Abstract
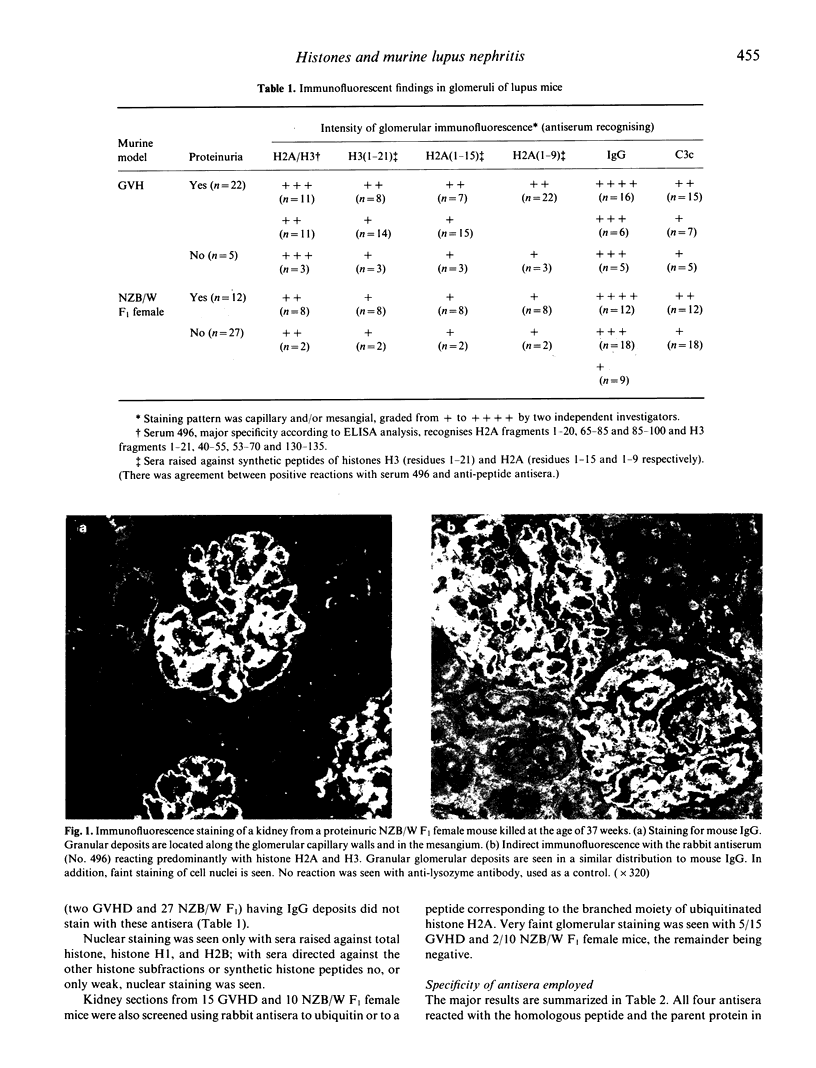
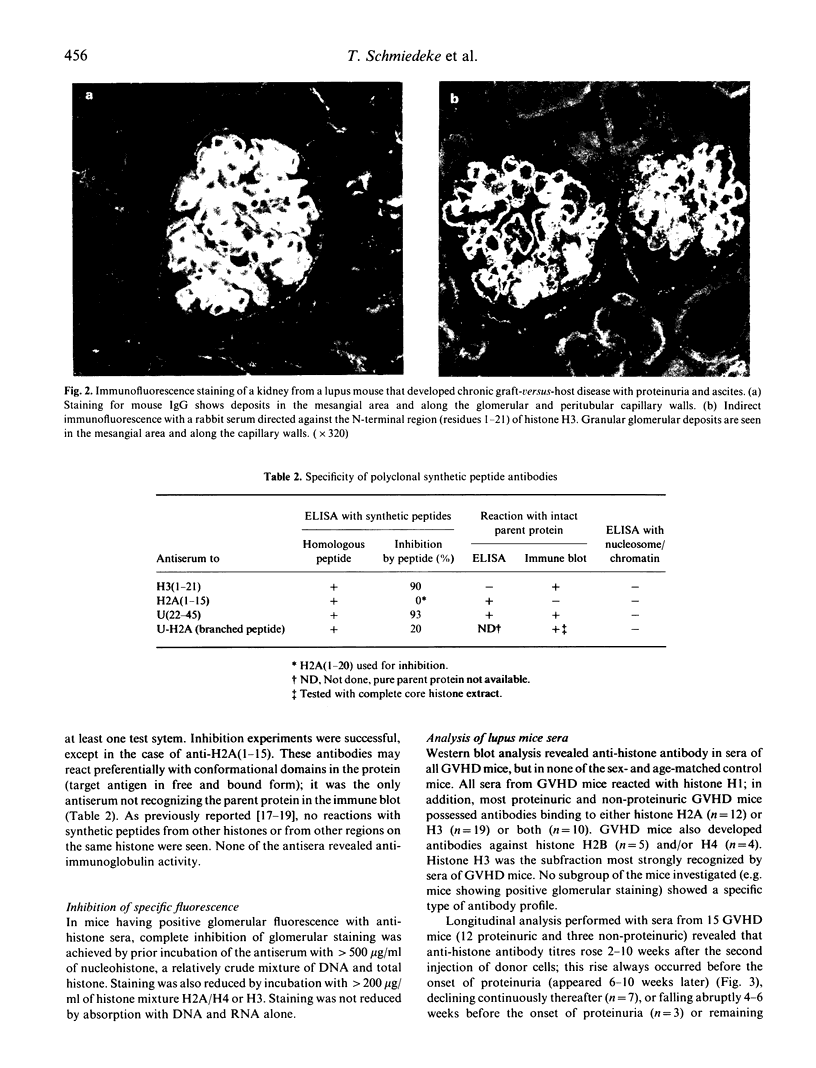
Two types of lupus mice, NZB/NZW F1 female hybrids and mice with graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), were studied. Histones H3 and H2A were detected by immunofluorescence in glomeruli of 22/22 proteinuric GVHD and 8/12 proteinuric NZB/W F1 female mice; in non-proteinuric animals, 3/5 GVHD and 2/27 NZB/W F1 female were positive. Using antibodies to histone peptides it was shown that mainly the N-terminal regions of histones H3 and H2A were exposed in glomerular deposits. Western blot analysis revealed antibodies to histone subfractions in sera of 33/34 lupus mice that developed proteinuria. This study provides evidence that histones are involved in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atanassov C., Briand J. P., Bonnier D., Van Regenmortel M. H., Muller S. New Zealand white rabbits immunized with RNA-complexed total histones develop an autoimmune-like response. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Oct;86(1):124–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05784.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkman K., Termaat R., Berden J. H., Smeenk R. J. Anti-DNA antibodies and lupus nephritis: the complexity of crossreactivity. Immunol Today. 1990 Jul;11(7):232–234. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90095-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Commerford S. L. Iodination of nucleic acids in vitro. Biochemistry. 1971 May 25;10(11):1993–2000. doi: 10.1021/bi00787a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faaber P., Rijke T. P., van de Putte L. B., Capel P. J., Berden J. H. Cross-reactivity of human and murine anti-DNA antibodies with heparan sulfate. The major glycosaminoglycan in glomerular basement membranes. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1824–1830. doi: 10.1172/JCI112508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournié G. J. Circulating DNA and lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 1988 Feb;33(2):487–497. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacques M. F., Muller S., De Murcia G., Van Regenmortel M. H., Marion C. Accessibility and structural role of histone domains in chromatin. biophysical and immunochemical studies of progressive digestion with immobilized proteases. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1990 Dec;8(3):619–641. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1990.10507832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardin J. A. The lupus autoantigens and the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Apr;29(4):457–460. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardin J. A., Thomas J. O. Antibodies to histones in systemic lupus erythematosus: localization of prominent autoantigens on histones H1 and H2B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns E. W. Studies on histones. 7. Preparative methods for histone fractions from calf thymus. Biochem J. 1964 Jul;92(1):55–59. doi: 10.1042/bj0920055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller S., Bonnier D., Thiry M., Van Regenmortel M. H. Reactivity of autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus with synthetic core histone peptides. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1989;89(2-3):288–296. doi: 10.1159/000234962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller S., Briand J. P., Van Regenmortel M. H. Presence of antibodies to ubiquitin during the autoimmune response associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8176–8180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller S., Chaix M. L., Briand J. P., Van Regenmortel M. H. Immunogenicity of free histones and of histones complexed with RNA. Mol Immunol. 1991 Jul;28(7):763–772. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(91)90119-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller S., Plaue S., Couppez M., Van Regenmortel M. H. Comparison of different methods for localizing antigenic regions in histone H2A. Mol Immunol. 1986 Jun;23(6):593–601. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaué S., Muller S., van Regenmortel M. H. A branched, synthetic octapeptide of ubiquitinated histone H2A as target of autoantibodies. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1607–1617. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portanova J. P., Arndt R. E., Kotzin B. L. Selective production of autoantibodies in graft-vs-host-induced and spontaneous murine lupus. Predominant reactivity with histone regions accessible in chromatin. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 1;140(3):755–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portanova J. P., Cheronis J. C., Blodgett J. K., Kotzin B. L. Histone autoantigens in murine lupus. Definition of a major epitope within an accessible region of chromatin. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4633–4640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumore P. M., Steinman C. R. Endogenous circulating DNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Occurrence as multimeric complexes bound to histone. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):69–74. doi: 10.1172/JCI114716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmiedeke T. M., Stöckl F. W., Weber R., Sugisaki Y., Batsford S. R., Vogt A. Histones have high affinity for the glomerular basement membrane. Relevance for immune complex formation in lupus nephritis. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):1879–1894. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.1879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D., Ward M. Rabbit antibodies to histone fractions as specific reagents for preparative and comparative studies. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 25;245(6):1261–1266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Termaat R. M., Brinkman K., Nossent J. C., Swaak A. J., Smeenk R. J., Berden J. H. Anti-heparan sulphate reactivity in sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus with renal or non-renal manifestations. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Nov;82(2):268–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05438.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Termaat R. M., Brinkman K., van Gompel F., van den Heuvel L. P., Veerkamp J. H., Smeenk R. J., Berden J. H. Cross-reactivity of monoclonal anti-DNA antibodies with heparan sulfate is mediated via bound DNA/histone complexes. J Autoimmun. 1990 Oct;3(5):531–545. doi: 10.1016/s0896-8411(05)80019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuaillon N., Martin T., Knapp A. M., Pasquali J. L., Muller S. Double reactivity of monoclonal and polyclonal rheumatoid factors for IgG and histones: mapping of binding sites by means of histone synthetic peptides and anti-Id antibodies. J Autoimmun. 1992 Feb;5(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/s0896-8411(05)80047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rappard-Van Der Veen F. M., Radaszkiewicz T., Terraneo L., Gleichmann E. Attempts at standardization of lupus-like graft-vs-host disease: inadvertent repopulation by DBA/2 spleen cells of H-2-different nonirradiated F1 mice. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2693–2701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zouali M., Fournié G. J., Thèze J. Quantitative clonal analysis of the B cell repertoire in human lupus. Cell Immunol. 1991 Mar;133(1):161–177. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90188-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]