Abstract
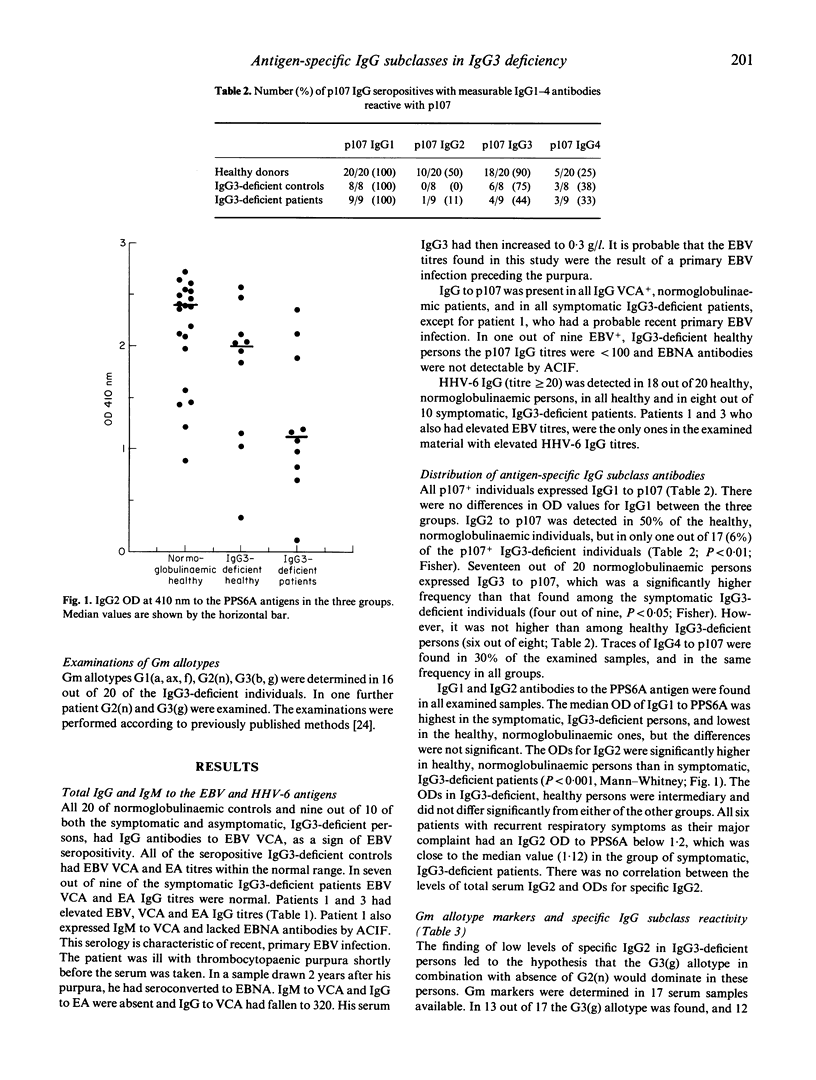
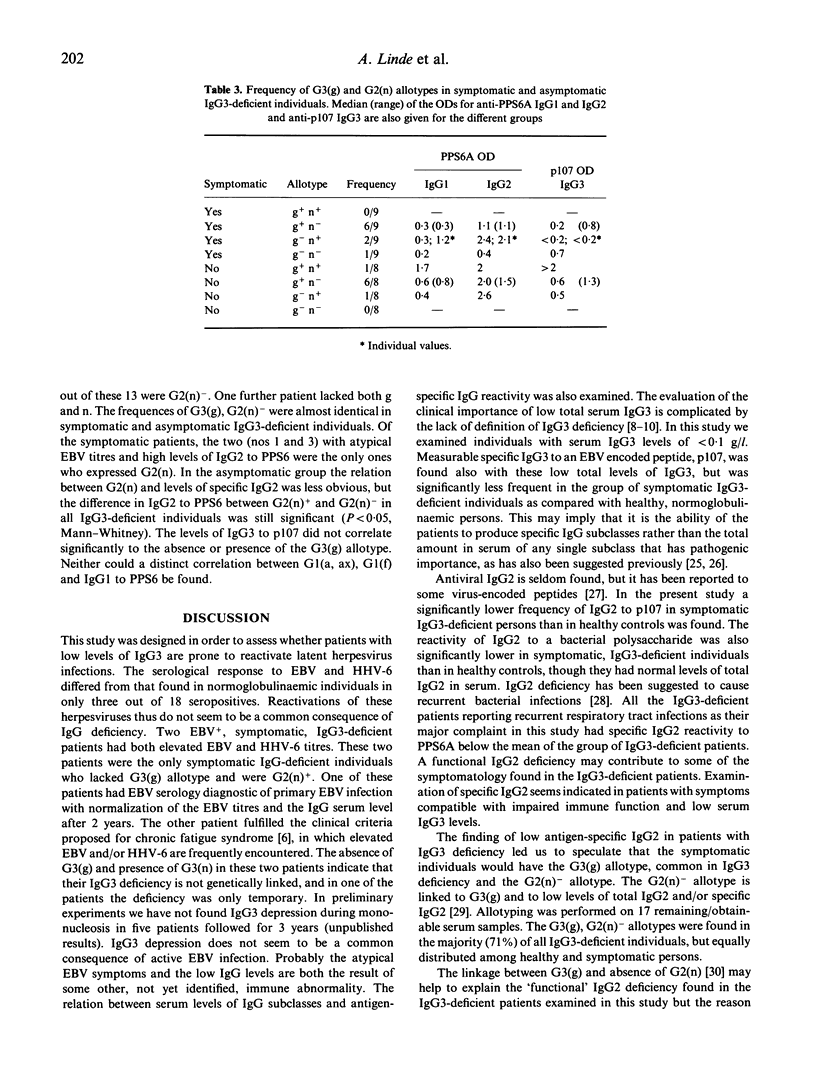
One objective of this study was to determine whether IgG3-deficient individuals have an increased frequency of reactivated herpesvirus infections. Serum titres to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and human herpesvirus-6 were examined in 10 healthy and in 10 symptomatic persons with serum IgG3 < 0.1 g/l. Atypical titres were found in 16% of the IgG3-deficient individuals. Reactivations of these viruses thus do not seem common in IgG3 deficiency. Antigen-specific IgG responses were also determined. A lowered frequency of IgG3 to an EBV-derived peptide was found only in symptomatic, IgG3-deficient individuals. Levels of IgG2 to a bacterial polysaccharide were lowered in the same group, despite normal serum levels of total IgG2. A functional IgG2 deficiency may contribute to symptoms in IgG3 deficiency. The G3(g) allotype, known to be associated with low total IgG3, dominated in IgG3-deficient persons (13/17) independently of presence or absence of symptoms. A linkage of G3(g) to the G2(n) negative allotype, associated with low IgG2, was equally common irrespective of symptoms. G3(g) and absence of G2(n) seem to be one prerequisite for most of IgG3 deficiency combined with low specific IgG2.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brüggemann M., Williams G. T., Bindon C. I., Clark M. R., Walker M. R., Jefferis R., Waldmann H., Neuberger M. S. Comparison of the effector functions of human immunoglobulins using a matched set of chimeric antibodies. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1351–1361. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl H., Linde A., Sundqvist V. A., Wahren B. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for IgG antibodies to human herpes virus 6. J Virol Methods. 1990 Sep;29(3):313–323. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(90)90058-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Sternås L., Kallin B., Alexander H., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Jörnvall H., Klein G., Lerner R. Antibodies against a synthetic peptide identify the Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4652–4656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Rowan-Kelly B., Beard L. J., Maxwell G. M. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the quantitation of human IgG subclasses using monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Nov 6;93(2):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90190-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freijd A., Hammarström L., Persson M. A., Smith C. I. Plasma anti-pneumococcal antibody activity of the IgG class and subclasses in otitis prone children. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 May;56(2):233–238. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French M. A., Harrison G. Serum IgG subclass concentrations in healthy adults: a study using monoclonal antisera. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 May;56(2):473–475. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S. IgG antibody response to polysaccharides in children with recurrent infections. Monogr Allergy. 1988;23:97–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubb R., Hallberg T., Hammarström L., Oxelius V. A., Smith C. I., Söderström R., Söderström T. Correlation between deficiency of immunoglobulin subclass G3 and Gm allotype. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1986 Oct;94(5):187–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1986.tb02110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes G. P., Kaplan J. E., Gantz N. M., Komaroff A. L., Schonberger L. B., Straus S. E., Jones J. F., Dubois R. E., Cunningham-Rundles C., Pahwa S. Chronic fatigue syndrome: a working case definition. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Mar;108(3):387–389. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-3-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutsen A. P. Patients with Igg subclass and/or selective antibody deficiency to polysaccharide antigens: initiation of a controlled clinical trial of intravenous immune globulin. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1989 Oct;84(4 Pt 2):640–647. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(89)90203-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komaroff A. L. Chronic fatigue syndromes: relationship to chronic viral infections. J Virol Methods. 1988 Sep;21(1-4):3–10. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(88)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linde A., Andersson J., Lundgren G., Wahren B. Subclass reactivity to Epstein-Barr virus capsid antigen in primary and reactivated EBV infections. J Med Virol. 1987 Feb;21(2):109–121. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890210203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linde A., Dahl H., Wahren B., Fridell E., Salahuddin Z., Biberfeld P. IgG antibodies to human herpesvirus-6 in children and adults and in primary Epstein-Barr virus infections and cytomegalovirus infections [corrected]. J Virol Methods. 1988 Sep;21(1-4):117–123. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(88)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linde A., Fridell E., Dahl H., Andersson J., Biberfeld P., Wahren B. Effect of primary Epstein-Barr virus infection on human herpesvirus 6, cytomegalovirus, and measles virus immunoglobulin G titers. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):211–215. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.211-215.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linde A., Hammarström L., Smith C. I. IgG subclass distribution of antiviral antibodies in common variable immunodeficiency: effect of substitution therapy. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Dec;49(3):341–348. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90124-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linde A., Kallin B., Dillner J., Andersson J., Jägdahl L., Lindvall A., Wahren B. Evaluation of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays with two synthetic peptides of Epstein-Barr virus for diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):903–909. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linde A., Sundqvist V. A., Mathiesen T., Wahren B. IgG subclasses to subviral components. Monogr Allergy. 1988;23:27–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linde G. A., Granström M., Orvell C. Immunoglobulin class and immunoglobulin G subclass enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays compared with microneutralization assay for serodiagnosis of mumps infection and determination of immunity. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1653–1658. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1653-1658.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathiesen T., Chiodi F., Broliden P. A., Albert J., Houghten R. A., Utter G., Wahren B., Norrby E. Analysis of a subclass-restricted HIV-1 gp41 epitope by omission peptides. Immunology. 1989 May;67(1):1–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathiesen T., Persson M. A., Sundqvist V. A., Wahren B. Neutralization capacity and antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity of separated IgG subclasses 1, 3 and 4 against herpes simplex virus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 May;72(2):211–215. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A., Skvaril F., Steinberg A. G., Van Loghem E., Terry W. D. Correlations between the concentrations of the four sub-classes of IgG and Gm Allotypes in normal human sera. J Immunol. 1972 Jan;108(1):195–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxelius V. A. IgG subclass levels in infancy and childhood. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1979 Jan;68(1):23–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1979.tb04424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson M. A. Preparation of human sera containing one single IgG subclass using affinity chromatography. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Apr 2;98(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90440-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarvas H., Rautonen N., Mäkelä O. Allotype-associated differences in concentrations of human IgG subclasses. J Clin Immunol. 1991 Jan;11(1):39–45. doi: 10.1007/BF00918793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarvas H., Rautonen N., Sipinen S., Mäkelä O. IgG subclasses of pneumococcal antibodies--effect of allotype G2m(n). Scand J Immunol. 1989 Feb;29(2):229–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skvaril F. IgG subclasses in viral infections. Monogr Allergy. 1986;19:134–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderström T., Söderström R., Bengtsson U., Björkander J., Hellstrand K., Holm J., Hanson L. A. Clinical and immunological evaluation of patients low in single or multiple IgG subclasses. Monogr Allergy. 1986;20:135–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount W. J., Kunkel H. G., Litwin S. D. Studies of the Vi (gamma-2c) subgroup of gamma-globulin. A relationship between concentration and genetic type among normal individuals. J Exp Med. 1967 Jan 1;125(1):177–190. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


