Abstract
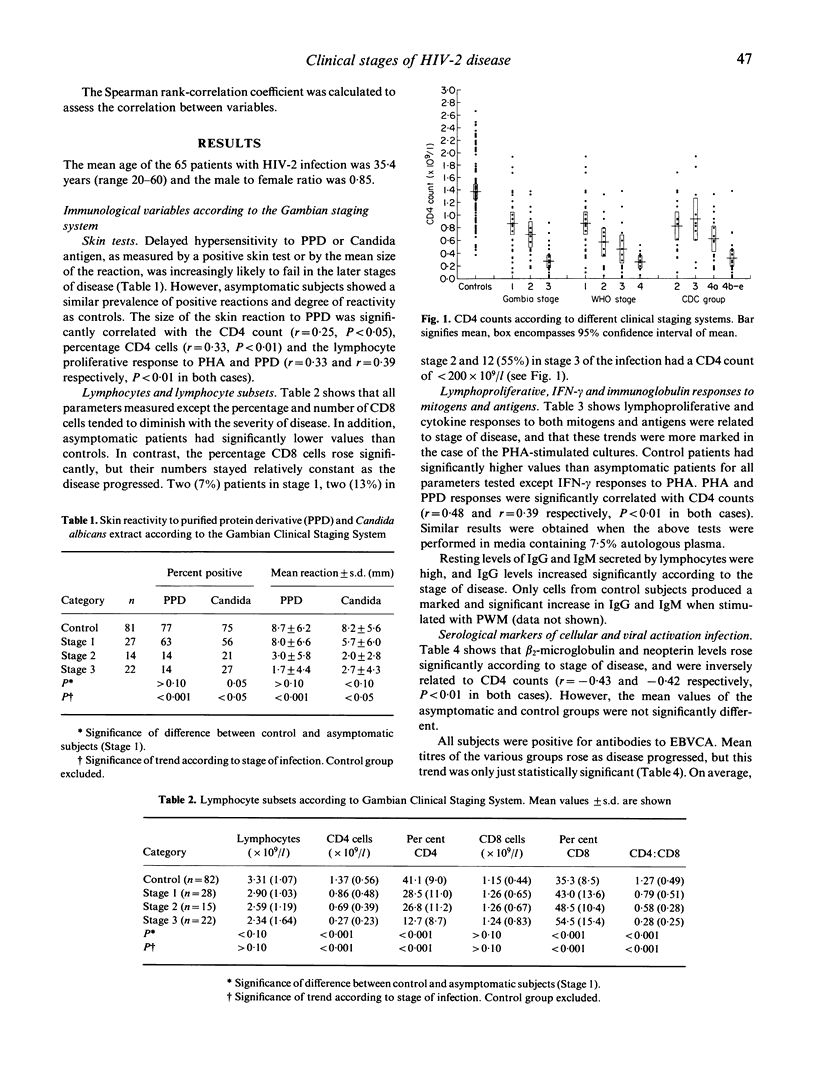
This study describes a broad spectrum of cellular and antibody-mediated immune responses found in 28 asymptomatic and 37 symptomatic Gambian patients with HIV-2 infection. It shows that these responses vary according to the stage of infection as described by three clinical staging systems. The first system was a local one based on the signs used for the WHO Bangui clinical definition of AIDS, the second, suggested by WHO, was based on a performance scale, and the third was that used by the Centre for Disease Control. Asymptomatic patients had significantly lower mean CD4 counts, lymphoproliferative and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) responses and lower IgG and IgM antibody responses to keyhole limpet haemocyanin (KLH) than controls. These measurements and the size of the skin test reaction to purified protein derivative (PPD) or Candida antigen declined significantly according to the stage of infection. Mean values of the serological markers beta 2-microglobulin and neopterin and antibody titres to Epstein-Barr virus capsid antigen (EBVCA) rose significantly according to severity of disease. The Gambian or WHO clinical staging systems, which are easy and cheap to apply, may serve as an alternative to sophisticated and expensive immunological measurements when trying to stage disease and predict prognosis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dobozin B. S., Judson F. N., Cohn D. L., Penley K. A., Rickmann P. E., Blaser M. J., Sarin P. S., Weiss S. H., Kirkpatrick C. H. The relationship of abnormalities of cellular immunity to antibodies to HTLV-III in homosexual men. Cell Immunol. 1986 Mar;98(1):156–171. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90276-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilks C. F., Brindle R. J., Otieno L. S., Simani P. M., Newnham R. S., Bhatt S. M., Lule G. N., Okelo G. B., Watkins W. M., Waiyaki P. G. Life-threatening bacteraemia in HIV-1 seropositive adults admitted to hospital in Nairobi, Kenya. Lancet. 1990 Sep 1;336(8714):545–549. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92096-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Barré-Sinoussi F., Nugeyre M. T., Danquet C., Vilmer E., Griscelli C., Brun-Veziret F., Rouzioux C., Gluckman J. C., Chermann J. C. Selective tropism of lymphadenopathy associated virus (LAV) for helper-inducer T lymphocytes. Science. 1984 Jul 6;225(4657):59–63. doi: 10.1126/science.6328660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Masur H., Edgar L. C., Whalen G., Rook A. H., Fauci A. S. Abnormalities of B-cell activation and immunoregulation in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1983 Aug 25;309(8):453–458. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198308253090803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Volkman D. J., Whalen G., Fauci A. S. In vitro antigen-induced, antigen-specific antibody production in man. Specific and polyclonal components, kinetics, and cellular requirements. J Exp Med. 1981 Oct 1;154(4):1043–1057. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.4.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Guenno B. M., Barabe P., Griffet P. A., Guiraud M., Morcillo R. J., Peghini M. E., Jean P. A., M'Baye P. S., Diallo A., Sarthou J. L. HIV-2 and HIV-1 AIDS cases in Senegal: clinical patterns and immunological perturbations. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1991;4(4):421–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lems-Van Kan P., Verspaget H. W., Peña A. S. ELISA assay for quantitative measurement of human immunoglobulins IgA, IgG, and IgM in nanograms. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Feb 25;57(1-3):51–57. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisse I. M., Poulsen A. G., Aaby P., Normark M., Kvinesdal B., Dias F., Mølbak K., Knudsen K. Immunodeficiency in HIV-2 infection: a community study from Guinea-Bissau. AIDS. 1990 Dec;4(12):1263–1266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlink R. G., Ricard D., M'Boup S., Kanki P. J., Romet-Lemonne J. L., N'Doye I., Diop K., Simpson M. A., Greco F., Chou M. J. Clinical, hematologic, and immunologic cross-sectional evaluation of individuals exposed to human immunodeficiency virus type-2 (HIV-2). AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1988 Apr;4(2):137–148. doi: 10.1089/aid.1988.4.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McChesney M. B., Oldstone M. B. Virus-induced immunosuppression: infections with measles virus and human immunodeficiency virus. Adv Immunol. 1989;45:335–380. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Rubin B. Y., Masur H., Roberts R. B. Impaired production of lymphokines and immune (gamma) interferon in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1984 Apr 5;310(14):883–889. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198404053101404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs H. D., Junker A. K., Collier A. C., Virant F. S., Handsfield H. H., Wedgwood R. J. Abnormal antibody responses in patients with persistent generalized lymphadenopathy. J Clin Immunol. 1988 Jan;8(1):57–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00915157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepin J., Morgan G., Dunn D., Gevao S., Mendy M., Gaye I., Scollen N., Tedder R., Whittle H. HIV-2-induced immunosuppression among asymptomatic West African prostitutes: evidence that HIV-2 is pathogenic, but less so than HIV-1. AIDS. 1991 Oct;5(10):1165–1172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer R. W., Chirgwin K. D., Glatt A. E., Dahdouh M. A., Landesman S. H., Suster B. HIV prevalence, immunosuppression, and drug resistance in patients with tuberculosis in an area endemic for AIDS. AIDS. 1991 Apr;5(4):399–405. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199104000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegal F. P., Lopez C., Hammer G. S., Brown A. E., Kornfeld S. J., Gold J., Hassett J., Hirschman S. Z., Cunningham-Rundles C., Adelsberg B. R. Severe acquired immunodeficiency in male homosexuals, manifested by chronic perianal ulcerative herpes simplex lesions. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1439–1444. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. D., Ohura K., Masur H., Lane H. C., Fauci A. S., Wahl S. M. Monocyte function in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Defective chemotaxis. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):2121–2128. doi: 10.1172/JCI111637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teeuwsen V. J., Logtenberg T., Siebelink K. H., Lange J. M., Goudsmit J., Uytdehaag F. G., Osterhaus A. D. Analysis of the antigen- and mitogen-induced differentiation of B lymphocytes from asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus-seropositive male homosexuals. Discrepancy between T cell-dependent and T cell-independent activation. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):2929–2935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troye-Blomberg M., Andersson G., Stoczkowska M., Shabo R., Romero P., Patarroyo M. E., Wigzell H., Perlmann P. Production of IL 2 and IFN-gamma by T cells from malaria patients in response to Plasmodium falciparum or erythrocyte antigens in vitro. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3498–3504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle H., Egboga A., Todd J., Corrah T., Wilkins A., Demba E., Morgan G., Rolfe M., Berry N., Tedder R. Clinical and laboratory predictors of survival in Gambian patients with symptomatic HIV-1 or HIV-2 infection. AIDS. 1992 Jul;6(7):685–689. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199207000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



