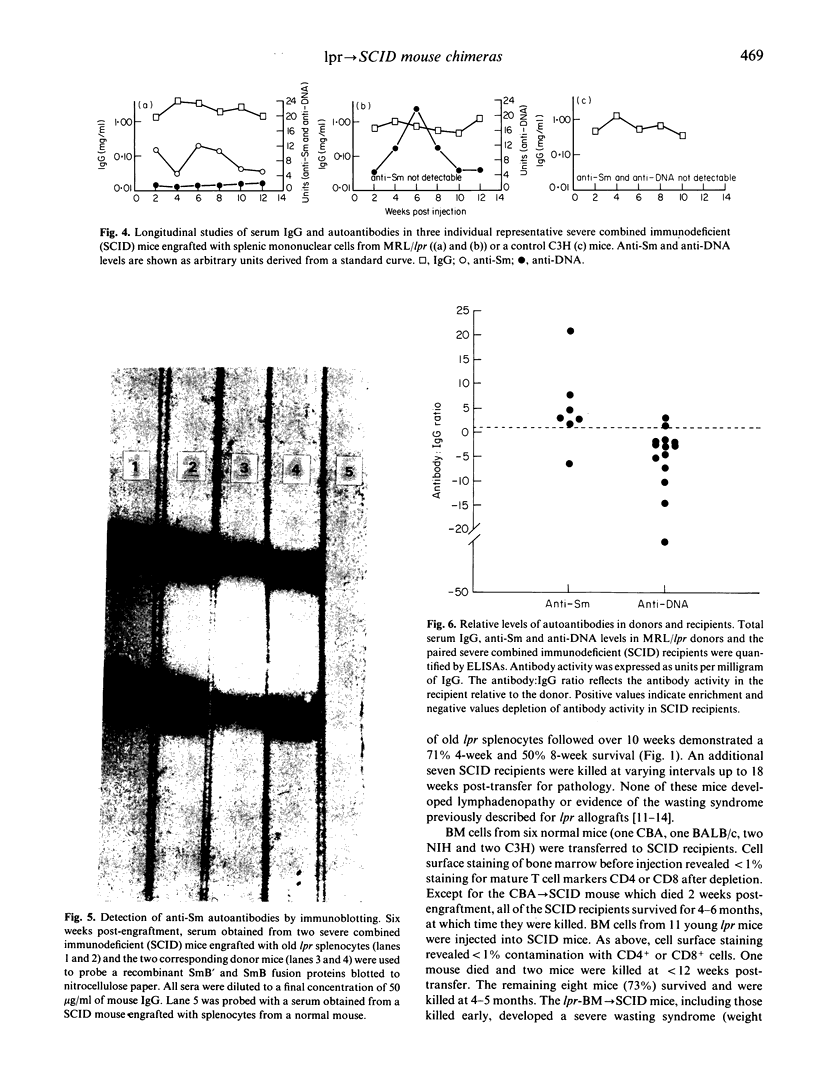
MRL/lpr (lpr) mice spontaneously develop a lupus-like illness as well as massive lymphadenopathy. Attempts to transfer autoimmunity by adoptive transfer or radiation bone marrow chimeras have been unsuccessful. Since severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mice have been engrafted with human and rat xenografts without apparent graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), we subjected SCID mice to low-dose irradiation and reconstituted the mice with spleen cells from young or old lpr mice or with lpr bone marrow. Fourteen out of twenty (70%) of SCID mice engrafted with spleen cells from old lpr mice produced autoantibodies (anti-DNA and anti-Sm) without evidence of the severe lymphoid atrophy previously described for lpr spleen-->+/+ chimeras. SCID mice engrafted with spleen cells from young lpr mice developed acute GVHD and 5/6 (83%) died within 4 weeks post-transfer. Although 8/11 (73%) of lpr-->SCID bone marrow allografts survived for at least 4 months, these mice developed a wasting disease characterized by lymphoid atrophy and fibrosis without the production of autoantibodies. None of the lpr-->SCID grafts resulted in the transfer of double negative T cells or the lymphoproliferative syndrome characteristic of MRL/lpr mice. These findings indicate that SCID mice can be engrafted with splenocytes from old MRL/lpr mice and that B cells continue to secrete autoantibodies for several months in the SCID recipients. This study also demonstrates that, unlike i.p. transplant of xenogeneic cells, acute GVHD is a consistent feature of i.p. transplants of normal allogeneic mononuclear cells into SCID mice.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. D., Marshall J. D., Roths J. B., Sidman C. L. Bone marrow transplantation from mutant lpr/lpr mice. Functional abnormalities rather than alloantigenic differences appear to determine the development of a graft-vs.-host-like syndrome. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Sep;20(9):2057–2066. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. D., Marshall J. D., Roths J. B., Sidman C. L. Differences defined by bone marrow transplantation suggest that lpr and gld are mutations of genes encoding an interacting pair of molecules. J Exp Med. 1990 Nov 1;172(5):1367–1375. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.5.1367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter B. J., Bach F. H. Cellular basis of the proliferative response of human T cells to mouse xenoantigens. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):333–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashany D., Hines J., Gharavi A., Mouradian J., Elkon K. B. Analysis of autoantibody production in SCID-systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) chimeras. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Apr;88(1):84–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb03043.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boers M., Dijkmans B. A., Breedveld F. C., Camps J. A., Chang P. C., van Brummelen P., Pauwels E. K., Cats A. Subclinical renal dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Jan;33(1):95–101. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonfa E., Marshak-Rothstein A., Weissbach H., Brot N., Elkon K. Frequency and epitope recognition of anti-ribosome P antibodies from humans with systemic lupus erythematosus and MRL/lpr mice are similar. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3434–3437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonfa E., Parnassa A. P., Rhoads D. D., Roufa D. J., Wool I. G., Elkon K. B. Antiribosomal S10 antibodies in humans and MRL/lpr mice with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Oct;32(10):1252–1261. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780321010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma G. C., Custer R. P., Bosma M. J. A severe combined immunodeficiency mutation in the mouse. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):527–530. doi: 10.1038/301527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma G. C., Davisson M. T., Ruetsch N. R., Sweet H. O., Shultz L. D., Bosma M. J. The mouse mutation severe combined immune deficiency (scid) is on chromosome 16. Immunogenetics. 1989;29(1):54–57. doi: 10.1007/BF02341614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon M. J., Pisa P., Fox R. I., Cooper N. R. Epstein-Barr virus induces aggressive lymphoproliferative disorders of human B cell origin in SCID/hu chimeric mice. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1333–1337. doi: 10.1172/JCI114573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesson M. H., Rudolphi A., Tscherning T., Reimann J. CD3+ T cells in severe combined immunodeficiency (scid) mice. IV. Graft-vs.-host resistance of H-2d scid mice to intravenous injection of allogeneic H-2b (C57BL/6) spleen cells. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Sep;21(9):2057–2062. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorshkind K., Pollack S. B., Bosma M. J., Phillips R. A. Natural killer (NK) cells are present in mice with severe combined immunodeficiency (scid). J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3798–3801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchosal M. A., McConahey P. J., Robinson C. A., Dixon F. J. Transfer of human systemic lupus erythematosus in severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):985–988. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont F. J. Stimulation of murine T cells via the Ly-6C antigen: lack of proliferative response in aberrant T cells from lpr/lpr and gld/gld mice despite high Ly-6C antigen expression. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4106–4113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. A., Tan E. M., Dixon F. J. Presence of anti-Sm reactivity in autoimmune mouse strains. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):582–587. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkon K. B., Gharavi A. E., Patel B. M., Hughes G. R., Frankel A. IgA and IgM rheumatoid factors in serum, saliva and other secretions: relationship to immunoglobulin ratios in systemic sicca syndrome and rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Apr;52(1):75–84. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkon K. B., Hines J. J., Chu J. L., Parnassa A. Epitope mapping of recombinant HeLa SmB and B' peptides obtained by the polymerase chain reaction. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 15;145(2):636–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara M., Kariyone A. One-way occurrence of graft-versus-host disease in bone marrow chimaeras between congenic MRL mice. Immunology. 1984 Oct;53(2):251–256. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulop G. M., Phillips R. A. The scid mutation in mice causes a general defect in DNA repair. Nature. 1990 Oct 4;347(6292):479–482. doi: 10.1038/347479a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharavi A. E., Harris E. N., Lockshin M. D., Hughes G. R., Elkon K. B. IgG subclass and light chain distribution of anticardiolipin and anti-DNA antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1988 Apr;47(4):286–290. doi: 10.1136/ard.47.4.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharavi A. E., Mellors R. C., Elkon K. B. IgG anti-cardiolipin antibodies in murine lupus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Nov;78(2):233–238. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Conjugation of antibodies with fluorochromes: modifications to the standard methods. J Immunol Methods. 1976;13(3-4):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greiner D. L., Shultz L. D., Rossini A. A., Mordes J. P., Handler E. S., Rajan T. V. Recapitulation of normal and abnormal BB rat immune system development in scid mouse/rat lymphohemopoietic chimeras. J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;88(2):717–719. doi: 10.1172/JCI115359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hines J. J., Weissbach H., Brot N., Elkon K. Anti-P autoantibody production requires P1/P2 as immunogens but is not driven by exogenous self-antigen in MRL mice. J Immunol. 1991 May 15;146(10):3386–3395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell C. D., Yoder T., Claman H. N., Vierling J. M. Hepatic homing of mononuclear inflammatory cells isolated during murine chronic graft-vs-host disease. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 15;143(2):476–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotzin B. L., Babcock S. K., Herron L. R. Deletion of potentially self-reactive T cell receptor specificities in L3T4-, Lyt-2- T cells of lpr mice. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):2221–2229. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.2221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macht L., Fukuma N., Leader K., Sarsero D., Pegg C. A., Phillips D. I., Yates P., McLachlan S. M., Elson C., Rees Smith B. Severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice: a model for investigating human thyroid autoantibody synthesis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Apr;84(1):34–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb08120.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malynn B. A., Blackwell T. K., Fulop G. M., Rathbun G. A., Furley A. J., Ferrier P., Heinke L. B., Phillips R. A., Yancopoulos G. D., Alt F. W. The scid defect affects the final step of the immunoglobulin VDJ recombinase mechanism. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):453–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune J. M., Namikawa R., Kaneshima H., Shultz L. D., Lieberman M., Weissman I. L. The SCID-hu mouse: murine model for the analysis of human hematolymphoid differentiation and function. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1632–1639. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Gulizia R. J., Baird S. M., Wilson D. B. Transfer of a functional human immune system to mice with severe combined immunodeficiency. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):256–259. doi: 10.1038/335256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park C. L., Balderas R. S., Fieser T. M., Slack J. H., Prud'Homme G. J., Dixon F. J., Theofilopoulos A. N. Isotypic profiles and other fine characteristics of immune responses to exogenous thymus-dependent and -independent antigens by mice with lupus syndromes. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2161–2167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins D. L., Michaelson J., Glaser R. M., Marshak-Rothstein A. Selective elimination of non-lpr lymphoid cells in mice undergoing lpr-mediated graft-vs-host disease. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1406–1413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins D. L., Michaelson J., Marshak-Rothstein A. The lpr gene is associated with resistance to engraftment by lymphoid but not erythroid stem cells from normal mice. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):466–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisetsky D. S., McCarty G. A., Peters D. V. Mechanisms of autoantibody production in autoimmune MRL mice. J Exp Med. 1980 Nov 1;152(5):1302–1310. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.5.1302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raveche E. S., Steinberg A. D., DeFranco A. L., Tjio J. H. Cell cycle analysis of lymphocyte activation in normal and autoimmune strains of mice. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):1219–1226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro T. J., Portanova J. P., Kotzin B. L. The contribution of L3T4+ T cells to lymphoproliferation and autoantibody production in MRL-lpr/lpr mice. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1713–1718. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler W., Weiler I. J., Schuler A., Phillips R. A., Rosenberg N., Mak T. W., Kearney J. F., Perry R. P., Bosma M. J. Rearrangement of antigen receptor genes is defective in mice with severe combined immune deficiency. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):963–972. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90695-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer P. A., Balderas R. S., McEvilly R. J., Bobardt M., Theofilopoulos A. N. Tolerance-related V beta clonal deletions in normal CD4-8-, TCR-alpha/beta + and abnormal lpr and gld cell populations. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):1869–1877. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.1869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Balderas R. S., Gozes Y., Aguado M. T., Hang L. M., Morrow P. R., Dixon F. J. Association of lpr gene with graft-vs.-host disease-like syndrome. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):1–18. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J. Murine models of systemic lupus erythematosus. Adv Immunol. 1985;37:269–390. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60342-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe-Fukunaga R., Brannan C. I., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Nagata S. Lymphoproliferation disorder in mice explained by defects in Fas antigen that mediates apoptosis. Nature. 1992 Mar 26;356(6367):314–317. doi: 10.1038/356314a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wofsy D., Hardy R. R., Seaman W. E. The proliferating cells in autoimmune MRL/lpr mice lack L3T4, an antigen on "helper" T cells that is involved in the response to class II major histocompatibility antigens. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2686–2689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wofsy D., Murphy E. D., Roths J. B., Dauphinée M. J., Kipper S. B., Talal N. Deficient interleukin 2 activity in MRL/Mp and C57BL/6J mice bearing the lpr gene. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1671–1680. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Rüedi E., Althage A., Hengartner H., Reimann G. Thymic selection of H-2-incompatible bone marrow cells in SCID mice. Differences in T help for induction of B cell IgG responses versus cytotoxic T cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Sep 1;168(3):1187–1192. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.3.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]