Abstract
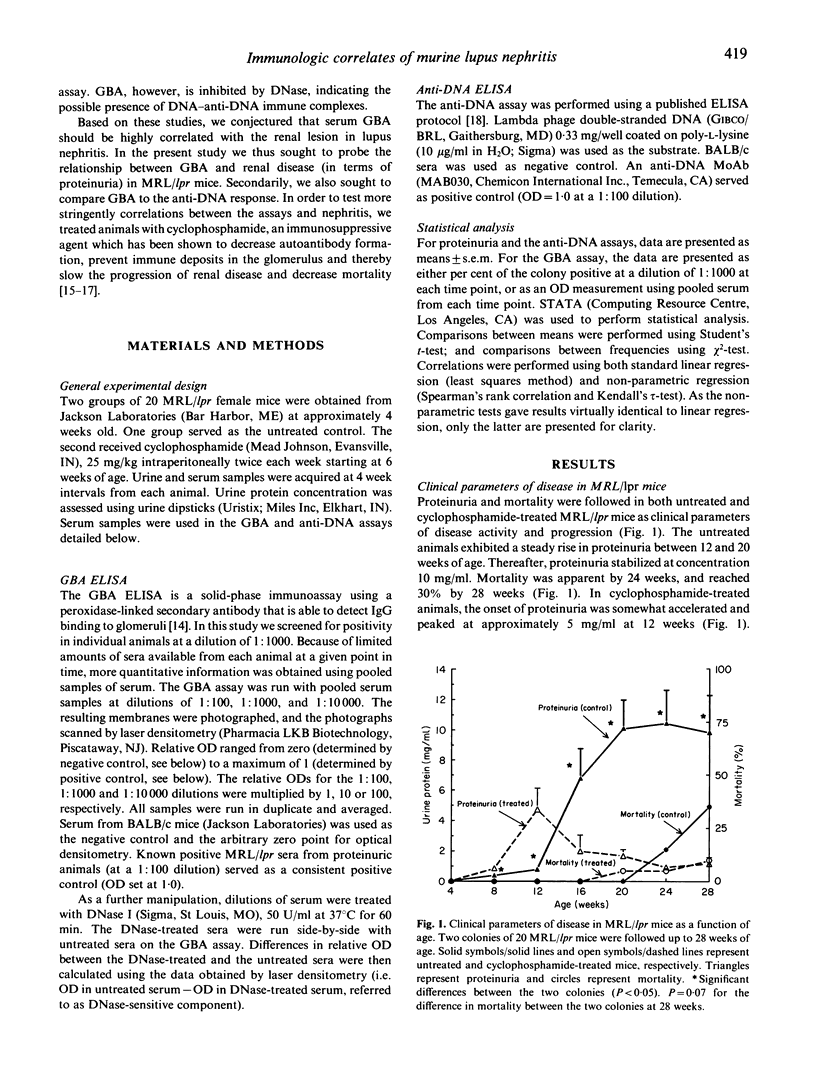
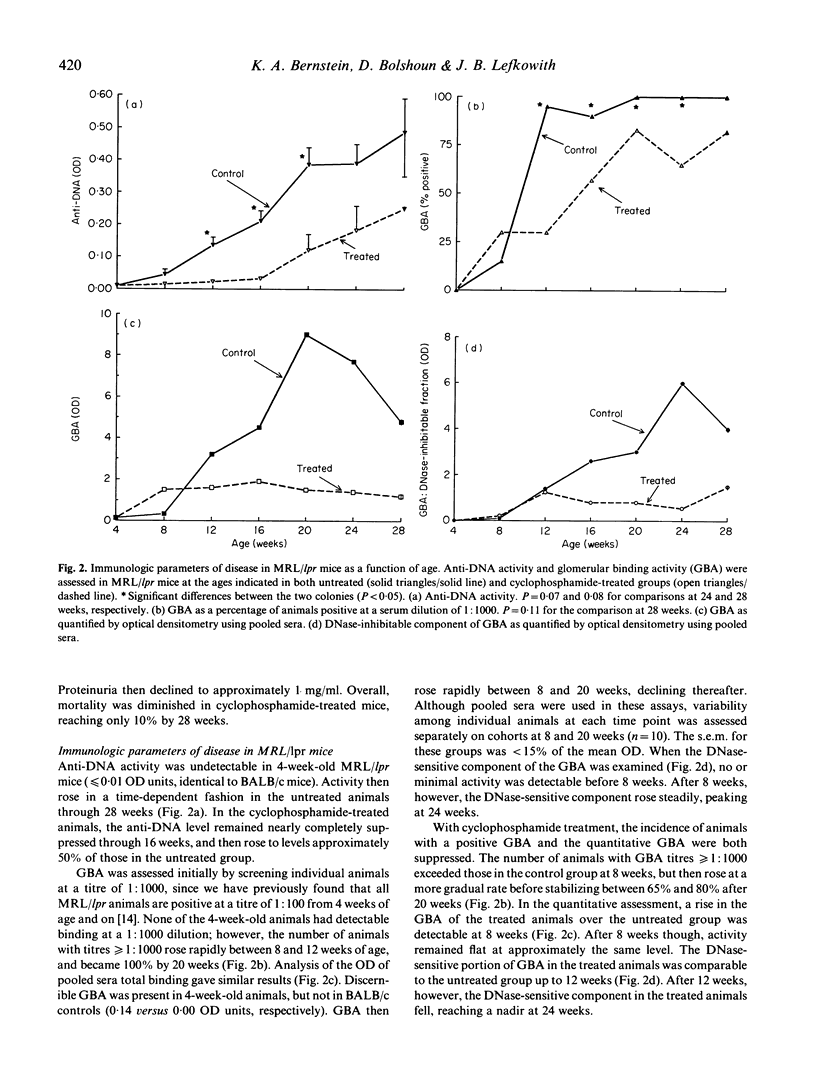
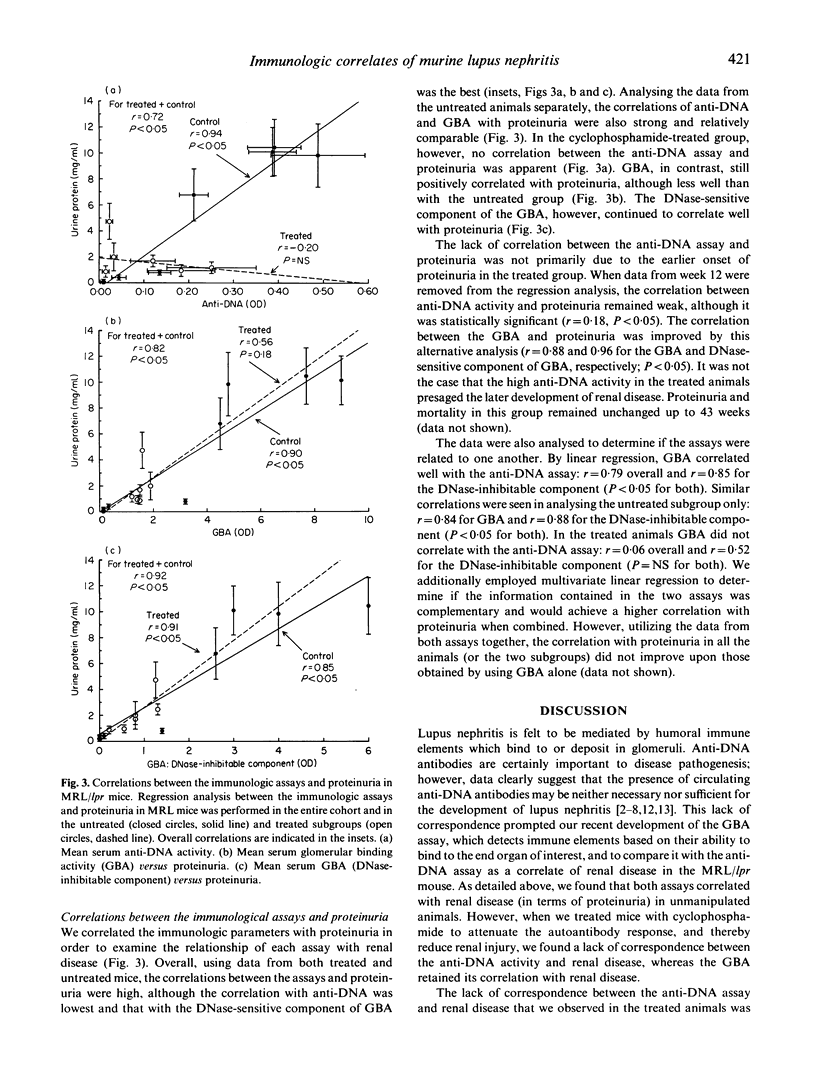
The pathogenesis of lupus nephritis is felt to be mediated by anti-DNA antibodies. However, the anti-DNA response and renal disease do not entirely correspond. We recently developed a new assay which detects immune elements based on their ability to bind glomeruli as an alternative approach to understanding the pathogenesis of this disorder. The glomerular binding activity (GBA) defined by this assay consists of immune elements containing IgG which interact specifically with renal tissue, the binding of which is DNase-inhibitable, but which do not bind to DNA directly. In the current study we assessed the relationship between GBA and renal disease in MRL/lpr mice (both untreated and cyclophosphamide-treated) and compared it with the anti-DNA assay. Both assays were highly correlated with renal disease in untreated mice in terms of proteinuria. In cyclophosphamide-treated mice, however, only a weak correlation between the anti-DNA assay and proteinuria was apparent. GBA, in contrast, was more strongly correlated with proteinuria in treated mice. This correlation improved substantially when the DNase-sensitive component of the GBA was used. GBA appeared related to, but not covariant with, the anti-DNA response. These results demonstrate that GBA is a better correlate of murine lupus nephritis than the anti-DNA assay, and suggest that the immune elements detected by this assay, the DNase-sensitive component in particular, may be pathogenically important.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews B. S., Eisenberg R. A., Theofilopoulos A. N., Izui S., Wilson C. B., McConahey P. J., Murphy E. D., Roths J. B., Dixon F. J. Spontaneous murine lupus-like syndromes. Clinical and immunopathological manifestations in several strains. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1198–1215. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett R. R., Popovic S., Raiss R. X. Development of autoimmunity in MRL/lpr mice and the effects of drugs on this murine disease. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1988;75:290–299. doi: 10.3109/03009748809096781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein K., Bolshoun D., Gilkeson G., Munns T., Lefkowith J. B. Detection of glomerular-binding immune elements in murine lupus using a tissue-based ELISA. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Mar;91(3):449–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb05923.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. R., Pesek-Diamond I. Sublethal X-irradiation during acute puromycin nephrosis prevents late renal injury: role of macrophages. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jun;260(6 Pt 2):F779–F786. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.6.F779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebling F., Hahn B. H. Restricted subpopulations of DNA antibodies in kidneys of mice with systemic lupus. Comparison of antibodies in serum and renal eluates. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Apr;23(4):392–403. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H., Knotts L., Ng M., Hamilton T. R. Influence of cyclophosphamide and other immunosuppressive drugs on immune disorders and neoplasia in NZB/NZW mice. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Mar-Apr;18(2):145–152. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui S., Kelley V. E., Masuda K., Yoshida H., Roths J. B., Murphy E. D. Induction of various autoantibodies by mutant gene lpr in several strains of mice. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):227–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui S., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Failure to detect circulating DNA--anti-DNA complexes by four radioimmunological methods in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Dec;30(3):384–392. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Schur P. H., Kunkel H. G. Immunological studies concerning the nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1967 Oct 1;126(4):607–624. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.4.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. H., Dixon F. J. Pathogenesis of the glomerulonephritis of NZB/W mice. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):507–522. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara M., Ohsugi Y. Effect of several kinds of drugs on the development of autoimmunity in MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr mice; lack of correlation between the suppression of autoantibody production and prevention of autoimmune disease. J Pharmacobiodyn. 1989 Feb;12(2):100–106. doi: 10.1248/bpb1978.12.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munns T. W., Freeman S. K. Antibody-nucleic acid complexes. Oligo(dG)n and -(dT)n specificities associated with anti-DNA antibodies from autoimmune MRL mice. Biochemistry. 1989 Dec 26;28(26):10048–10054. doi: 10.1021/bi00452a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley R. L., Addis D. J., Taylor R. P. Stability of DNA/anti-DNA complexes. II. Salt lability and avidity. J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano H., Morimoto C. Isolation of DNA from DNA/anti-DNA antibody immune complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):538–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Muryoi T., Hatakeyama A., Suzuki M., Sato H., Seino J., Saito T., Yoshinaga K. Circulating anti-DNA immune complexes in active lupus nephritis. Am J Med. 1991 Oct;91(4):355–362. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(91)90152-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Termaat R. M., Assmann K. J., Dijkman H. B., van Gompel F., Smeenk R. J., Berden J. H. Anti-DNA antibodies can bind to the glomerulus via two distinct mechanisms. Kidney Int. 1992 Dec;42(6):1363–1371. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Balderas R., Shawler D. L., Izui S., Kotzin B. L., Strober S., Dixon F. J. Inhibition of T cells proliferation and SLE-like syndrome of MRL/1 mice by whole body or total lymphoid irradiation. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):2137–2142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao B. P., Ohnishi K., Cheroutre H., Mitchell B., Teitell M., Mixter P., Kronenberg M., Hahn B. H. Failed self-tolerance and autoimmunity in IgG anti-DNA transgenic mice. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 1;149(1):350–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlahakos D. V., Foster M. H., Adams S., Katz M., Ucci A. A., Barrett K. J., Datta S. K., Madaio M. P. Anti-DNA antibodies form immune deposits at distinct glomerular and vascular sites. Kidney Int. 1992 Jun;41(6):1690–1700. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Kohno A., Ohta K., Hirose S., Maruyama N., Shirai T. Genetic studies of autoimmunity in New Zealand mice. III. Associations among anti-DNA antibodies, NTA, and renal disease in (NZB x NZW)F1 x NZW backcross mice. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):433–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



