Abstract
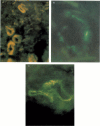
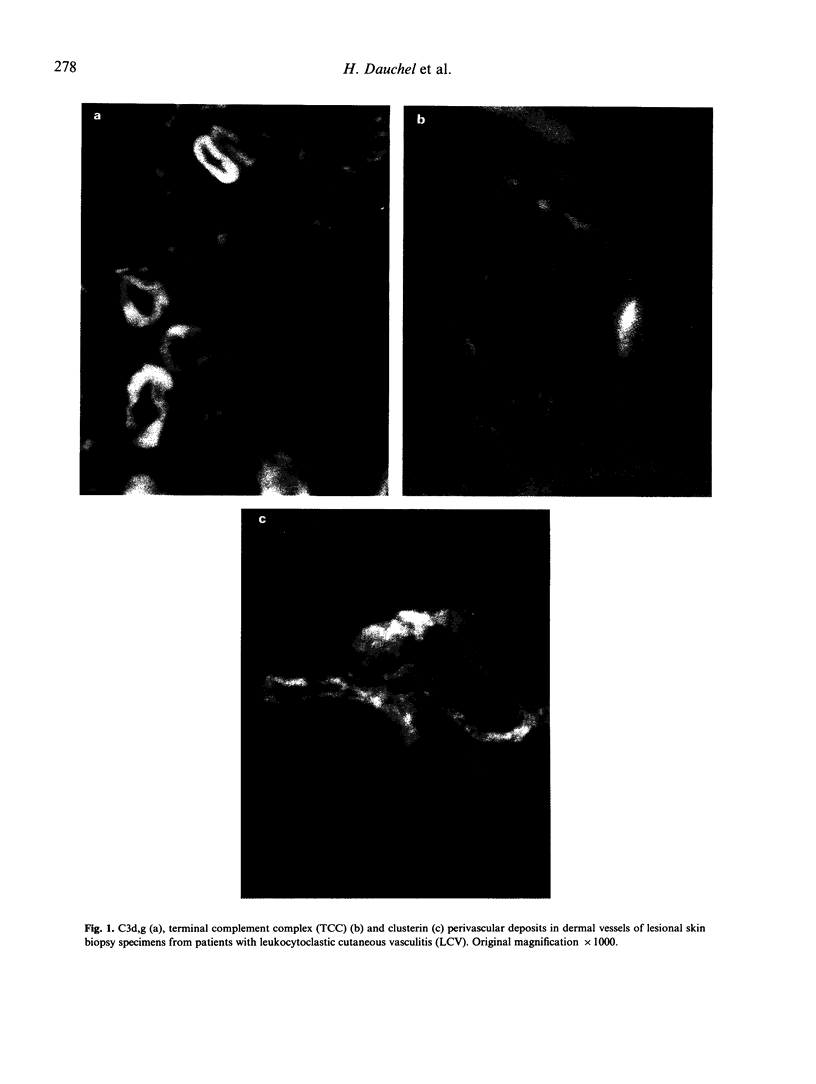
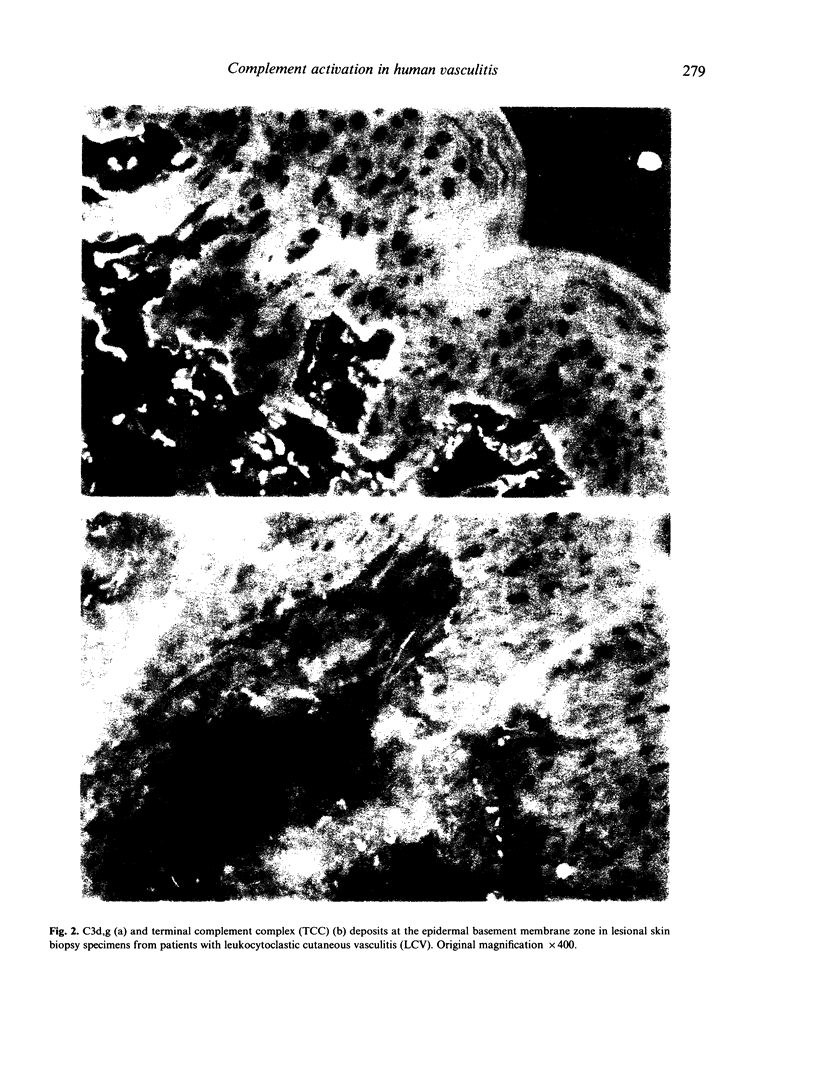
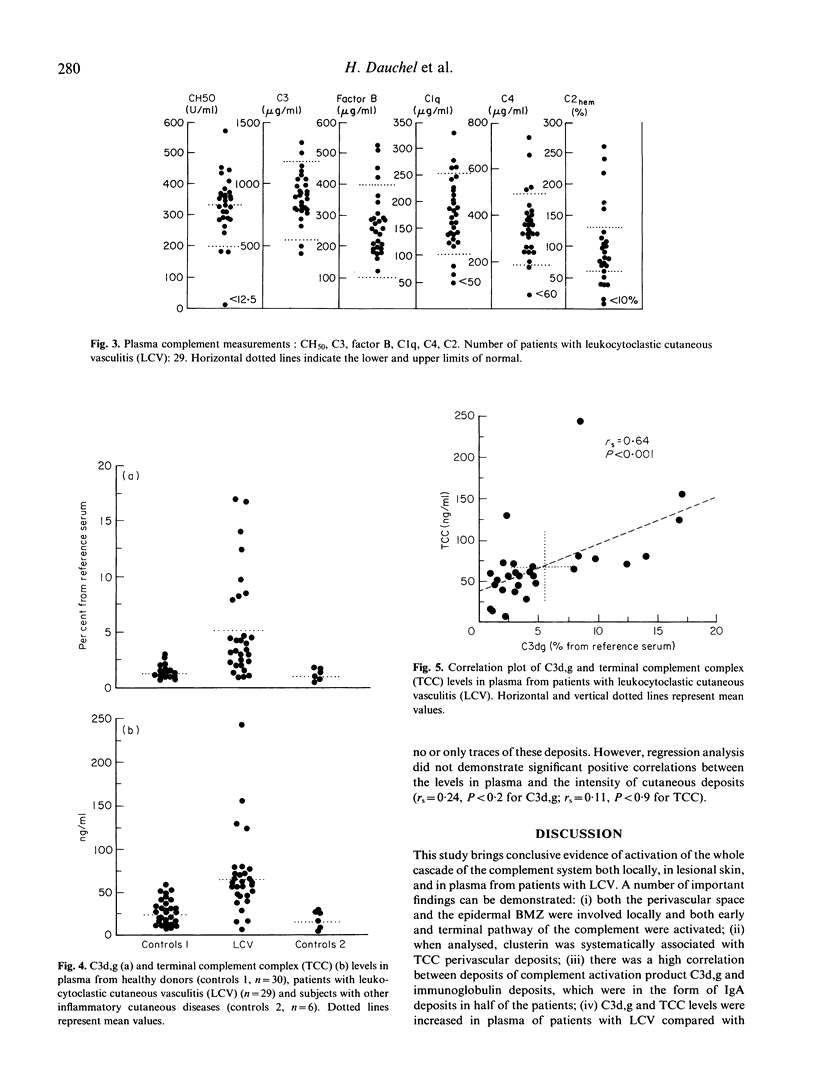
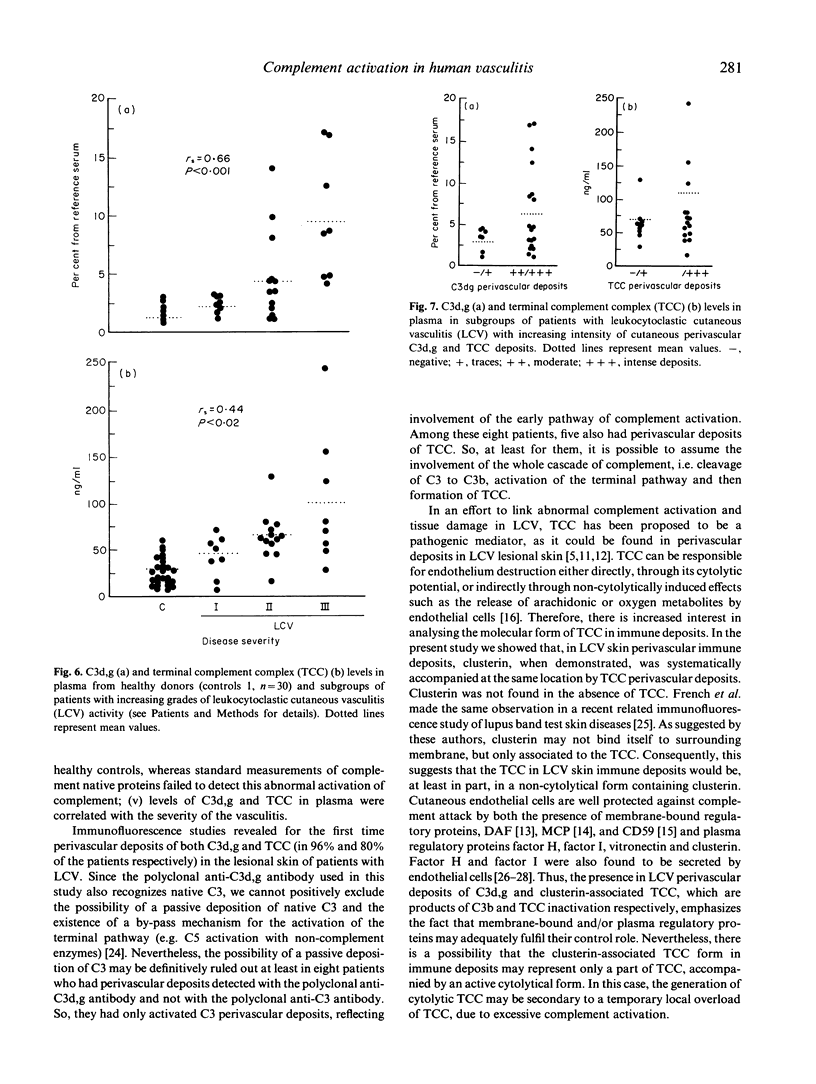
We have studied complement activation both in plasma samples and in lesional skin from patients with leukocytoclastic cutaneous vasculitis (LCV). Enzyme immunoassay (EIA) quantification of the complement activation markers, C3d,g and the terminal complement complex (TCC) in plasma, showed that their levels were significantly increased in 66% and 55% of the patients, respectively (n = 29) compared with healthy controls, whereas the standard measurements of C3, factor B, C1q, C4 and C2 were generally within normal range. Elevations of C3d,g and TCC levels in plasma were significantly correlated. Importantly, a significant correlation was found between the severity of the vasculitis and both C3d,g and TCC plasma levels. Immunofluorescence studies of skin biopsy specimens demonstrated simultaneous presence of perivascular dermal deposits of C3d,g and TCC in lesional skin from 96% and 80% respectively of the patients (n = 25). There was a significant correlation between the intensity of the deposits of both markers. Clusterin, a TCC inhibitory protein, was always found at the same sites of perivascular TCC deposits. Immunofluorescence studies at the epidermal basement membrane zone (BMZ) revealed in each case deposits of C3d,g which were accompanied by TCC deposits in 52% of the biopsy specimens. These data demonstrate that there is a local and systemic activation of the whole complement cascade in human LCV. The presence of both C3d,g and clusterin-associated TCC perivascular deposits suggests an intervention of a regulatory mechanism of local complement activation in LCV. Finally, measurement of plasma C3d,g and TCC appears to be a sensitive indicator of systemic complement activation and disease severity in LCV.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basset-Seguin N., Dersookian M., Cehrs K., Yancey K. B. C3d,g is present in normal human epidermal basement membrane. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 15;141(4):1273–1280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Käflein R., Halstensen T. S., Hugo F., Preissner K. T., Mollnes T. E. Complement S-protein (vitronectin) is associated with cytolytic membrane-bound C5b-9 complexes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Dec;74(3):459–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boom B. W., Out-Luiting C. J., Baldwin W. M., Westedt M. L., Daha M. R., Vermeer B. J. Membrane attack complex of complement in leukocytoclastic vasculitis of the skin. Presence and possible pathogenetic role. Arch Dermatol. 1987 Sep;123(9):1192–1195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooimans R. A., Hiemstra P. S., van der Ark A. A., Sim R. B., van Es L. A., Daha M. R. Biosynthesis of complement factor H by human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Regulation by T cell growth factor and IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):2024–2030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi N. H., Nakano Y., Tobe T., Mazda T., Tomita M. Incorporation of SP-40,40 into the soluble membrane attack complex (SMAC, SC5b-9) of complement. Int Immunol. 1990;2(5):413–417. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.5.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dauchel H., Julen N., Lemercier C., Daveau M., Ozanne D., Fontaine M., Ripoche J. Expression of complement alternative pathway proteins by endothelial cells. Differential regulation by interleukin 1 and glucocorticoids. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Aug;20(8):1669–1675. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faille-Kuyber E. H., Kater L., Kooiker C. J., Dorhout Mees E. J. IgA-deposits in cutaneous blood-vessel walls and mesangium in Henoch-Schönlein syndrome. Lancet. 1973 Apr 21;1(7808):892–893. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91471-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French L. E., Polla L. L., Tschopp J., Schifferli J. A. Membrane attack complex (MAC) deposits in skin are not always accompanied by S-protein and clusterin. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 May;98(5):758–763. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12499946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz I. B. What is clusterin? Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Jun;88(3):375–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06456.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawryl M. S., Chudwin D. S., Langlois P. F., Lint T. F. The terminal complement complex, C5b-9, a marker of disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Feb;31(2):188–195. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay-Crosier F., Polla L. L., Tschopp J., Schifferli J. A. Complement activation by pulsed tunable dye laser in normal skin and hemangioma. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Apr;94(4):426–431. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12874510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugo F., Jenne D., Bhakdi S. Monoclonal antibodies against neoantigens of the terminal C5b-9 complex of human complement. Biosci Rep. 1985 Aug;5(8):649–658. doi: 10.1007/BF01116996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunder G. G., Arend W. P., Bloch D. A., Calabrese L. H., Fauci A. S., Fries J. F., Leavitt R. Y., Lie J. T., Lightfoot R. W., Jr, Masi A. T. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of vasculitis. Introduction. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Aug;33(8):1065–1067. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julen N., Dauchel H., Lemercier C., Daveau M., Fontaine M., Sauger F., Maitrot B., Ripoche J. L'exploration du système du complément. Principes généraux et perspectives. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1990;48(6):349–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julen N., Dauchel H., Lemercier C., Sim R. B., Fontaine M., Ripoche J. In vitro biosynthesis of complement factor I by human endothelial cells. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jan;22(1):213–217. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawana S., Shen G. H., Kobayashi Y., Nishiyama S. Membrane attack complex of complement in Henoch-Schönlein purpura skin and nephritis. Arch Dermatol Res. 1990;282(3):183–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00372620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. D., Adelsberg B. R., Schulman P., Spiera H. Factor B activation products in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. A marker of severe disease activity. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Nov;32(11):1406–1413. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780321109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirszbaum L., Sharpe J. A., Murphy B., d'Apice A. J., Classon B., Hudson P., Walker I. D. Molecular cloning and characterization of the novel, human complement-associated protein, SP-40,40: a link between the complement and reproductive systems. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):711–718. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03430.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makinde V. A., Senaldi G., Jawad A. S., Berry H., Vergani D. Reflection of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis by indices of activation of the classical complement pathway. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 Apr;48(4):302–306. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.4.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meri S., Waldmann H., Lachmann P. J. Distribution of protectin (CD59), a complement membrane attack inhibitor, in normal human tissues. Lab Invest. 1991 Nov;65(5):532–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyagawa S., Shiiki H., Nakatani C., Ko T., Dohi K., Shirai T. Association of IgA immune complex vasculitis and rheumatoid arthritis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991 Feb;24(2 Pt 1):295–297. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(08)80614-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mlynek Y., Nilsson M. The quantitation of C3d by routine methods after the direct absorption of human plasma with anti-C3c. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1985 Oct;93(5):195–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1985.tb02944.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan B. P. Complement membrane attack on nucleated cells: resistance, recovery and non-lethal effects. Biochem J. 1989 Nov 15;264(1):1–14. doi: 10.1042/bj2640001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow W. J., Williams D. J., Ferec C., Casburn-Budd R., Isenberg D. A., Paice E., Snaith M. L., Youinou P., Le Goff P. The use of C3d as a means of monitoring clinical activity in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1983 Dec;42(6):668–671. doi: 10.1136/ard.42.6.668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. F., Davies D. J., Morrow W., d'Apice A. J. Localization of terminal complement components S-protein and SP-40,40 in renal biopsies. Pathology. 1989 Oct;21(4):275–278. doi: 10.3109/00313028909061073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. F., Kirszbaum L., Walker I. D., d'Apice A. J. SP-40,40, a newly identified normal human serum protein found in the SC5b-9 complex of complement and in the immune deposits in glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1858–1864. doi: 10.1172/JCI113531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sams W. M., Jr, Claman H. N., Kohler P. F., McIntosh R. M., Small P., Mass M. F. Human necrotizing vasculitis: immunoglobulins and complement in vessel walls of cutaneous lesions and normal skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1975 Jun;64(6):441–445. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12512411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayama K., Shiraishi S., Shirakata Y., Kobayashi Y., Miki Y. Characterization of decay-accelerating factor (DAF) in human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Jan;96(1):61–64. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12514737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayama K., Shiraishi S., Shirakata Y., Kobayashi Y., Seya T., Miki Y. Expression and characterization of membrane co-factor protein (MCP) in human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Oct;97(4):722–724. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12484155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smoller B. R., McNutt N. S., Contreras F. The natural history of vasculitis. What the histology tells us about pathogenesis. Arch Dermatol. 1990 Jan;126(1):84–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stad R. K., Bogers W. M., Thoomes-van der Sluys M. E., Van Es L. A., Daha M. R. In vivo activation of complement by IgA in a rat model. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Jan;87(1):138–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06427.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]