Abstract
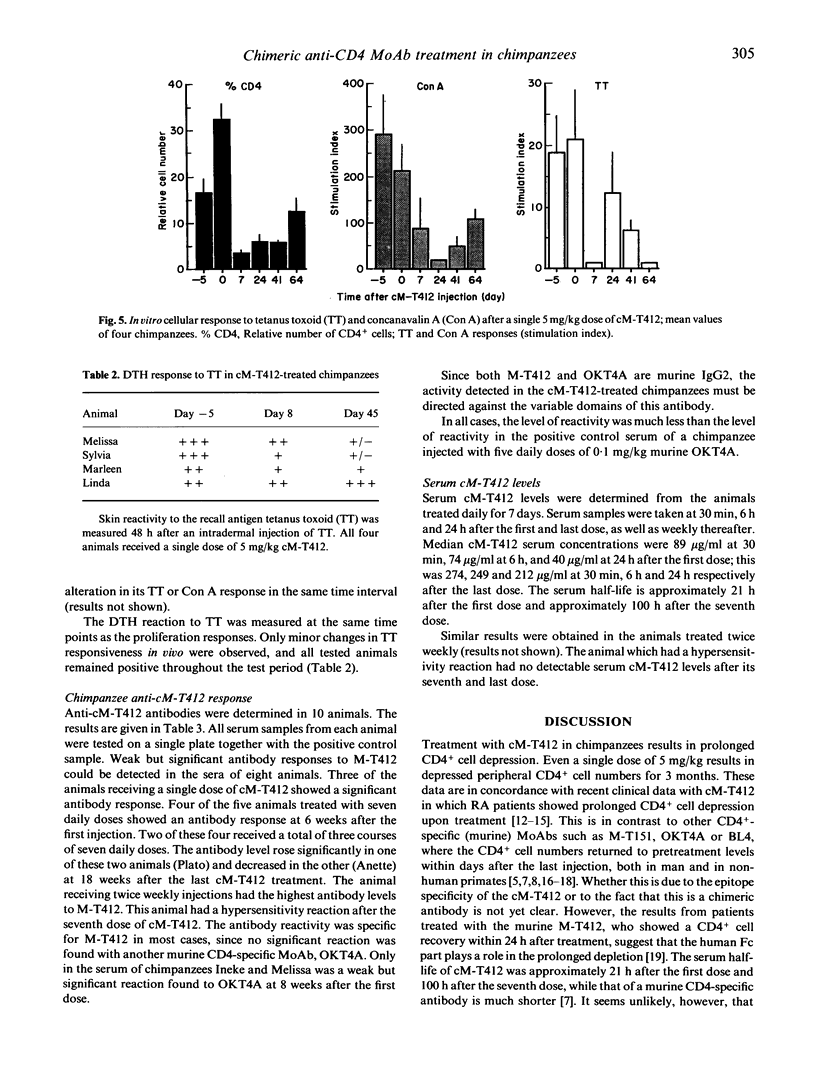
Chimeric M-T412 (cM-T412), an anti-CD4 antibody, was tolerated in chimpanzees at a dosage of 5 mg/kg per day for up to 7 consecutive days, or 5 mg/kg per dose, twice weekly for 4 weeks. All cM-T412-treated chimpanzees showed a prolonged CD4 cell depression. Weak chimpanzee antibody responses to chimeric M-T412 were observed. One of the chimpanzees on the biweekly dosage regimen exhibited a hypersensitivity reaction immediately after receiving its seventh dose. Following supportive treatment, the animal recovered and remained asymptomatic during the non-treatment observation period. The hypersensitivity reaction was not an unexpected response considering the animal received repeated intermittent i.v. administration of a foreign protein. This animal also showed a chimpanzee antibody response to chimeric M-T412 after the seventh dose. Chimeric M-T412 also induced an anti-cM-T412 response in some of the other animals. The level of this response was lower than the anti-mouse responses observed in animals treated with murine anti-CD4. Moreover, the anti-cM-T412 response was mainly directed to idiotypic determinants. The decrease in CD4+ cells observed for all chimeric M-T412-treated chimpanzees is an expected effect of the anti-CD4 antibody. The duration of this CD4+ cell decrease is, however, much longer than observed for other CD4-specific MoAbs described. No selective loss of either memory or naive CD4+ cells was observed after either the single, 7-day or twice-weekly treatments. The CD4+ cell depression was reversible, although individual variation in time to recovery was observed. Therefore, cM-T412 could be a good candidate for clinical use in autoimmune conditions.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker N. P., van Erck M. G., Botman C. A., Jonker M., 't Hart B. A. Collagen-induced arthritis in an outbred group of rhesus monkeys comprising responder and nonresponder animals. Relationship between the course of arthritis and collagen-specific immunity. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 May;34(5):616–624. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostoff S. W., Mason D. W. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: successful treatment in vivo with a monoclonal antibody that recognizes T helper cells. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1938–1942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choy E. H., Chikanza I. C., Kingsley G. H., Panayi G. S. Chimaeric anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody for relapsing polychondritis. Lancet. 1991 Aug 17;338(8764):450–450. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D., Morel P., Chatenoud L., Boitard C., Menkes C. J., Bertoye P. H., Revillard J. P., Bach J. F. Immunological effects of high dose administration of anti-CD4 antibody in rheumatoid arthritis patients. J Autoimmun. 1991 Aug;4(4):617–630. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(91)90181-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafler D. A., Ritz J., Schlossman S. F., Weiner H. L. Anti-CD4 and anti-CD2 monoclonal antibody infusions in subjects with multiple sclerosis. Immunosuppressive effects and human anti-mouse responses. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):131–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzog C., Walker C., Pichler W., Aeschlimann A., Wassmer P., Stockinger H., Knapp W., Rieber P., Müller W. Monoclonal anti-CD4 in arthritis. Lancet. 1987 Dec 19;2(8573):1461–1462. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91158-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonker M., Den Brok J. H. Idiotype switching of CD4-specific monoclonal antibodies can prolong the therapeutic effectiveness in spite of host anti-mouse IgG antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Nov;17(11):1547–1553. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonker M., Neuhaus P., Zurcher C., Fucello A., Goldstein G. OKT4 and OKT4A antibody treatment as immunosuppression for kidney transplantation in rhesus monkeys. Transplantation. 1985 Mar;39(3):247–253. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198503000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike T., Itoh Y., Ishii T., Ito I., Takabayashi K., Maruyama N., Tomioka H., Yoshida S. Preventive effect of monoclonal anti-L3T4 antibody on development of diabetes in NOD mice. Diabetes. 1987 Apr;36(4):539–541. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.4.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LoBuglio A. F., Wheeler R. H., Trang J., Haynes A., Rogers K., Harvey E. B., Sun L., Ghrayeb J., Khazaeli M. B. Mouse/human chimeric monoclonal antibody in man: kinetics and immune response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4220–4224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas J. F., Chamchick N., Thivolet J., Wijdenes J., Morel P., Revillard J. P. CD4 antibody treatment of severe psoriasis. Lancet. 1991 Aug 3;338(8762):321–321. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90465-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prinz J., Braun-Falco O., Meurer M., Daddona P., Reiter C., Rieber P., Riethmüller G. Chimaeric CD4 monoclonal antibody in treatment of generalised pustular psoriasis. Lancet. 1991 Aug 3;338(8762):320–321. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90464-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranges G. E., Sriram S., Cooper S. M. Prevention of type II collagen-induced arthritis by in vivo treatment with anti-L3T4. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):1105–1110. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter C., Kakavand B., Rieber E. P., Schattenkirchner M., Riethmüller G., Krüger K. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with monoclonal CD4 antibody M-T151. Clinical results and immunopharmacologic effects in an open study, including repeated administration. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 May;34(5):525–536. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldor M. K., Sriram S., Hardy R., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A., Lanier L., Lim M., Steinman L. Reversal of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis with monoclonal antibody to a T-cell subset marker. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):415–417. doi: 10.1126/science.3155574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wofsy D., Seaman W. E. Successful treatment of autoimmunity in NZB/NZW F1 mice with monoclonal antibody to L3T4. J Exp Med. 1985 Feb 1;161(2):378–391. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wraith D. C., McDevitt H. O., Steinman L., Acha-Orbea H. T cell recognition as the target for immune intervention in autoimmune disease. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):709–715. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90786-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Lambalgen R., Jonker M. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in rhesus monkeys: I. Immunological parameters in EAE resistant and susceptible rhesus monkeys. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Apr;68(1):100–107. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Lubbe P. A., Miltenburg A. M., Breedveld F. C. Anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody for relapsing polychondritis. Lancet. 1991 Jun 1;337(8753):1349–1349. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)93023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


