Abstract
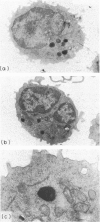
Large granular lymphocytes (LGL) were observed in the peripheral blood, spleen, lung and, to a lesser extent, bone marrow and lymph nodes, but not in the thymus of C3H/HeN mice 8 weeks old. The organ distribution of natural-killer (NK) cytotoxicity closely followed that of LGL. Nude mice had higher LGL percentages and NK activity than normal mice. In addition, the age distribution of LGL from the peripheral blood followed that of NK activity. Employing discontinuous Percoll density gradients the percentage of LGL and the NK cytotoxicity of the low density fractions could be enriched in comparison with the original populations of lymphocytes from peripheral blood and spleen, but not from thymus. These results suggest that, as recently shown for humans and rats, in mice too LGL are associated with NK activity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnaud-Battandier F., Bundy B. M., O'Neill M., Bienenstock J., Nelson D. L. Cytotoxic activities of gut mucosal lymphoid cells in guinea pigs. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1059–1065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy-Grand D., Griscelli C., Vassalli P. The mouse gut T lymphocyte, a novel type of T cell. Nature, origin, and traffic in mice in normal and graft-versus-host conditions. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1661–1677. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Holden H. T. Natural cell-mediated immunity. Adv Cancer Res. 1978;27:305–377. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani A., Luini W., Peri G., Vecchi A., Spreafico F. Effect of chemotherapeutic agents on natural cell-mediated cytotoxicity in mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978 Nov;61(5):1255–1261. doi: 10.1093/jnci/61.5.1255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puccetti P., Santoni A., Riccardi C., Herberman R. B. Cytotoxic effector cells with the characteristics of natural killer cells in the lungs of mice. Int J Cancer. 1980 Jan 15;25(1):153–158. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910250121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder J. C., Kiessling R., Biberfeld P., Andersson B. Target-effector interaction in the natural killer (NK) cell system. II. The isolation of NK cells and studies on the mechanism of killing. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2509–2517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudzik O., Bienenstock J. Isolation and characteristics of gut mucosal lymphocytes. Lab Invest. 1974 Mar;30(3):260–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliabue A., Mantovani A., Kilgallen M., Herberman R. B., McCoy J. L. Natural cytotoxicity of mouse monocytes and macrophages. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2363–2370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Saksela E., Ranki A., Häyry P. Fractionation, morphological and functional characterization of effector cells responsible for human natural killer activity against cell-line targets. Cell Immunol. 1979 Nov;48(1):133–148. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90106-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]