Abstract
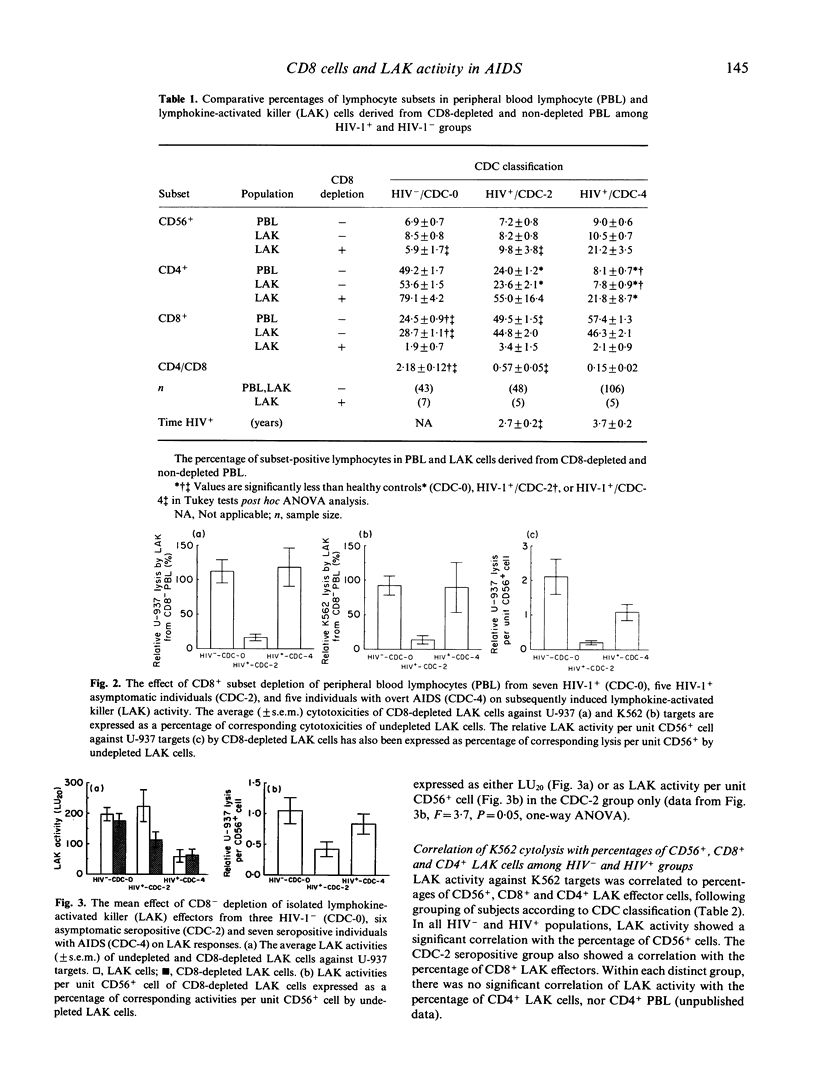
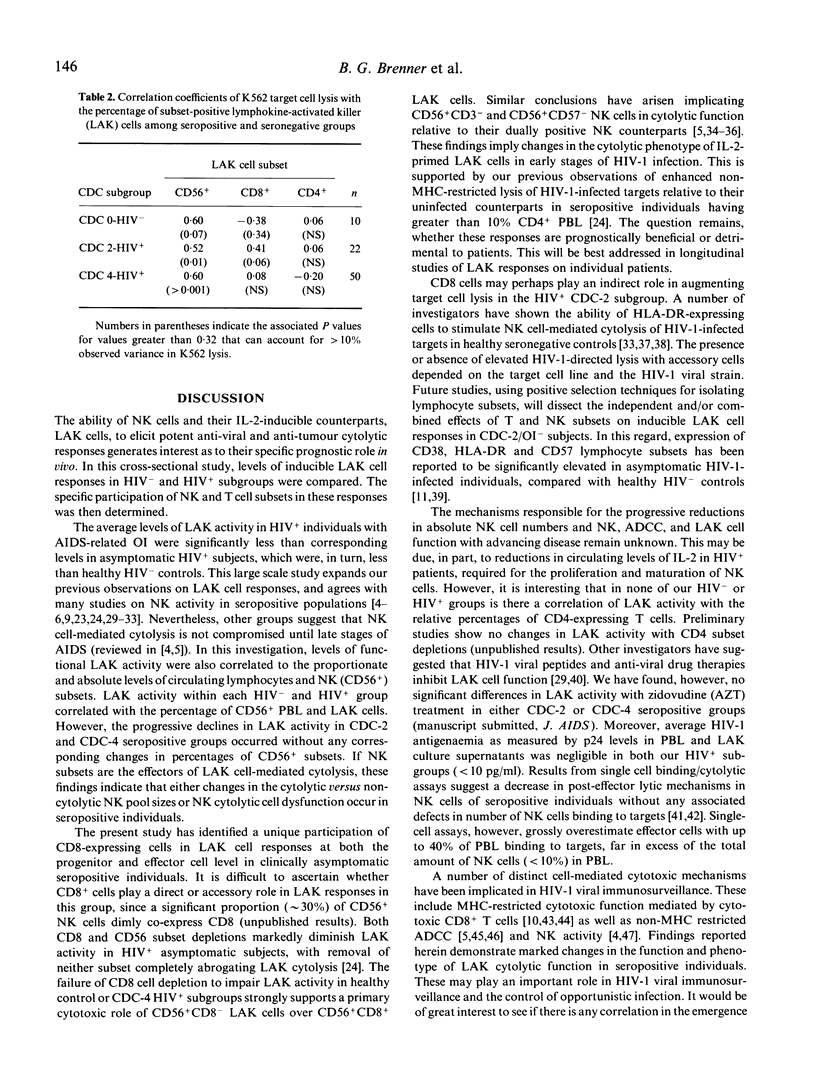
The role of natural killer (NK) and lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cell-mediated cytotoxicity in AIDS has yet to be established. The objective of this study was to determine inducible LAK cell responses at different stages of HIV-1 infection, and specifically to establish the participation of CD8 lymphocytes in these responses. Peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) were isolated from healthy seronegative (CDC-0) subjects and HIV-1+ individuals who were clinically asymptomatic (Centre for Disease Control group 2, CDC-2) or symptomatic (CDC-4) with regard to secondary opportunistic infection (OI). LAK cells were generated upon incubation of PBL with IL-2 and their cytolysis of K562 and U-937 targets was determined using chromium release assays. The role of CD8+ lymphocytes as progenitors and effectors of these LAK cell responses was determined by immunomagnetic depletion of CD8+ cells from precursor PBL and LAK cells, respectively. LAK cell-mediated cytotoxicities in HIV-1-infected individuals were reduced compared with seronegative controls without any corresponding changes in the relative proportions of CD56+ (NK) cells among groups. Depletions of CD8+ subsets from either PBL or LAK cells dramatically reduced total LAK cytotoxic responses and LAK activities per unit CD56+ cell in the OI-/CDC-2 seropositive population. No corresponding changes in LAK activities in seronegative control or HIV+/OI+/CDC-4 groups were observed. Levels of LAK activity against K562 targets in CDC-0/HIV- and CDC-4/HIV+ groups correlated with the percentage of CD56+ LAK cells; corresponding LAK activity in the CDC-2/HIV+ group correlated with the percentage of both CD56+ and CD8+ subsets. These findings suggest that adaptive changes in non-MHC restricted cytotoxic responses occur in HIV-1 individuals at early stages post-HIV infection, before the onset of opportunistic infection.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Cooper M. D., Balch C. M. Characterization of HNK-1+ (Leu-7) human lymphocytes. I. Two distinct phenotypes of human NK cells with different cytotoxic capability. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1752–1757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azogui O., Avril M. F., Margulis A., Guillard M., Caillou B., Prade M. Tumor-infiltrating CD3- NK cells are more effective than CD3+ T cells in killing autologous melanoma cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Sep;97(3):425–429. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12481140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay S., Ziegner U., Campbell D. E., Miller D. S., Hoxie J. A., Starr S. E. Natural killer cell-mediated lysis of T cell lines chronically infected with HIV-1. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Mar;79(3):430–435. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb08107.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. G., Benarrosh S., Margolese R. G. Peripheral blood natural killer cell activity in human breast cancer patients and its modulation by T-cell growth factor and autologous plasma. Cancer. 1986 Aug 15;58(4):895–902. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19860815)58:4<895::aid-cncr2820580416>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. G., Dascal A., Margolese R. G., Wainberg M. A. Natural killer cell function in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and related diseases. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Jul;46(1):75–83. doi: 10.1002/jlb.46.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. G., Gryllis C., Gornitsky M., Cupples W., Wainberg M. Differential effects of chemotherapy-induced and HIV-1-induced immunocompromise on NK and LAK activities using breast cancer and HIV-1 seropositive patient populations. Anticancer Res. 1991 Mar-Apr;11(2):969–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. G., Gryllis C., Wainberg M. A. Role of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and lymphokine-activated killer cells in AIDS and related diseases. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Dec;50(6):628–640. doi: 10.1002/jlb.50.6.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. G., Jothy S., Shuster J., Fuks A. Monoclonal antibodies to human lung tumor antigens demonstrated by immunofluorescence and immunoprecipitation. Cancer Res. 1982 Aug;42(8):3187–3192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cauda R., Tumbarello M., Ortona L., Kennedy R. C., Shuler K. R., Chanh T. C., Kanda P. Inhibition of lymphokine-activated killer activity during HIV infection: role of HIV-1 gp41 synthetic peptides. Nat Immun Cell Growth Regul. 1990;9(6):366–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chehimi J., Bandyopadhyay S., Prakash K., Perussia B., Hassan N. F., Kawashima H., Campbell D., Kornbluth J., Starr S. E. In vitro infection of natural killer cells with different human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1812–1822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1812-1822.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin T. W., Plaeger-Marshall S., Haas A., Ank B. J., Stiehm E. R. Lymphokine-activated killer cells in primary immunodeficiencies and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Dec;53(3):449–459. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Schnittman S. M., Poli G., Koenig S., Pantaleo G. NIH conference. Immunopathogenic mechanisms in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Apr 15;114(8):678–693. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-114-8-678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gambacorti-Passerini C., Rivoltini L., Radrizzani M., Belli F., Sciorelli G., Ravagnani F., Galazka A. R., Cascinelli N., Parmiani G. Differences between in vivo and in vitro activation of cancer patient lymphocytes by recombinant interleukin 2: possible role for lymphokine-activated killer cell infusion in the in vivo-induced activation. Cancer Res. 1989 Sep 15;49(18):5230–5234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm E. A. Human lymphokine-activated killer cells (LAK cells) as a potential immunotherapeutic modality. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Dec 17;865(3):267–279. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(86)90017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryllis C., Wainberg M. A., Bentwich Z., Gornitsky M., Brenner B. G. Increased LAK activity against HIV-infected cell lines in HIV-1+ individuals. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Sep;89(3):356–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06962.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryllis C., Wainberg M. A., Gornitsky M., Brenner B. Diminution of inducible lymphokine-activated killer cell activity in individuals with AIDS-related disorders. AIDS. 1990 Dec;4(12):1205–1212. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199012000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J. D., Mitsuyasu R., Gottlieb M. S., Lebow L. T., Bonavida B. Mechanism of defective NK cell activity in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and AIDS-related complex. II. Normal antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) mediated by effector cells defective in natural killer (NK) cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):55–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landay A., Ohlsson-Wilhelm B., Giorgi J. V. Application of flow cytometry to the study of HIV infection. AIDS. 1990 Jun;4(6):479–497. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199006000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levacher M., Hulstaert F., Tallet S., Ullery S., Pocidalo J. J., Bach B. A. The significance of activation markers on CD8 lymphocytes in human immunodeficiency syndrome: staging and prognostic value. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Dec;90(3):376–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb05854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMannis J. D., Fisher R. I., Creekmore S. P., Braun D. P., Harris J. E., Ellis T. M. In vivo effects of recombinant IL-2. I. Isolation of circulating Leu-19+ lymphokine-activated killer effector cells from cancer patients receiving recombinant IL-2. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 15;140(4):1335–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melder R. J., Balachandran R., Rinaldo C. R., Gupta P., Whiteside T. L., Herberman R. B. Cytotoxic activity against HIV-infected monocytes by recombinant interleukin 2-activated natural killer cells. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Aug;6(8):1011–1015. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon D. F., McMichael A. J. Cytotoxic T-cell recognition of HIV proteins and peptides. AIDS. 1991 Sep;5(9):1049–1059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortaldo J. R., Longo D. L. Human natural lymphocyte effector cells: definition, analysis of activity, and clinical effectiveness. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1988 Sep 7;80(13):999–1010. doi: 10.1093/jnci/80.13.999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortaldo J. R., Mason A., Overton R. Lymphokine-activated killer cells. Analysis of progenitors and effectors. J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1193–1205. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortaldo J. R., Winkler-Pickett R. T., Yagita H., Young H. A. Comparative studies of CD3- and CD3+ CD56+ cells: examination of morphology, functions, T cell receptor rearrangement, and pore-forming protein expression. Cell Immunol. 1991 Sep;136(2):486–495. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90369-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki A., Nakano H., Minato K., Nakagawa K., Sasaki Y., Saijo N. The difference in surface phenotypes between cytotoxic lymphocytes induced in vivo by systemic administration of human recombinant interleukin-2 and lymphokine activated killer cells induced in vitro. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1988 Jun;24(6):1055–1060. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(88)90159-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. H., Gemlo B. T., Myers W. W., Rayner A. A., Lanier L. L. In vivo and in vitro activation of natural killer cells in advanced cancer patients undergoing combined recombinant interleukin-2 and LAK cell therapy. J Clin Oncol. 1987 Dec;5(12):1933–1941. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1987.5.12.1933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. Dissection of the lymphokine-activated killer phenomenon. Relative contribution of peripheral blood natural killer cells and T lymphocytes to cytolysis. J Exp Med. 1986 Sep 1;164(3):814–825. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.3.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pross H. F., Baines M. G., Rubin P., Shragge P., Patterson M. S. Spontaneous human lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity against tumor target cells. IX. The quantitation of natural killer cell activity. J Clin Immunol. 1981 Jan;1(1):51–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00915477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappocciolo G., Toso J. F., Torpey D. J., 3rd, Gupta P., Rinaldo C. R., Jr Association of alpha interferon production with natural killer cell lysis of U937 cells infected with human immunodeficiency virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):41–48. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.41-48.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddell S. R., Watanabe K. S., Goodrich J. M., Li C. R., Agha M. E., Greenberg P. D. Restoration of viral immunity in immunodeficient humans by the adoptive transfer of T cell clones. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):238–241. doi: 10.1126/science.1352912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritz J., Schmidt R. E., Michon J., Hercend T., Schlossman S. F. Characterization of functional surface structures on human natural killer cells. Adv Immunol. 1988;42:181–211. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60845-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riviere Y., Tanneau-Salvadori F., Regnault A., Lopez O., Sansonetti P., Guy B., Kieny M. P., Fournel J. J., Montagnier L. Human immunodeficiency virus-specific cytotoxic responses of seropositive individuals: distinct types of effector cells mediate killing of targets expressing gag and env proteins. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2270–2277. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2270-2277.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. J., Ritz J. Biology and clinical relevance of human natural killer cells. Blood. 1990 Dec 15;76(12):2421–2438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti F. W., Mikovits J. A., Kalyanaraman V. S., Overton R., Stevenson H., Stromberg K., Herberman R. B., Farrar W. L., Ortaldo J. R. Analysis of effector mechanisms against HTLV-I- and HTLV-III/LAV-infected lymphoid cells. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3619–3624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. H., Merigan T. C. Interleukin-2 in the treatment of HIV disease. Biotherapy. 1990;2(2):119–136. doi: 10.1007/BF02173452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirianni M. C., Soddu S., Malorni W., Arancia G., Aiuti F., Soddus S. Mechanism of defective natural killer cell activity in patients with AIDS is associated with defective distribution of tubulin. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2565–2568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skibber J. M., Lotze M. T., Muul L. M., Uppenkamp I. K., Ross W., Rosenberg S. A. Human lymphokine-activated killer cells: further isolation and characterization of the precursor and effector cell. Nat Immun Cell Growth Regul. 1987;6(6):291–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stine K. C., Tyler D. S., Stanley S. D., Bartlett J. A., Bolognesi D. P., Weinhold K. J. The effect of AZT on in vitro lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) activity in human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1) infected individuals. Cell Immunol. 1991 Aug;136(1):165–172. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90391-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G. Biology of natural killer cells. Adv Immunol. 1989;47:187–376. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)60664-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler D. S., Stanley S. D., Nastala C. A., Austin A. A., Bartlett J. A., Stine K. C., Lyerly H. K., Bolognesi D. P., Weinhold K. J. Alterations in antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity during the course of HIV-1 infection. Humoral and cellular defects. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3375–3384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuillier F., Bianco N. E., Montagnier L., Dighiero G. Selective depletion of low-density CD8+, CD16+ lymphocytes during HIV infection. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1988 Apr;4(2):121–129. doi: 10.1089/aid.1988.4.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker B. D., Plata F. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes against HIV. AIDS. 1990 Mar;4(3):177–184. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199003000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil-Hillman G., Fisch P., Prieve A. F., Sosman J. A., Hank J. A., Sondel P. M. Lymphokine-activated killer activity induced by in vivo interleukin 2 therapy: predominant role for lymphocytes with increased expression of CD2 and leu19 antigens but negative expression of CD16 antigens. Cancer Res. 1989 Jul 1;49(13):3680–3688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinhold K. J., Lyerly H. K., Matthews T. J., Tyler D. S., Ahearne P. M., Stine K. C., Langlois A. J., Durack D. T., Bolognesi D. P. Cellular anti-GP120 cytolytic reactivities in HIV-1 seropositive individuals. Lancet. 1988 Apr 23;1(8591):902–905. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91713-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinhold K. J., Lyerly H. K., Matthews T. J., Tyler D. S., Ahearne P. M., Stine K. C., Langlois A. J., Durack D. T., Bolognesi D. P. Cellular anti-GP120 cytolytic reactivities in HIV-1 seropositive individuals. Lancet. 1988 Apr 23;1(8591):902–905. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91713-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinhold K. J., Lyerly H. K., Stanley S. D., Austin A. A., Matthews T. J., Bolognesi D. P. HIV-1 GP120-mediated immune suppression and lymphocyte destruction in the absence of viral infection. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3091–3097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


