Abstract
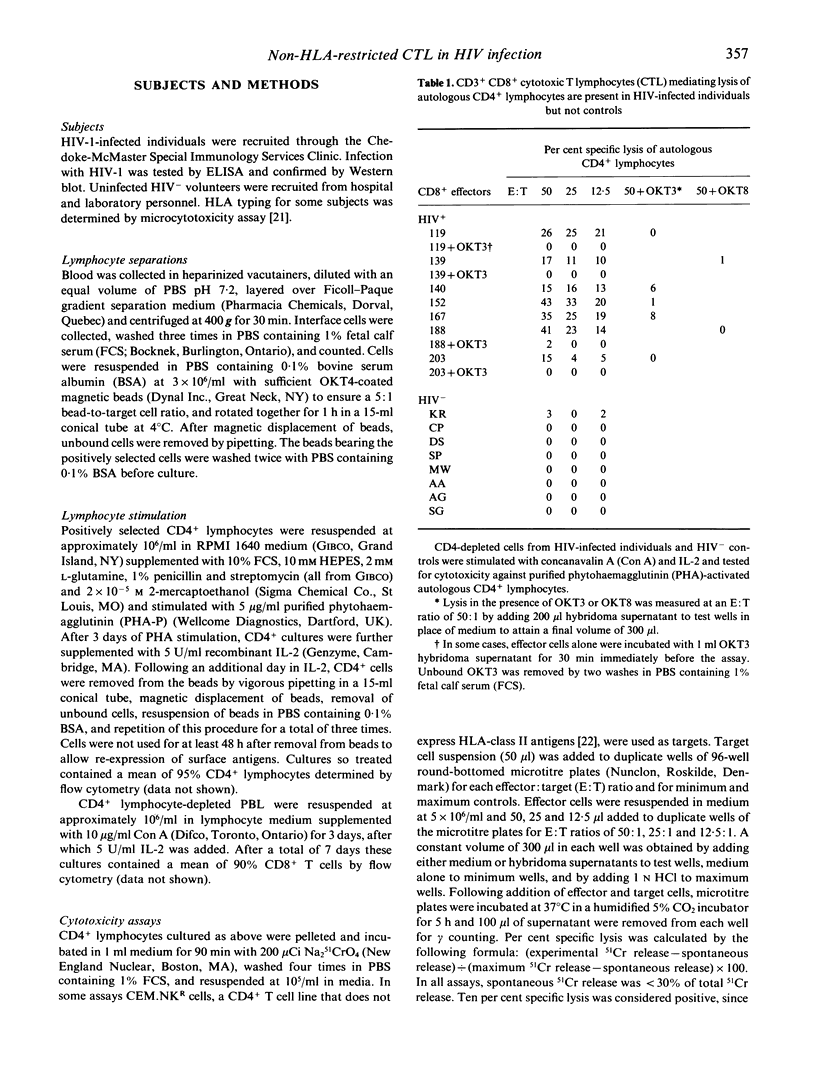
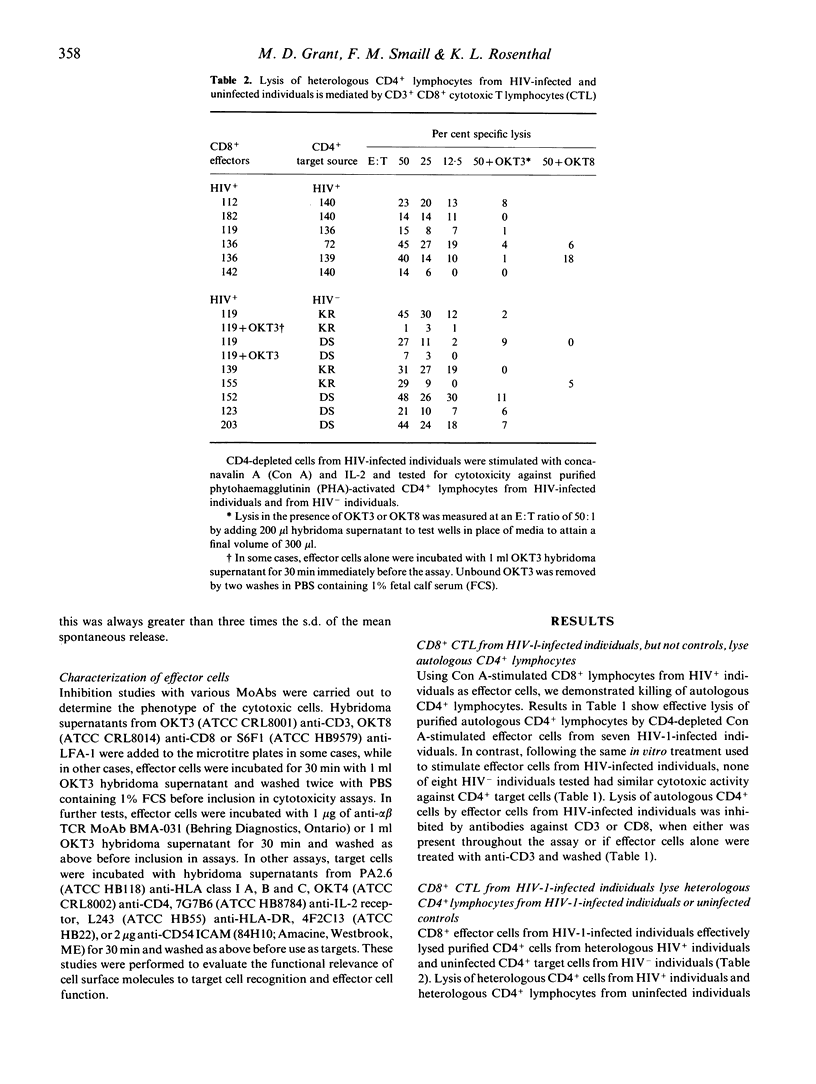
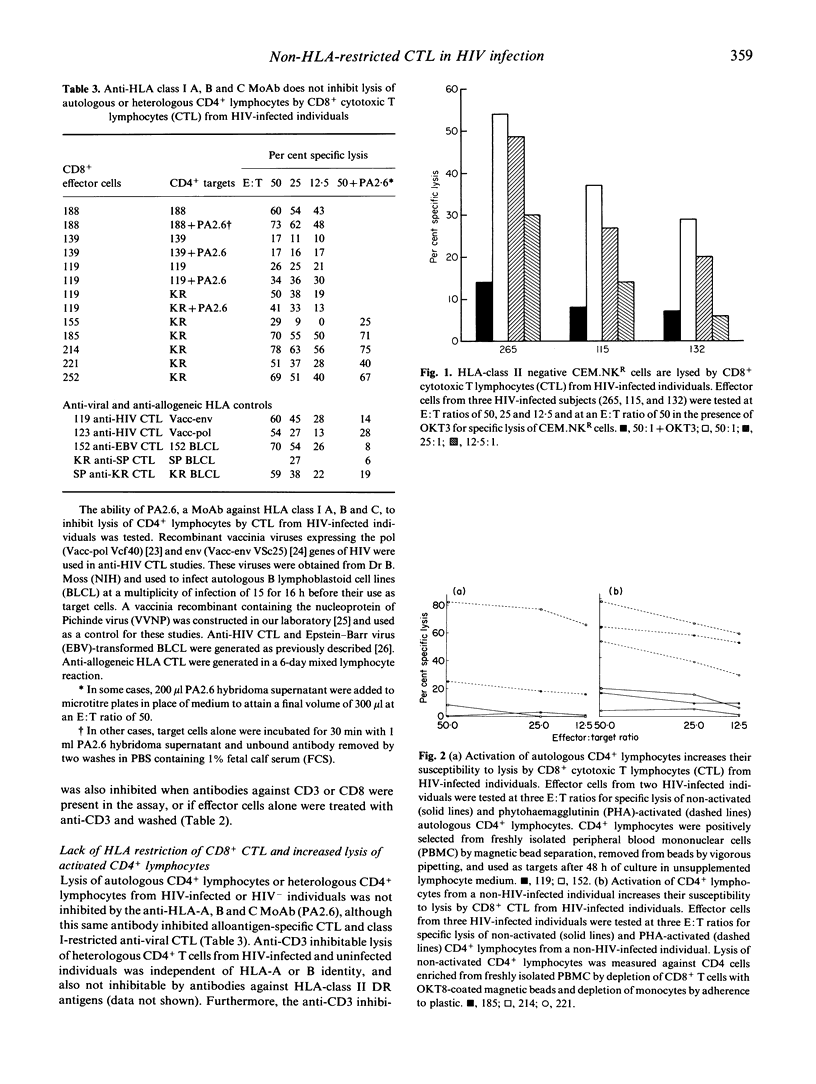
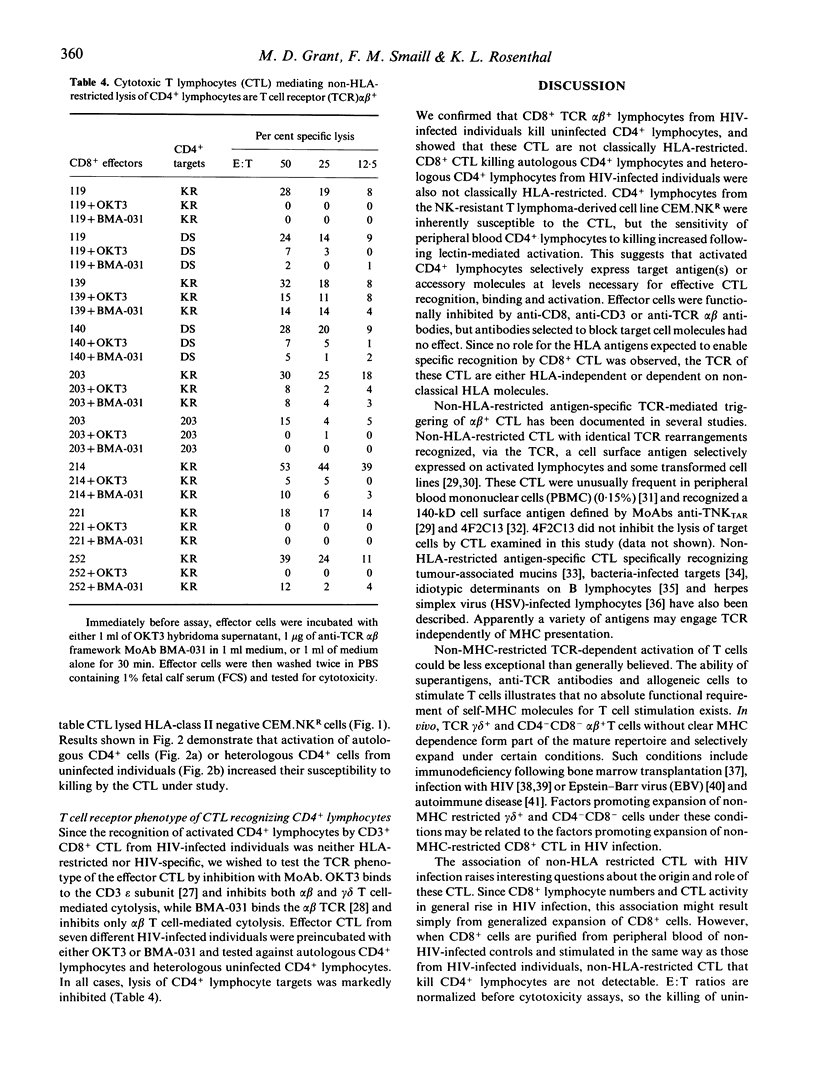
Individuals infected with HIV have elevated numbers of total and activated CD8+ lymphocytes in peripheral blood. CD8+ lymphocytes from HIV-infected individuals have been shown to mediate non-human histocompatibility-linked antigen (HLA)-restricted suppression of viral replication, HLA-restricted killing of cells expressing HIV antigens, and killing of uninfected lymphocytes. We studied CD8+ T lymphocytes that lysed autologous CD4+ lymphocytes. heterologous CD4+ lymphocytes from HIV-infected individuals and uninfected CD4+ lymphocytes. Killing in all cases required T cell receptor (TCR)-mediated recognition or triggering. However, these CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) killed HLA class I mismatched CD4+ lymphocytes and CD4+ lymphocytes treated with a MoAb against HLA-A, B and C antigens (PA2.6) which blocks HLA class I-restricted killing. HLA class II-negative CD4+ T lymphoma cells (CEM.NKR) were also killed by anti-CD3 inhibited CTL. Stimulation of peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) from HIV-infected individuals, but not uninfected controls, with concanavalin A (Con A) and IL-2, induced non-HLA-restricted TCR alpha beta+, CD8+ CTL which lysed CD4+ lymphocytes. Activation of CD4+ lymphocytes increased their susceptibility to CD8+ CTL-mediated lysis. In HIV infection, a population of non-HLA-restricted CTL which lyse activated CD4+ lymphocytes is expanded. The expansion of CTL with unusual characteristics is interesting, because the stimulus for this expansion is unknown. CTL which recognize activated CD4+ cells could play a role in immune regulation and the pathogenesis of AIDS.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. E., Shiboski S. C., Royce R., Jewell N. P., Lang W., Winkelstein W., Jr CD8+ T lymphocytes and progression to AIDS in HIV-infected men: some observations. AIDS. 1991 Feb;5(2):213–215. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199102000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Autran B., Mayaud C. M., Raphael M., Plata F., Denis M., Bourguin A., Guillon J. M., Debre P., Akoun G. Evidence for a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte alveolitis in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients. AIDS. 1988 Jun;2(3):179–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Autran B., Triebel F., Katlama C., Rozenbaum W., Hercend T., Debre P. T cell receptor gamma/delta+ lymphocyte subsets during HIV infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Feb;75(2):206–210. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnd D. L., Lan M. S., Metzgar R. S., Finn O. J. Specific, major histocompatibility complex-unrestricted recognition of tumor-associated mucins by human cytotoxic T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7159–7163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese L. H., Estes M., Yen-Lieberman B., Proffitt M. R., Tubbs R., Fishleder A. J., Levin K. H. Systemic vasculitis in association with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 May;32(5):569–576. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney W. P., Rubin R. H., Hoffman R. A., Hansen W. P., Healey K., Hirsch M. S. Analysis of T lymphocyte subsets in cytomegalovirus mononucleosis. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2114–2116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti S., Robert-Guroff M., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Moss B. Expression of the HTLV-III envelope gene by a recombinant vaccinia virus. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):535–537. doi: 10.1038/320535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Paoli P., Gennari D., Martelli P., Basaglia G., Crovatto M., Battistin S., Santini G. A subset of gamma delta lymphocytes is increased during HIV-1 infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Feb;83(2):187–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05612.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Paoli P., Gennari D., Martelli P., Cavarzerani V., Comoretto R., Santini G. Gamma delta T cell receptor-bearing lymphocytes during Epstein-Barr virus infection. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):1013–1016. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyster M. E., Gail M. H., Ballard J. O., Al-Mondhiry H., Goedert J. J. Natural history of human immunodeficiency virus infections in hemophiliacs: effects of T-cell subsets, platelet counts, and age. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Jul;107(1):1–6. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey J. L., Prince H., Weaver M., Groopman J., Visscher B., Schwartz K., Detels R. Quantitative changes in T helper or T suppressor/cytotoxic lymphocyte subsets that distinguish acquired immune deficiency syndrome from other immune subset disorders. Am J Med. 1984 Jan;76(1):95–100. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90756-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flexner C., Broyles S. S., Earl P., Chakrabarti S., Moss B. Characterization of human immunodeficiency virus gag/pol gene products expressed by recombinant vaccinia viruses. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):339–349. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90504-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi J. V., Detels R. T-cell subset alterations in HIV-infected homosexual men: NIAID Multicenter AIDS cohort study. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Jul;52(1):10–18. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90188-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant M. D., Smaill F. M., Singal D. P., Rosenthal K. L. The influence of lymphocyte counts and disease progression on circulating and inducible anti-HIV-1 cytotoxic T-cell activity in HIV-1-infected subjects. AIDS. 1992 Oct;6(10):1085–1094. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199210000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Hemler M. E., Mann D. L., Eisenbarth G. S., Shelhamer J., Mostowski H. S., Thomas C. A., Strominger J. L., Fauci A. S. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody (4F2) that binds to human monocytes and to a subset of activated lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1409–1414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hercend T., Meuer S., Brennan A., Edson M. A., Acuto O., Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F., Ritz J. Identification of a clonally restricted 90 kD heterodimer on two human cloned natural killer cell lines. Its role in cytotoxic effector function. J Exp Med. 1983 Nov 1;158(5):1547–1560. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.5.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hercend T., Schmidt R., Brennan A., Edson M. A., Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F., Ritz J. Identification of a 140-kDa activation antigen as a target structure for a series of human cloned natural killer cell lines. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Sep;14(9):844–852. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann E., Mayet W. J., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Fleischer B. MHC-unrestricted recognition of bacteria-infected target cells by human CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1992 Sep;143(2):253–260. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90023-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël-Biet D., Venet A., Beldjord K., Andrieu J. M., Even P. Autoreactive cytotoxicity in HIV-infected individuals. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Jul;81(1):18–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05285.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itescu S., Brancato L. J., Buxbaum J., Gregersen P. K., Rizk C. C., Croxson T. S., Solomon G. E., Winchester R. A diffuse infiltrative CD8 lymphocytosis syndrome in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection: a host immune response associated with HLA-DR5. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Jan 1;112(1):3–10. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-1-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jassoy C., Johnson R. P., Navia B. A., Worth J., Walker B. D. Detection of a vigorous HIV-1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte response in cerebrospinal fluid from infected persons with AIDS dementia complex. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 1;149(9):3113–3119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kestens L., Vanham G., Gigase P., Young G., Hannet I., Vanlangendonck F., Hulstaert F., Bach B. A. Expression of activation antigens, HLA-DR and CD38, on CD8 lymphocytes during HIV-1 infection. AIDS. 1992 Aug;6(8):793–797. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199208000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levacher M., Hulstaert F., Tallet S., Ullery S., Pocidalo J. J., Bach B. A. The significance of activation markers on CD8 lymphocytes in human immunodeficiency syndrome: staging and prognostic value. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Dec;90(3):376–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb05854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levacher M., Tallet S., Dazza M. C., Dournon E., Rouveix B., Pocidalo J. J. T activation marker evaluation in ARC patients treated with AZT. Comparison with CD4+ lymphocyte count in non-progressors and progressors towards AIDS. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Aug;81(2):177–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb03314.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maccario R., Revello M. G., Comoli P., Montagna D., Locatelli F., Gerna G. HLA-unrestricted killing of HSV-1-infected mononuclear cells. Involvement of either gamma/delta+ or alpha/beta+ human cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 15;150(4):1437–1445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavligit G. M., Talpaz M., Hsia F. T., Wong W., Lichtiger B., Mansell P. W., Mumford D. M. Chronic immune stimulation by sperm alloantigens. Support for the hypothesis that spermatozoa induce immune dysregulation in homosexual males. JAMA. 1984 Jan 13;251(2):237–241. doi: 10.1001/jama.251.2.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. J., Askonas B. A. Influenza virus-specific cytotoxic T cells in man; induction and properties of the cytotoxic cell. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Oct;8(10):705–711. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830081007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. E., Daul C. B., de Shazo R. D., Andes W. A., Hyslop N. H. T cells expressing high levels of non-major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-restricted cytotoxicity are present in early and late clinical phases of human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) infection. J Clin Immunol. 1989 Mar;9(2):97–102. doi: 10.1007/BF00916936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozols D. Y., Harnish D. G., Rawls W. E., Rosenthal K. L. Assessment of the specificity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes for the nucleoprotein of Pichinde virus using recombinant vaccinia viruses. Arch Virol. 1990;115(3-4):209–225. doi: 10.1007/BF01310531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen C., Dickmeiss E., Gaub J., Ryder L. P., Platz P., Lindhardt B. O., Lundgren J. D. T-cell subset alterations and lymphocyte responsiveness to mitogens and antigen during severe primary infection with HIV: a case series of seven consecutive HIV seroconverters. AIDS. 1990 Jun;4(6):523–526. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199006000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polk B. F., Fox R., Brookmeyer R., Kanchanaraksa S., Kaslow R., Visscher B., Rinaldo C., Phair J. Predictors of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome developing in a cohort of seropositive homosexual men. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jan 8;316(2):61–66. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198701083160201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince H. E., Arens L., Kleinman S. H. CD4 and CD8 subsets defined by dual-color cytofluorometry which distinguish symptomatic from asymptomatic blood donors seropositive for human immunodeficiency virus. Diagn Clin Immunol. 1987;5(4):188–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Hussey R. E., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody blocking human T cell function. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Oct;10(10):758–762. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830101006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. E., Bartley G. T., Lee S. S., Daley J. F., Royer H. D., Levine H., Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F., Ritz J. Expression of the NKTa clonotype in a series of human natural killer clones with identical cytotoxic specificity. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):812–825. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneller M. C., Straus S. E., Jaffe E. S., Jaffe J. S., Fleisher T. A., Stetler-Stevenson M., Strober W. A novel lymphoproliferative/autoimmune syndrome resembling murine lpr/gld disease. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):334–341. doi: 10.1172/JCI115867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terasaki P. I., Bernoco D., Park M. S., Ozturk G., Iwaki Y. Microdroplet testing for HLA-A, -B, -C, and -D antigens. The Phillip Levine Award Lecture. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Feb;69(2):103–120. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/69.2.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A. R., Rothbard J., Gotch F. M., Bahadur G., Wraith D., McMichael A. J. The epitopes of influenza nucleoprotein recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes can be defined with short synthetic peptides. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):959–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanham G., Kestens L., Gigase P., Colebunders R., Vandenbruaene M., Brijs L., Ceuppens J. L. Evidence for circulating activated cytotoxic T cells in HIV-infected subjects before the onset of opportunistic infections. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Oct;82(1):3–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05395.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanham G., Kestens L., Penne G., Goilav C., Gigase P., Colebunders R., Vandenbruaene M., Goeman J., van der Groen G., Ceuppens J. L. Subset markers of CD8(+) cells and their relation to enhanced cytotoxic T-cell activity during human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Clin Immunol. 1991 Nov;11(6):345–356. doi: 10.1007/BF00918800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilmer E., Guglielmi P., David V., Leca G., Rabian C., Degos L., Boiron M., Bensussan A. Predominant expression of circulating CD3+ lymphocytes bearing gamma T cell receptor in a prolonged immunodeficiency after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):755–761. doi: 10.1172/JCI113675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker B. D., Chakrabarti S., Moss B., Paradis T. J., Flynn T., Durno A. G., Blumberg R. S., Kaplan J. C., Hirsch M. S., Schooley R. T. HIV-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in seropositive individuals. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):345–348. doi: 10.1038/328345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C. M., Moody D. J., Stites D. P., Levy J. A. CD8+ lymphocytes can control HIV infection in vitro by suppressing virus replication. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1563–1566. doi: 10.1126/science.2431484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M. Regulation and role of large granular lymphocytes in arenavirus infections. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1987;134:185–209. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71726-0_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A., George A. J., King C. A., Stevenson F. K. Recognition of a B cell lymphoma by anti-idiotypic T cells. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 1;145(11):3937–3943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrightham M., Schimpf A., Pennington T. H., Walker F., Sewell H. F. HIV induces modulation of functionally important cellular antigens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jul;85(1):75–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05685.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi M. J., Joesten M. E., Wallace J., Roboz J. P., Bekesi J. G. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) genomic sequences and distinct changes in CD8+ lymphocytes precede detectable levels of HIV-1 antibodies in high-risk homosexuals. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jul;164(1):183–188. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling J. M., Ledbetter J. A., Sias J., Fultz P., Eichberg J., Gjerset G., Moran P. A. HIV-infected humans, but not chimpanzees, have circulating cytotoxic T lymphocytes that lyse uninfected CD4+ cells. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):2992–2998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. MHC-restricted cytotoxic T cells: studies on the biological role of polymorphic major transplantation antigens determining T-cell restriction-specificity, function, and responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:51–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


