Abstract
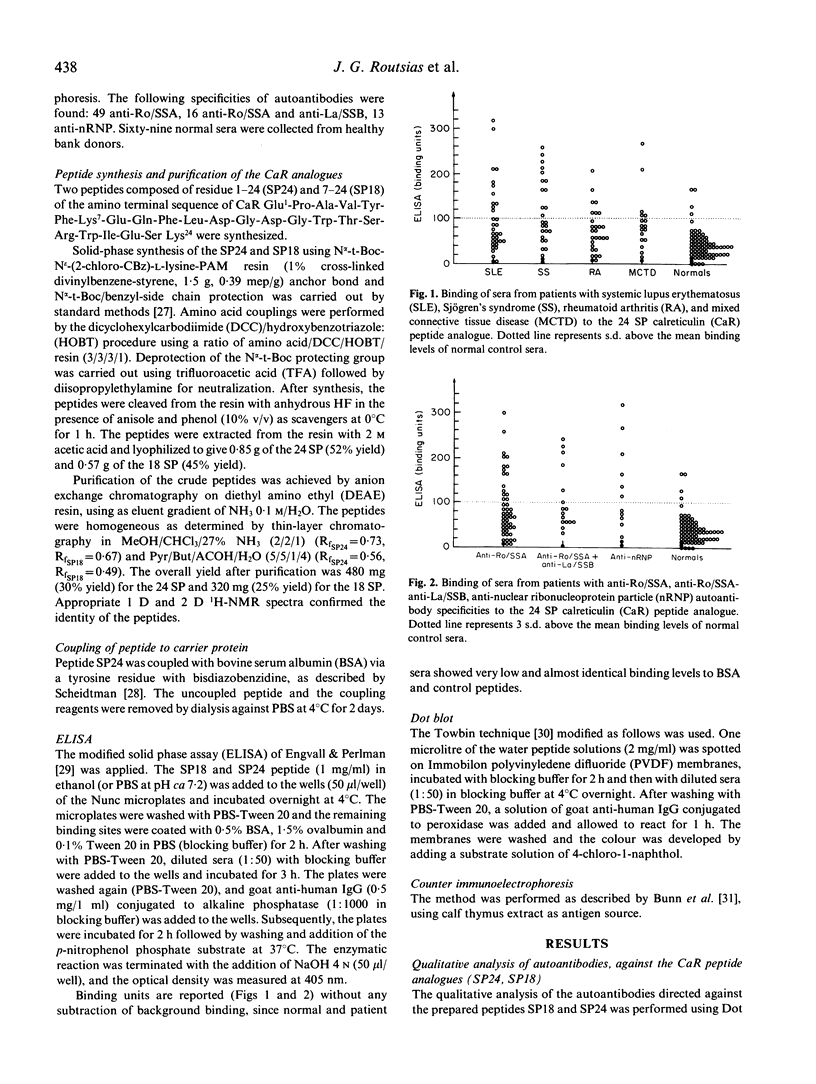
Autoantibodies in sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and onchocerciasis recognize calreticulin (CaR), a calcium-binding protein, as antigen. In this study we present the immunological properties of two synthetic peptides prepared to correspond to the 1-24 and 7-24 amino acid sequence of CaR. In contrast to information previously reported for the recombinant protein, the CaR-peptide analogues appeared immunoreactive to anti-Ro/SSA autoimmune sera. Human sera from patients with SLE, Sjögren's syndrome (SS), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), as well as mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD), demonstrated a positive autoimmune response (binding of antibodies), to the CaR-peptide analogues. These findings suggest that anti-calreticulin autoantibodies are not restricted to any disease specificity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Chetrit E., Chan E. K., Sullivan K. F., Tan E. M. A 52-kD protein is a novel component of the SS-A/Ro antigenic particle. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1560–1571. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Chetrit E., Gandy B. J., Tan E. M., Sullivan K. F. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone encoding the 60-kD component of the human SS-A/Ro ribonucleoprotein autoantigen. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1284–1292. doi: 10.1172/JCI114013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennion S. D., Ferris C., Lieu T. S., Reimer C. B., Lee L. A. IgG subclasses in the serum and skin in subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus and neonatal lupus erythematosus. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Dec;95(6):643–646. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12514311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boire G., Craft J. Biochemical and immunological heterogeneity of the Ro ribonucleoprotein particles. Analysis with sera specific for the RohY5 particle. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):270–279. doi: 10.1172/JCI114150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boire G., Craft J. Human Ro ribonucleoprotein particles: characterization of native structure and stable association with the La polypeptide. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1182–1190. doi: 10.1172/JCI114551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn C. C., Gharavi A. E., Hughes G. R. Antibodies to extractable nuclear antigens in 173 patients with DNA-binding positive SLE: an association between antibodies to ribonucleoprotein and Sm antigens observed by counterimmunoelectrophoresis. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1982 May;8(1):13–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark G., Reichlin M., Tomasi T. B., Jr Characterization of a soluble cytoplasmic antigen reactive with sera from patients with systemic lupus erythmatosus. J Immunol. 1969 Jan;102(1):117–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. H., Xi Z. J., Alderson-Lang B. H., Treves S., Volpe P. Sequence homology of a canine brain calcium-binding protein with calregulin and the human Ro/SS-A antigen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Oct 16;164(1):575–579. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91758-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher S. L., Harley J. B., Keene J. D. Molecular analysis of the 60-kDa human Ro ribonucleoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9479–9483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliegel L., Burns K., MacLennan D. H., Reithmeier R. A., Michalak M. Molecular cloning of the high affinity calcium-binding protein (calreticulin) of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21522–21528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gersten D. M., Bijwaard K. E., Law L. W., Hearing V. J. Homology of the B50 murine melanoma antigen to the Ro/SS-A antigen of human systemic lupus erythematosus and to calcium-binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Nov 14;1096(1):20–25. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(90)90007-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley J. B. Autoantibodies in Sjögren's syndrome. J Autoimmun. 1989 Aug;2(4):383–394. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(89)90167-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh Y., Rader M. D., Reichlin M. Heterogeneity of the Ro/SSA antigen and autoanti-Ro/SSA response: evidence of the four antigenically distinct forms. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Jul;81(1):45–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05289.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James J. A., Dickey W. D., Fujisaku A., O'Brien C. A., Deutscher S. L., Keene J. D., Harley J. B. Antigenicity of a recombinant Ro (SS-A) fusion protein. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Jan;33(1):102–106. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser E. T., Kézdy F. J. Secondary structures of proteins and peptides in amphiphilic environments. (A review). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1137–1143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieu T. S., Newkirk M. M., Capra J. D., Sontheimer R. D. Molecular characterization of human Ro/SS-A antigen. Amino terminal sequence of the protein moiety of human Ro/SS-A antigen and immunological activity of a corresponding synthetic peptide. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jul;82(1):96–101. doi: 10.1172/JCI113607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCauliffe D. P., Lux F. A., Lieu T. S., Sanz I., Hanke J., Newkirk M. M., Bachinski L. L., Itoh Y., Siciliano M. J., Reichlin M. Molecular cloning, expression, and chromosome 19 localization of a human Ro/SS-A autoantigen. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1379–1391. doi: 10.1172/JCI114582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCauliffe D. P., Zappi E., Lieu T. S., Michalak M., Sontheimer R. D., Capra J. D. A human Ro/SS-A autoantigen is the homologue of calreticulin and is highly homologous with onchocercal RAL-1 antigen and an aplysia "memory molecule". J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):332–335. doi: 10.1172/JCI114704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn G. J., Slobbe R. L., van Venrooij W. J. Analysis of protein--RNA interactions within Ro ribonucleoprotein complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5173–5180. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROPES M. W., BENNETT G. A., COBB S., JACOX R., JESSAR R. A. 1958 Revision of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Bull Rheum Dis. 1958 Dec;9(4):175–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichlin M., Rader M., Harley J. B. Autoimmune response to the Ro/SSA particle is directed to the human antigen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Jun;76(3):373–377. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichlin M. Significance of the Ro antigen system. J Clin Immunol. 1986 Sep;6(5):339–348. doi: 10.1007/BF00915372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rokeach L. A., Haselby J. A., Meilof J. F., Smeenk R. J., Unnasch T. R., Greene B. M., Hoch S. O. Characterization of the autoantigen calreticulin. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 1;147(9):3031–3039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. C., Irvin W. S., Tan E. M., Gould R. G., Holman H. R. Mixed connective tissue disease--an apparently distinct rheumatic disease syndrome associated with a specific antibody to an extractable nuclear antigen (ENA). Am J Med. 1972 Feb;52(2):148–159. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90064-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slobbe R. L., Pruijn G. J., Damen W. G., van der Kemp J. W., van Venrooij W. J. Detection and occurrence of the 60- and 52-kD Ro (SS-A) antigens and of autoantibodies against these proteins. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Oct;86(1):99–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05780.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. J., Koch G. L. Multiple zones in the sequence of calreticulin (CRP55, calregulin, HACBP), a major calcium binding ER/SR protein. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3581–3586. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08530.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitali C., Bombardieri S. Diagnostic criteria for Sjögren's syndrome: the state of the art. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1990 Jul-Aug;8 (Suppl 5):13–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield J. B. Stress proteins, arthritis, and autoimmunity. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Dec;32(12):1497–1504. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780321202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. The Ro small cytoplasmic ribonucleoproteins: identification of the antigenic protein and its binding site on the Ro RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1996–2000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]