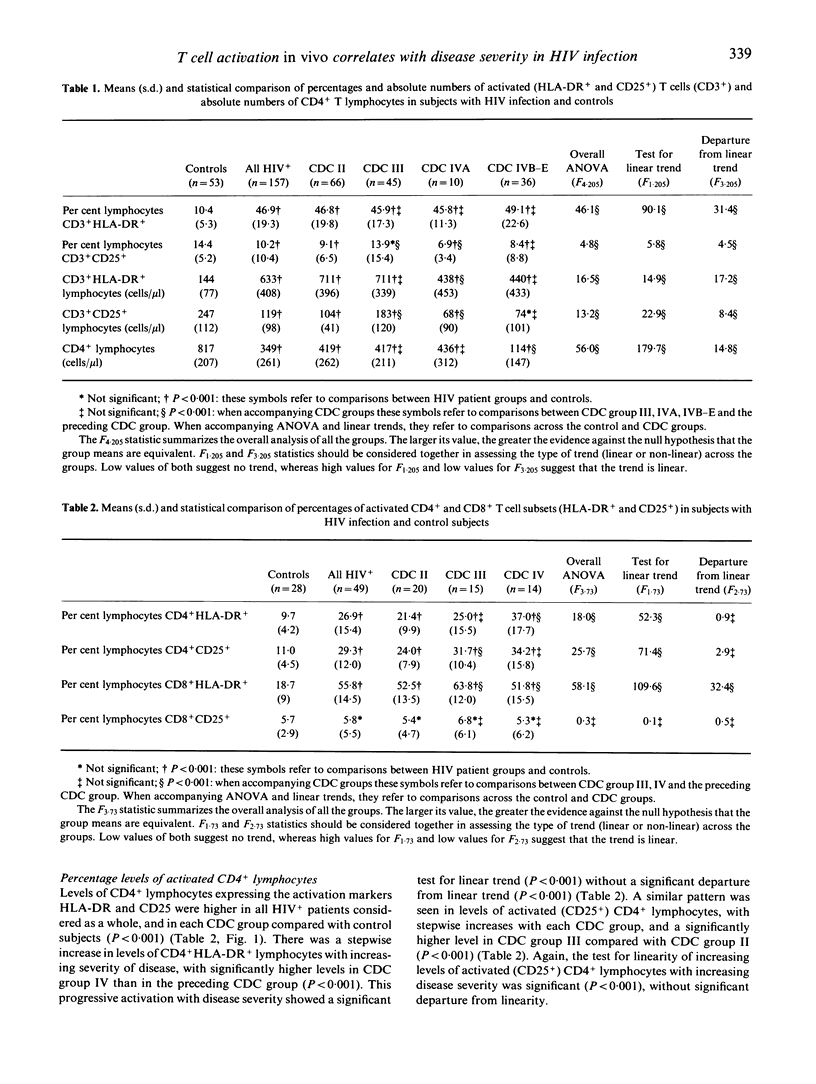
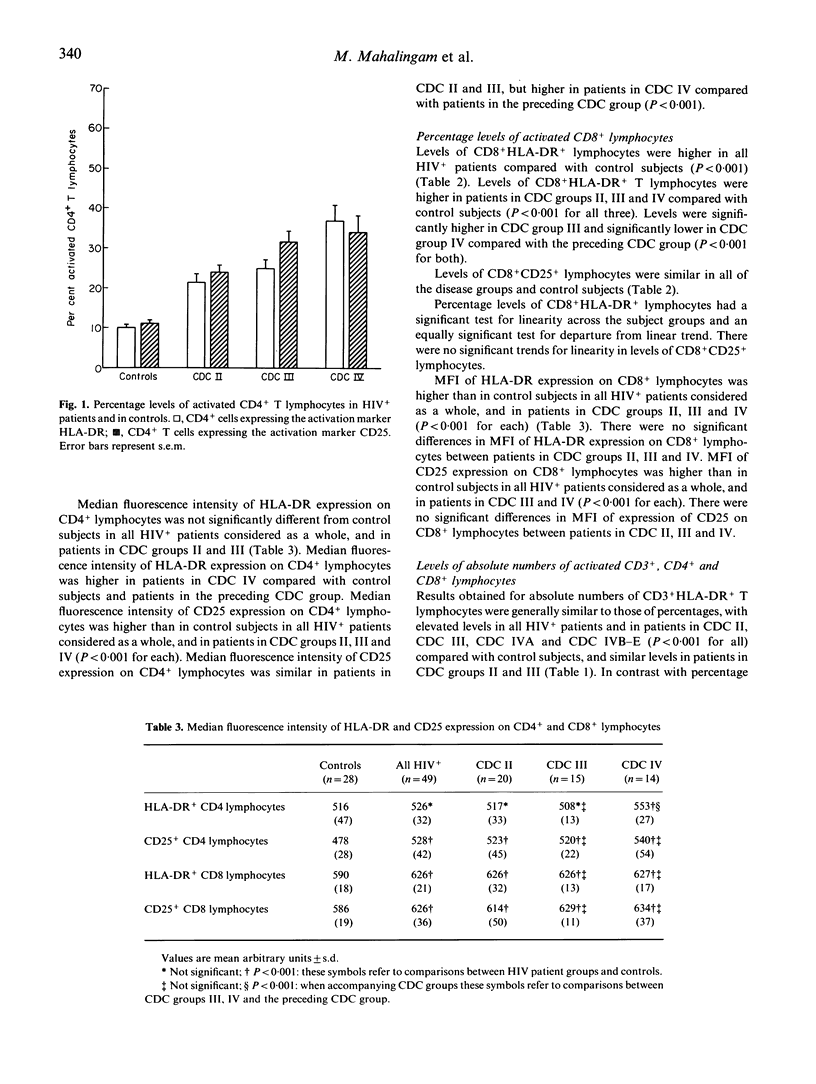
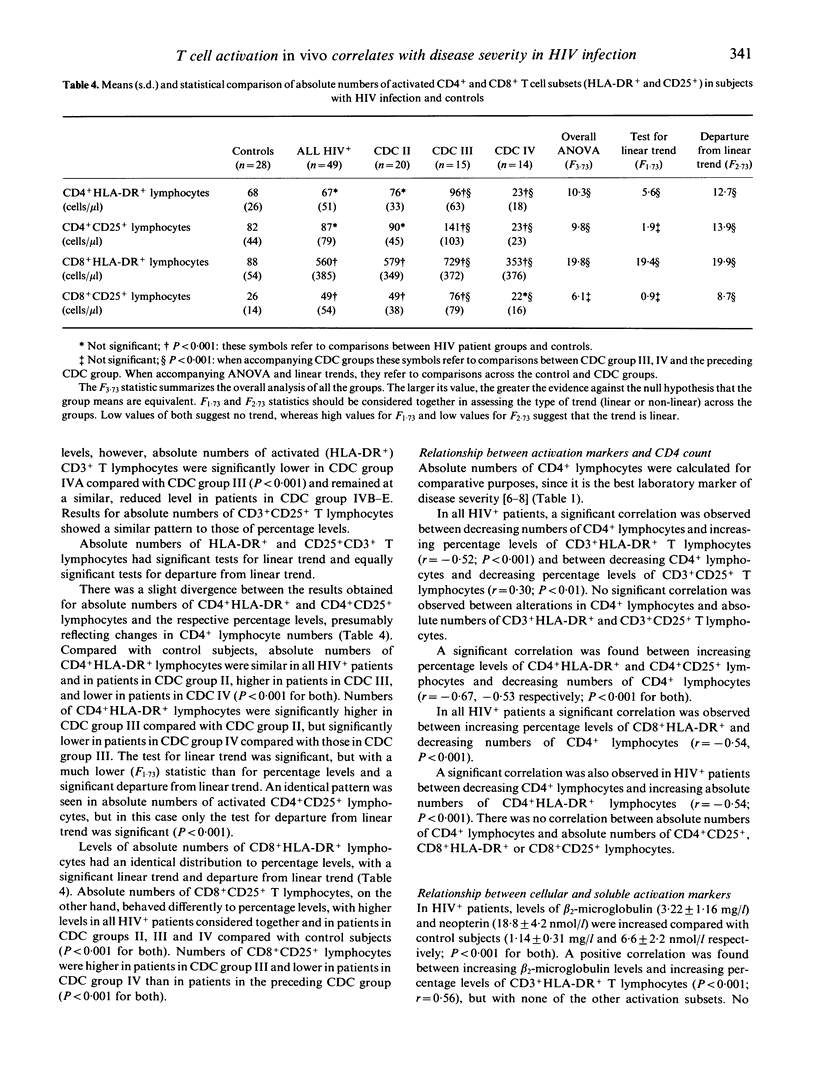
Abstract
In vitro studies have indicated that T lymphocyte activation may be of importance in the pathogenesis of HIV infection. In order to define the role of immune activation in vivo, we assessed the expression of the T cell activation markers HLA-DR and CD25 by flow cytometry in peripheral blood in relation to disease severity and the surrogate markers CD4 and beta 2-microglobulin in 157 patients with HIV infection and 53 healthy seronegative blood donors. Percentage levels of CD3+HLA-DR+ T lymphocytes were significantly higher (P < 0.0001) and percentage levels of CD3+CD25+ T lymphocytes significantly lower (P < 0.0001) in all HIV+ patients compared with controls. A significant correlation was observed between increasing percentage levels of CD3+HLA-DR+ T lymphocytes and both declining CD4 counts (r = 0.52; P < 0.001) and increasing beta 2-microglobulin levels (r = 0.56; P < 0.001). Percentage levels of CD4+HLA-DR+ and CD4+ CD25+ lymphocytes were significantly higher in all HIV+ patients compared with controls (P < 0.001). Levels of activated (HLA-DR+ and CD25+) CD4+ lymphocytes showed a significant step-wise linear increase with increasing disease severity (P < 0.001). High levels of CD3+HLA-DR+ T lymphocytes were found in a greater proportion (81.8%) of asymptomatic HIV+ patients (Centres for Disease Control (CDC) group II) than low CD4 counts (51.5%) (P < 0.001). Compared with controls, HIV+ patients had higher percentage levels of CD8+HLA-DR+ lymphocytes (P < 0.001), but similar levels of CD8+CD25+ lymphocytes. These results indicate that T cell activation is not only a consistent but also an early feature in HIV infection. Monitoring levels of activated T cells and their subsets is of value in assessing progression of HIV-related disease.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachelerie F., Alcami J., Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Virelizier J. L. HIV enhancer activity perpetuated by NF-kappa B induction on infection of monocytes. Nature. 1991 Apr 25;350(6320):709–712. doi: 10.1038/350709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D., Feinberg M. B. HIV revealed: toward a natural history of the infection. N Engl J Med. 1989 Dec 14;321(24):1673–1675. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198912143212409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gowda S. D., Stein B. S., Mohagheghpour N., Benike C. J., Engleman E. G. Evidence that T cell activation is required for HIV-1 entry in CD4+ lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):773–780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann B., Nishanian P., Fahey J. L., Esmail I., Jackson A. L., Detels R., Cumberland W. Serum increases and lymphoid cell surface losses of IL-2 receptor CD25 in HIV infection: distinctive parameters of HIV-induced change. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Nov;61(2 Pt 1):212–224. doi: 10.1016/s0090-1229(05)80025-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levacher M., Hulstaert F., Tallet S., Ullery S., Pocidalo J. J., Bach B. A. The significance of activation markers on CD8 lymphocytes in human immunodeficiency syndrome: staging and prognostic value. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Dec;90(3):376–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb05854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levacher M., Tallet S., Dazza M. C., Dournon E., Rouveix B., Pocidalo J. J. T activation marker evaluation in ARC patients treated with AZT. Comparison with CD4+ lymphocyte count in non-progressors and progressors towards AIDS. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Aug;81(2):177–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb03314.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackewicz C., Levy J. A. CD8+ cell anti-HIV activity: nonlytic suppression of virus replication. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Jun;8(6):1039–1050. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Mawle A., Cort S. P., Nicholson J. K., Cross G. D., Scheppler-Campbell J. A., Hicks D., Sligh J. Cellular tropism of the human retrovirus HTLV-III/LAV. I. Role of T cell activation and expression of the T4 antigen. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3151–3162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohagheghpour N., Chakrabarti R., Stein B. S., Gowda S. D., Engleman E. G. Early activation events render T cells susceptible to HIV-1-induced syncytia formation. Role of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):7233–7238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss A. R., Bacchetti P., Osmond D., Krampf W., Chaisson R. E., Stites D., Wilber J., Allain J. P., Carlson J. Seropositivity for HIV and the development of AIDS or AIDS related condition: three year follow up of the San Francisco General Hospital cohort. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1988 Mar 12;296(6624):745–750. doi: 10.1136/bmj.296.6624.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss A. R. Predicting who will progress to AIDS. BMJ. 1988 Oct 29;297(6656):1067–1068. doi: 10.1136/bmj.297.6656.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G. J. HIV. Tampering with transcription. Nature. 1991 Apr 25;350(6320):658–658. doi: 10.1038/350658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmond D. H., Shiboski S., Bacchetti P., Winger E. E., Moss A. R. Immune activation markers and AIDS prognosis. AIDS. 1991 May;5(5):505–511. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199105000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peakman M., Senaldi G., Foote N., McManus T. J., Vergani D. Naturally occurring soluble CD4 in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Infect Dis. 1992 May;165(5):799–804. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.5.799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips A. N., Lee C. A., Elford J., Janossy G., Kernoff P. B. The cumulative risk of AIDS as the CD4 lymphocyte count declines. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1992;5(2):148–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips A. N., Lee C. A., Elford J., Janossy G., Timms A., Bofill M., Kernoff P. B. Serial CD4 lymphocyte counts and development of AIDS. Lancet. 1991 Feb 16;337(8738):389–392. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91166-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince H. E., Czaplicki C. D. In vitro activation of T lymphocytes from HIV-seropositive blood donors. II. Decreased mitogen-induced expression of interleukin 2 receptor by both CD4 and CD8 cell subsets. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Aug;48(2):132–139. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90077-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivière Y., Blank V., Kourilsky P., Israël A. Processing of the precursor of NF-kappa B by the HIV-1 protease during acute infection. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):625–626. doi: 10.1038/350625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senaldi G., Peakman M., McManus T., Davies E. T., Tee D. E., Vergani D. Activation of the complement system in human immunodeficiency virus infection: relevance of the classical pathway to pathogenesis and disease severity. J Infect Dis. 1990 Dec;162(6):1227–1232. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.6.1227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler-Heitbrock H. W., Stachel D., Schlunk T., Gürtler L., Schramm W., Fröschl M., Bogner J. R., Riethmüller G. Class II (DR) antigen expression on CD8+ lymphocyte subsets in acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). J Clin Immunol. 1988 Nov;8(6):473–478. doi: 10.1007/BF00916953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zola H., Koh L. Y., Mantzioris B. X., Rhodes D. Patients with HIV infection have a reduced proportion of lymphocytes expressing the IL2 receptor p55 chain (TAC, CD25). Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Apr;59(1):16–25. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(91)90078-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


