Abstract
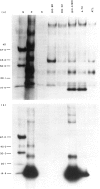
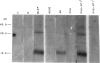
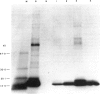
ABA-1 is a major allergen of nematode parasites of the genus Ascaris which includes the large roundworms of humans and pigs, A. lumbricoides and A. suum, respectively. The allergen was purified from A. suum by immunoaffinity chromatography for immunochemical examination. The IgE antibody repertoire is under MHC control in infected rodents and the IgE-binding epitopes were robust to treatment with heat or periodate, and electroblotting on nitrocellulose. This implies that the IgE epitopes comprise primary peptide sequence or an unusually stable secondary or tertiary structure. The molecular mass of ABA-1 is controversial, but mass spectrometry analysis indicated that there were five components of similar size, with the major species being 14,643.2 +/- 1.4 D. Finally, N-terminal sequence analysis of ABA-1 and TBA-1 (the homologue in the canine nematode infective to humans, Toxocara canis) revealed a high degree of similarity, and we have previous evidence that ABA-1 homologues are widespread amongst ascaridid parasites of humans. ABA-1 and its homologues might, therefore, be important to the immunopathology of many infections with nematode parasites, upon which the genetic constitution of the hosts will also have a bearing.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler J., Croft A. R., Doe J. E., Gemmell D. K., Miller J. N., Orr T. S. Biological techniques for studying the allergenic components of nematodes. II. The characterisation of the allergen released by Ascaris suum maintaind in saline. J Immunol Methods. 1973 Apr;2(3):315–323. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(73)90058-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler J., Miller J. N., Johnson P., Orr T. S. Characterisation of an allergen extracted from Ascaris suum. Determination of the molecular weight, isoelectric point, amino acid and carbohydrate content of the native allergen. Immunochemistry. 1973 Dec;10(12):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(73)90185-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atassi H., Atassi M. Z. Antibody recognition of ragweed allergen Ra3: localization of the full profile of the continuous antigenic sites by synthetic overlapping peptides representing the entire protein chain. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Mar;16(3):229–235. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baur X., Aschauer H., Mazur G., Dewair M., Prelicz H., Steigemann W. Structure, antigenic determinants of some clinically important insect allergens: chironomid hemoglobins. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):351–354. doi: 10.1126/science.2425431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie J. F., Dunbar B., Davidson I., Kennedy M. W. N-terminal amino acid sequence identity between a major allergen of Ascaris lumbricoides and Ascaris suum, and MHC-restricted IgE responses to it. Immunology. 1990 Apr;69(4):596–602. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie J. F., Fraser E. M., Kennedy M. W. Comparison between the MHC-restricted antibody repertoire to Ascaris antigens in adjuvant-assisted immunization or infection. Parasite Immunol. 1992 Jan;14(1):59–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1992.tb00006.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culpepper J., Grieve R. B., Friedman L., Mika-Grieve M., Frank G. R., Dale B. Molecular characterization of a Dirofilaria immitis cDNA encoding a highly immunoreactive antigen. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Aug;54(1):51–62. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90094-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Else K. J., Grencis R. K. Cellular immune responses to the murine nematode parasite Trichuris muris. I. Differential cytokine production during acute or chronic infection. Immunology. 1991 Apr;72(4):508–513. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene W. K., Chua K. Y., Stewart G. A., Thomas W. R. Antigenic analysis of group I house dust mite allergens using random fragments of Der p I expressed by recombinant DNA libraries. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1990;92(1):30–38. doi: 10.1159/000235220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspon L. W., White J., Shields R. L., Fügner A., Gold W. M. Purification of Ascaris suum antigen: its allergenic activity in vitro and in vivo. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986 Mar;77(3):443–451. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(86)90178-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grencis R. K., Hültner L., Else K. J. Host protective immunity to Trichinella spiralis in mice: activation of Th cell subsets and lymphokine secretion in mice expressing different response phenotypes. Immunology. 1991 Oct;74(2):329–332. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett E. E., Miller H. R. Production and activities of IgE in helminth infection. Prog Allergy. 1982;31:178–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. W., Fraser E. M., Christie J. F. MHC class II (I-A) region control of the IgE antibody repertoire to the ABA-1 allergen of the nematode Ascaris. Immunology. 1991 Apr;72(4):577–579. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. W., Qureshi F., Fraser E. M., Haswell-Elkins M. R., Elkins D. B., Smith H. V. Antigenic relationships between the surface-exposed, secreted and somatic materials of the nematode parasites Ascaris lumbricoides, Ascaris suum, and Toxocara canis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Mar;75(3):493–500. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. W., Qureshi F. Stage-specific secreted antigens of the parasitic larval stages of the nematode Ascaris. Immunology. 1986 Jul;58(3):515–522. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. W., Tierney J., Ye P., McMonagle F. A., McIntosh A., McLaughlin D., Smith J. W. The secreted and somatic antigens of the third stage larva of Anisakis simplex, and antigenic relationship with Ascaris suum, Ascaris lumbricoides, and Toxocara canis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Oct;31(1):35–46. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90143-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. W., Tomlinson L. A., Fraser E. M., Christie J. F. The specificity of the antibody response to internal antigens of Ascaris: heterogeneity in infected humans, and MHC (H-2) control of the repertoire in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 May;80(2):219–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05237.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattei D., Scherf A., Bensaude O., da Silva L. P. A heat shock-like protein from the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum induces autoantibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Oct;19(10):1823–1828. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGibbon A. M., Christie J. F., Kennedy M. W., Lee T. D. Identification of the major Ascaris allergen and its purification to homogeneity by high-performance liquid chromatography. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Mar;39(2):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90055-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole C. B., Grandea A. G., 3rd, Maina C. V., Jenkins R. E., Selkirk M. E., McReynolds L. A. Cloning of a cuticular antigen that contains multiple tandem repeats from the filarial parasite Dirofilaria immitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5986–5990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson L. A., Christie J. F., Fraser E. M., McLaughlin D., McIntosh A. E., Kennedy M. W. MHC restriction of the antibody repertoire to secretory antigens, and a major allergen, of the nematode parasite Ascaris. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;143(7):2349–2356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Gordon J. Immunoblotting and dot immunobinding--current status and outlook. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Sep 4;72(2):313–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]