Abstract
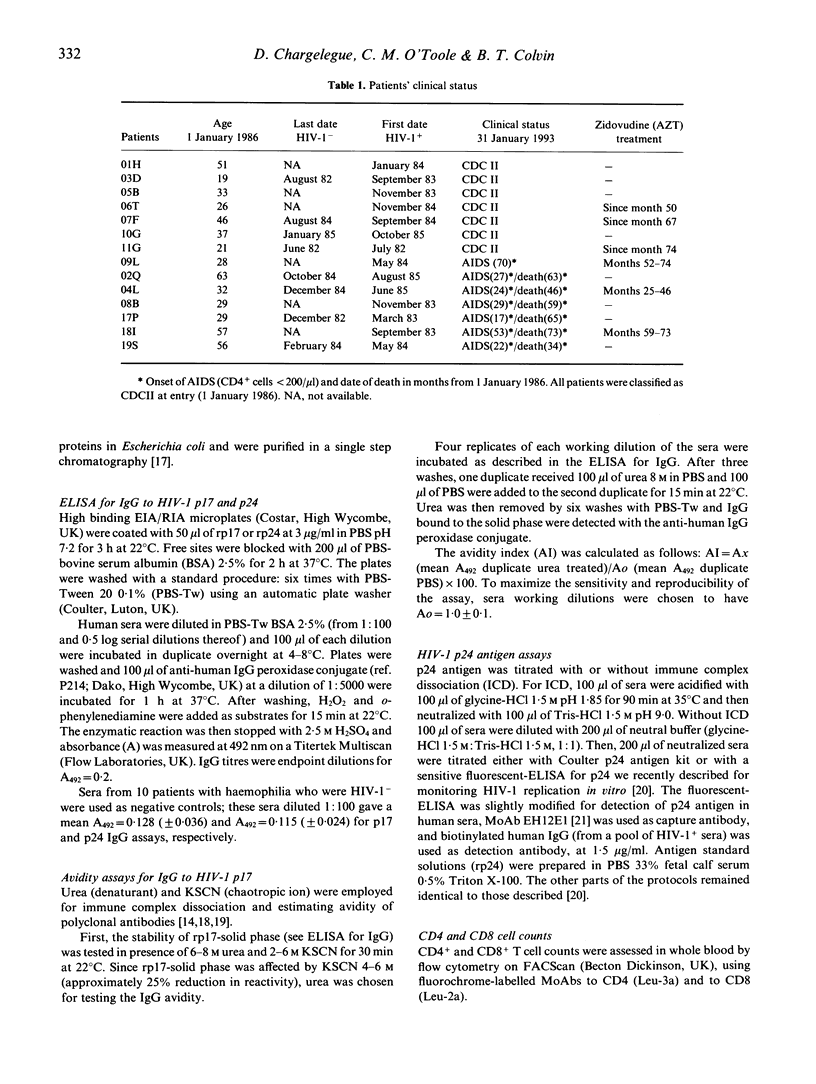
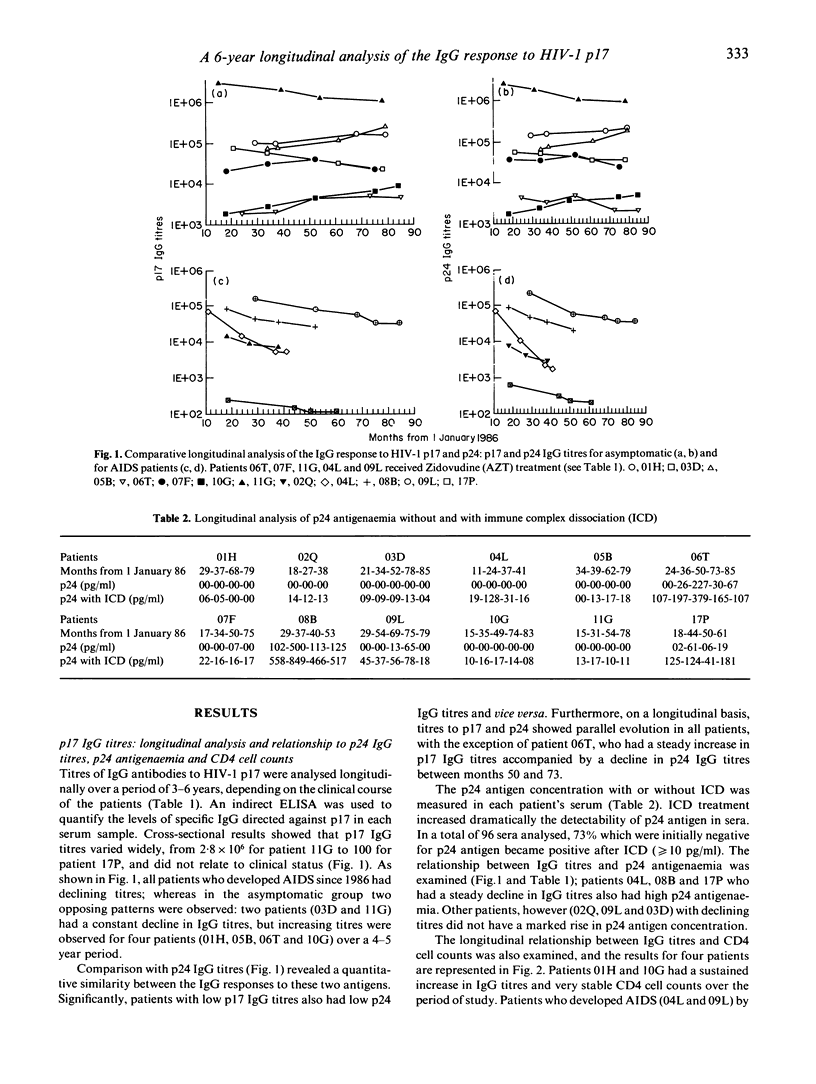
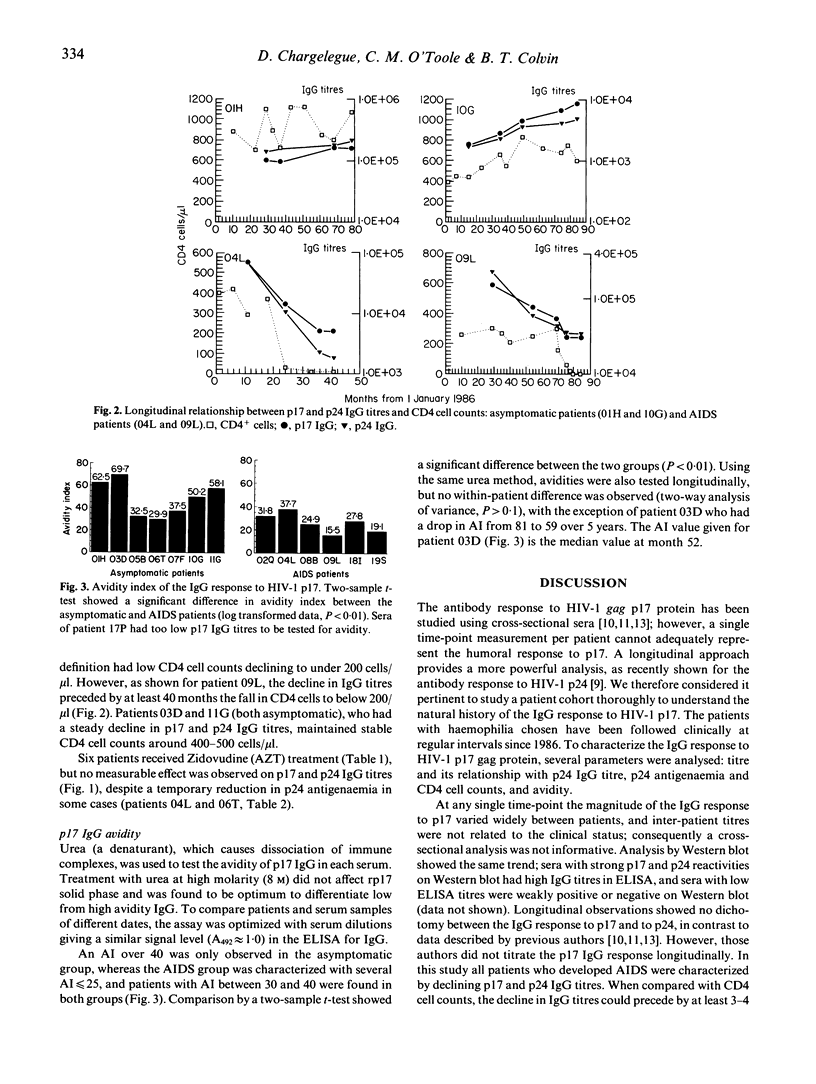
The IgG response to HIV-1 p17 gag protein was studied for up to 6 years in 12 HIV-1-infected patients with haemophilia, who had seroconverted between 1982 and 1985. To assess any prognostic value, p17 IgG titres were compared with p24 IgG titres, CD4 cell counts and p24 antigenaemia. p17 IgG avidity index was also examined. A strong similarity was found between the IgG titre to HIV-1 p17 and that to p24. In patients who developed AIDS the decline in p17 IgG titres could precede by several years the drop in CD4 cells to under 200 cells/microliters; whereas some long-term asymptomatic patients (CDCII) had increasing p17 IgG titres and stable CD4 cell counts. Declining p17 and p24 IgG titres were not always associated with an increase in p24 antigenaemia. IgG titres were found to be better predictors of disease progression than CD4 cell counts or p24 antigenaemia. Patients who developed AIDS during the study were also characterized by a lower p17 IgG avidity than patients who remained asymptomatic. This result suggests that IgG avidity could have prognostic relevance and be of importance for host resistance to AIDS onset.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allain J. P., Laurian Y., Einstein M. H., Braun B. P., Delaney S. R., Stephens J. E., Daluga C. K., Dahlen S. J., Knigge K. M. Monitoring of specific antibodies to human immunodeficiency virus structural proteins: clinical significance. Blood. 1991 Mar 1;77(5):1118–1123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barin F., McLane M. F., Allan J. S., Lee T. H., Groopman J. E., Essex M. Virus envelope protein of HTLV-III represents major target antigen for antibodies in AIDS patients. Science. 1985 May 31;228(4703):1094–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.2986291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baur A., Vornhagen R., Korn K., Sonneborn H. H., Eberlein B., Harrer T., Brockhaus W., Jahn G. Viral culture and p24 antigenemia of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected individuals correlated with antibody profiles determined with recombinant polypeptides of all HIV-1 open-reading frames. J Infect Dis. 1992 Mar;165(3):419–426. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.3.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollinger R. C., Jr, Kline R. L., Francis H. L., Moss M. W., Bartlett J. G., Quinn T. C. Acid dissociation increases the sensitivity of p24 antigen detection for the evaluation of antiviral therapy and disease progression in asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus-infected persons. J Infect Dis. 1992 May;165(5):913–916. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.5.913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broliden P. A., Morfeldt-Månsson L., Rosen J., Jondal M., Wahren B. Fine specificity of IgG subclass response to group antigens in HIV-1-infected patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 May;76(2):216–221. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chargelegue D., O'Toole C. M. Development of a sensitive ELISA for HIV-1 p24 antigen using a fluorogenic substrate for monitoring HIV-1 replication in vitro. J Virol Methods. 1992 Aug-Sep;38(3):323–332. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(92)90077-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheingsong-Popov R., Panagiotidi C., Bowcock S., Aronstam A., Wadsworth J., Weber J. Relation between humoral responses to HIV gag and env proteins at seroconversion and clinical outcome of HIV infection. BMJ. 1991 Jan 5;302(6767):23–26. doi: 10.1136/bmj.302.6767.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou M. J., Lee T. H., Hatzakis A., Mandalaki T., McLane M. F., Essex M. Antibody responses in early human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in hemophiliacs. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):805–811. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Converse P. J., Fehniger T. E., Ehrnst A., Strannegård O., Britton S. Immune responses to fractionated cytomegalovirus (CMV) antigens after HIV infection. Loss of cellular and humoral reactivity to antigens recognized by HIV-, CMV+ individuals. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Dec;82(3):559–566. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05490.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Prete G. F., De Carli M., Mastromauro C., Biagiotti R., Macchia D., Falagiani P., Ricci M., Romagnani S. Purified protein derivative of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and excretory-secretory antigen(s) of Toxocara canis expand in vitro human T cells with stable and opposite (type 1 T helper or type 2 T helper) profile of cytokine production. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):346–350. doi: 10.1172/JCI115300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenouillet E., Blanes N., Coutellier A., Demarquest J., Rozenbaum W., Gluckman J. C. Monitoring of antibodies against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 p25 core protein as prognostic marker. J Infect Dis. 1992 Sep;166(3):611–616. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.3.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferns R. B., Partridge J. C., Spence R. P., Hunt N., Tedder R. S. Epitope location of 13 anti-gag HIV-1 monoclonal antibodies using oligopeptides and their cross reactivity with HIV-2. AIDS. 1989 Dec;3(12):829–834. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198912000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzman E. J., Yaari S., Goldbourt U. Serum cholesterol and the risk of colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 9;317(2):114–114. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707093170211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J. D., Chu F. N., Naylor P. H., Kirkley J. E., Mandeli J., Wallace J. I., Sarin P. S., Goldstein A. L., Holland J. F., Bekesi J. G. Specific antibody responses to synthetic peptides of HIV-1 p17 correlate with different stages of HIV-1 infection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1992;5(4):382–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly P., Guillon J. M., Mayaud C., Plata F., Theodorou I., Denis M., Debre P., Autran B. Cell-mediated suppression of HIV-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;143(7):2193–2201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange J. M., de Wolf F., Krone W. J., Danner S. A., Coutinho R. A., Goudsmit J. Decline of antibody reactivity to outer viral core protein p17 is an earlier serological marker of disease progression in human immunodeficiency virus infection than anti-p24 decline. AIDS. 1987 Sep;1(3):155–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathiesen T., Sundqvist V. A., Albert J., Ohlsson E., Wahren B. Acid hydrolysis of serum samples to increase detection of HIV antigen. J Virol Methods. 1988 Dec;22(2-3):143–148. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(88)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRae B., Lange J. A., Ascher M. S., de Wolf F., Sheppard H. W., Goudsmit J., Allain J. P. Immune response to HIV p24 core protein during the early phases of human immunodeficiency virus infection. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Aug;7(8):637–643. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta S. U., Rupprecht K. R., Hunt J. C., Kramer D. E., McRae B. J., Allen R. G., Dawson G. J., Devare S. G. Prevalence of antibodies to the core protein P17, a serological marker during HIV-1 infection. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Apr;6(4):443–454. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole C. M., Lowdell M. W., Chargelegue D., Colvin B. T. Decline in CTL and antibody responses to HIV-1 p17 and p24 antigens in HIV-1-infected hemophiliacs irrespective of disease progression. A 5-year follow-up study. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Aug;8(8):1361–1368. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.1361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Re M. C., Zauli G., Furlini G., Ranieri S., La Placa M. Progressive and selective impairment of IL-3 and IL-4 production by peripheral blood CD4+ T-lymphocytes during the course of HIV-1 infection. Viral Immunol. 1992 Fall;5(3):185–194. doi: 10.1089/vim.1992.5.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüpbach J., Haller O., Vogt M., Lüthy R., Joller H., Oelz O., Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Gallo R. C. Antibodies to HTLV-III in Swiss patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS and in groups at risk for AIDS. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 31;312(5):265–270. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501313120502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer G. M., Clerici M. Early T-helper cell defects in HIV infection. AIDS. 1991 Mar;5(3):245–253. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199103000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward M. W., Stanley C. M., Dimarchi R., Mulcahy G., Doel T. R. High-affinity antibody induced by immunization with a synthetic peptide is associated with protection of cattle against foot-and-mouth disease. Immunology. 1991 Jan;72(1):99–103. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas H. I., Morgan-Capner P. Rubella-specific IgG1 avidity: a comparison of methods. J Virol Methods. 1991 Feb-Mar;31(2-3):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(91)90160-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Fernandez-Botran R., Myers C. D., Sanders V. M. Cellular interactions in the humoral immune response. Adv Immunol. 1989;45:1–105. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60692-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen Y. M., Duan S. C., Howard C. R., Frew A. F., Steward M. W. The affinity of anti-HBc antibodies in acute and chronic hepatitis B infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Jan;79(1):83–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05131.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney C., Ant J., Moncla B., Johnson B., Page R. C., Engel D. Serum immunoglobulin G antibody to Porphyromonas gingivalis in rapidly progressive periodontitis: titer, avidity, and subclass distribution. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2194–2200. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2194-2200.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



