Abstract
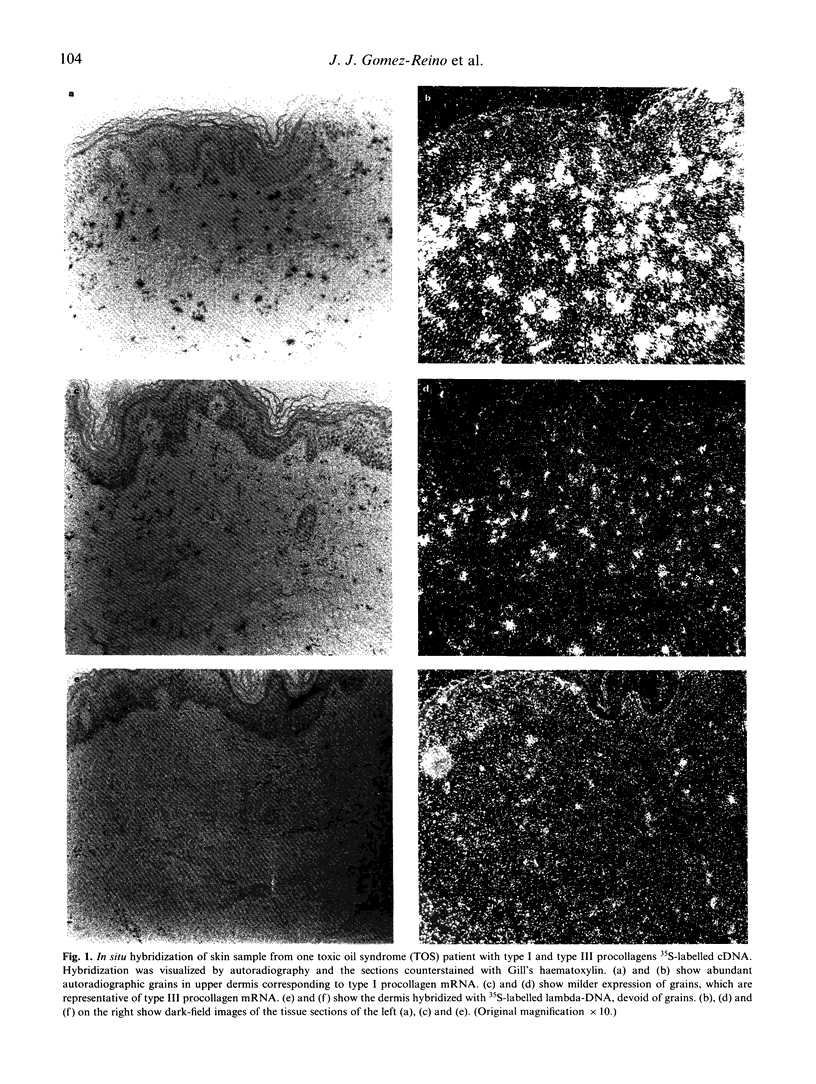
We have studied the skin and nerve fibrosis in toxic oil syndrome by in situ hybridization using specific cDNA probes for types I, III, and IV collagens. Fibroblasts with high levels of type I and III collagen mRNA were observed in biopsies from fibrotic skin areas. Similarly, type IV collagen mRNA was abundant in cells within the fibrotic process of the nerves. These results suggest that the excessive accumulation of collagen in toxic oil syndrome results from transcriptional activation of collagen genes in a subpopulation of fibroblasts.
Full text
PDF

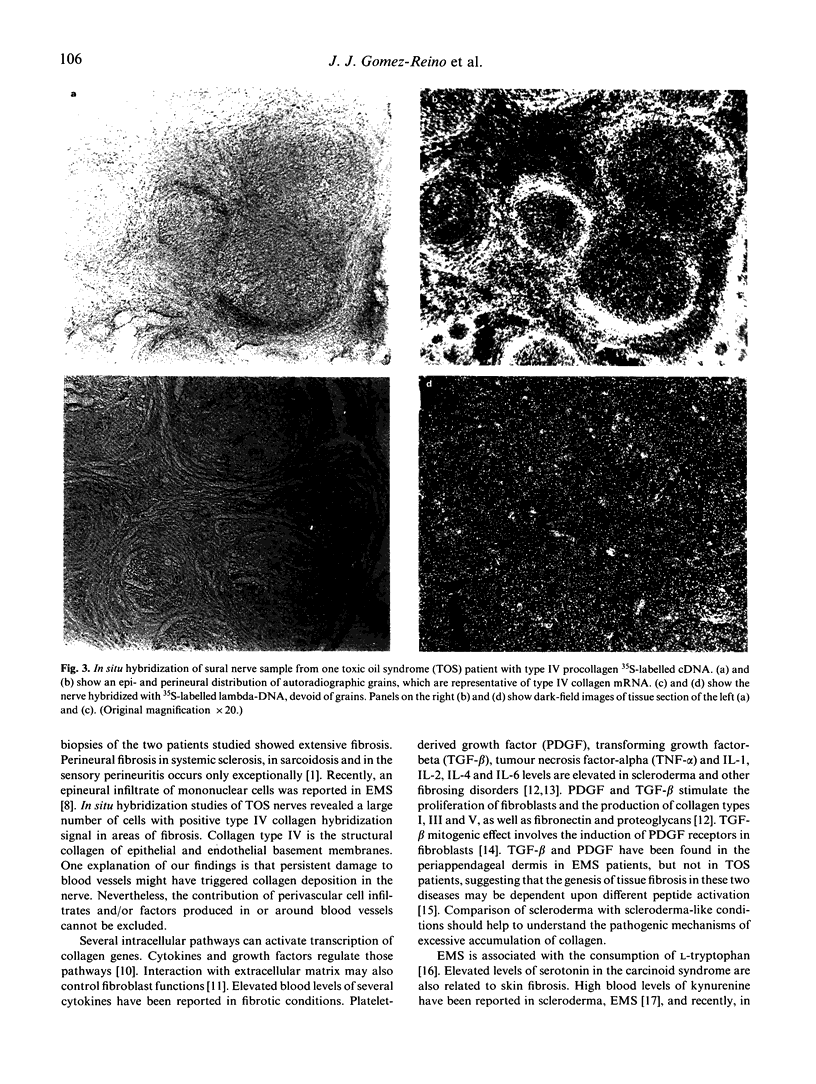

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fleischmajer R., Gay S., Meigel W. N., Perlish J. S. Collagen in the cellular and fibrotic stages of scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 May;21(4):418–428. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzman P. A., Blevins W. L., Mayer J., Greenfield B., Ting M., Gleich G. J. Association of the eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome with the ingestion of tryptophan. N Engl J Med. 1990 Mar 29;322(13):869–873. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199003293221301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa O., LeRoy E. C., Trojanowska M. Mitogenic effect of transforming growth factor beta 1 on human fibroblasts involves the induction of platelet-derived growth factor alpha receptors. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Oct;145(1):181–186. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041450124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez S. A., Feldman G., Bashey R. I., Bienkowski R., Rosenbloom J. Co-ordinate increase in the expression of type I and type III collagen genes in progressive systemic sclerosis fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 1;237(3):837–843. doi: 10.1042/bj2370837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman L. D., Seidman R. J., Gruber B. L. L-tryptophan-associated eosinophilic perimyositis, neuritis, and fasciitis. A clinicopathologic and laboratory study of 25 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 1990 Jul;69(4):187–199. doi: 10.1097/00005792-199007000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs E. J. Fibrogenic cytokines: the role of immune mediators in the development of scar tissue. Immunol Today. 1991 Jan;12(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kähäri V. M., Multimäki P., Vuorio E. Elevated pro alpha 2(I) collagen mRNA levels in cultured scleroderma fibroblasts result from an increased transcription rate of the corresponding gene. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 11;215(2):331–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80172-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kähäri V. M., Sandberg M., Kalimo H., Vuorio T., Vuorio E. Identification of fibroblasts responsible for increased collagen production in localized scleroderma by in situ hybridization. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 May;90(5):664–670. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12560826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackel A. M., DeLustro F., Harper F. E., LeRoy E. C. Antibodies to collagen in scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 May;25(5):522–531. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Tello F. J., Navas-Palacios J. J., Ricoy J. R., Gil-Martín R., Conde-Zurita J. M., Colina-Ruiz Delgado F., Tellez I., Cabello A., Madero-García S. Pathology of a new toxic syndrome caused by ingestion of adulterated oil in Spain. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1982;397(3):261–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00496569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauch C., Kreig T. Fibroblast-matrix interactions and their role in the pathogenesis of fibrosis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1990 Feb;16(1):93–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman B. W., Wigley F. M., Stair R. W. Interleukin-1, interleukin-2, interleukin-4, interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and interferon-gamma levels in sera from patients with scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Jan;35(1):67–72. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira R. S., Black C. M., Arnaiz-Villena A., Vicario J. L., Gomez-Reino J. J. Collagen antibodies in toxic oil disease. Lancet. 1985 Feb 2;1(8423):273–273. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91045-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pihlajaniemi T., Tryggvason K., Myers J. C., Kurkinen M., Lebo R., Cheung M. C., Prockop D. J., Boyd C. D. cDNA clones coding for the pro-alpha1(IV) chain of human type IV procollagen reveal an unusual homology of amino acid sequences in two halves of the carboxyl-terminal domain. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7681–7687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg M., Vuorio E. Localization of types I, II, and III collagen mRNAs in developing human skeletal tissues by in situ hybridization. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):1077–1084. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver R. M., Heyes M. P., Maize J. C., Quearry B., Vionnet-Fuasset M., Sternberg E. M. Scleroderma, fasciitis, and eosinophilia associated with the ingestion of tryptophan. N Engl J Med. 1990 Mar 29;322(13):874–881. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199003293221302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver R. M., Sutherland S. E., Carreira P., Heyes M. P. Alterations in tryptophan metabolism in the toxic oil syndrome and in the eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome. J Rheumatol. 1992 Jan;19(1):69–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varga J., Peltonen J., Uitto J., Jimenez S. Development of diffuse fasciitis with eosinophilia during L-tryptophan treatment: demonstration of elevated type I collagen gene expression in affected tissues. A clinicopathologic study of four patients. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Mar 1;112(5):344–351. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-5-344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Crombrugghe B., Vuorio T., Karsenty G. Control of type I collagen genes in scleroderma and normal fibroblasts. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1990 Feb;16(1):109–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]