Abstract
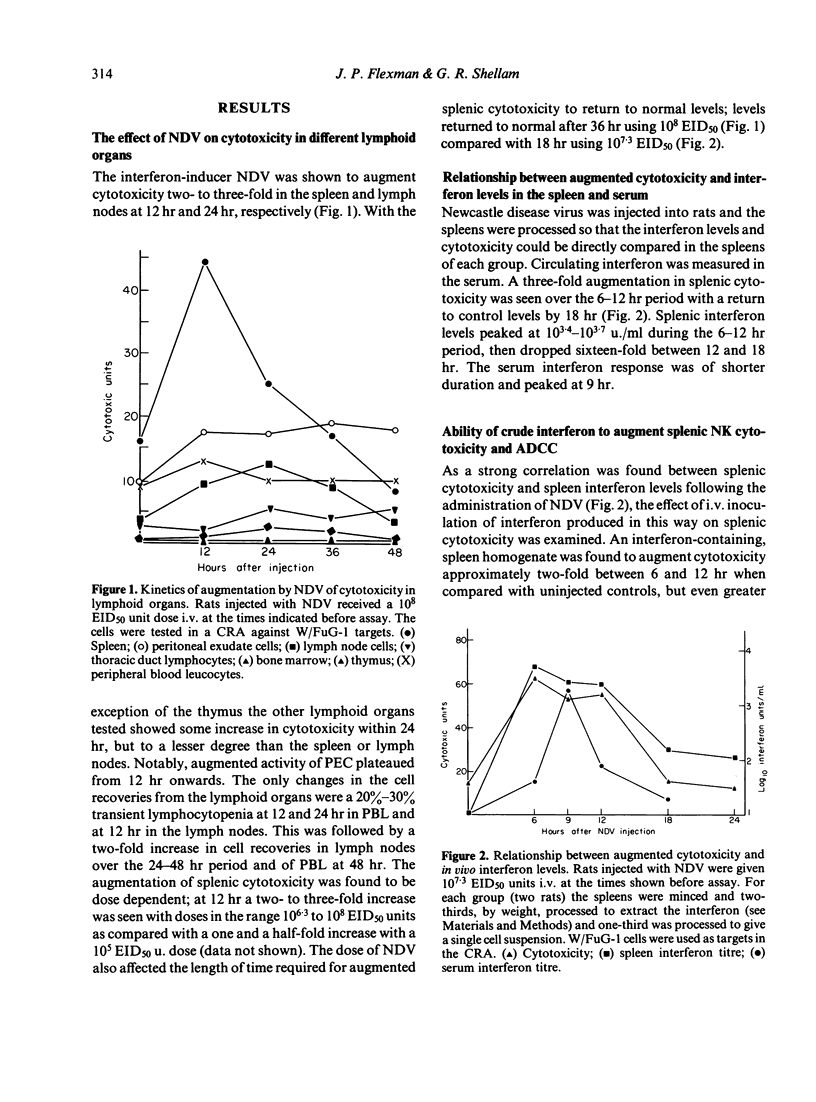
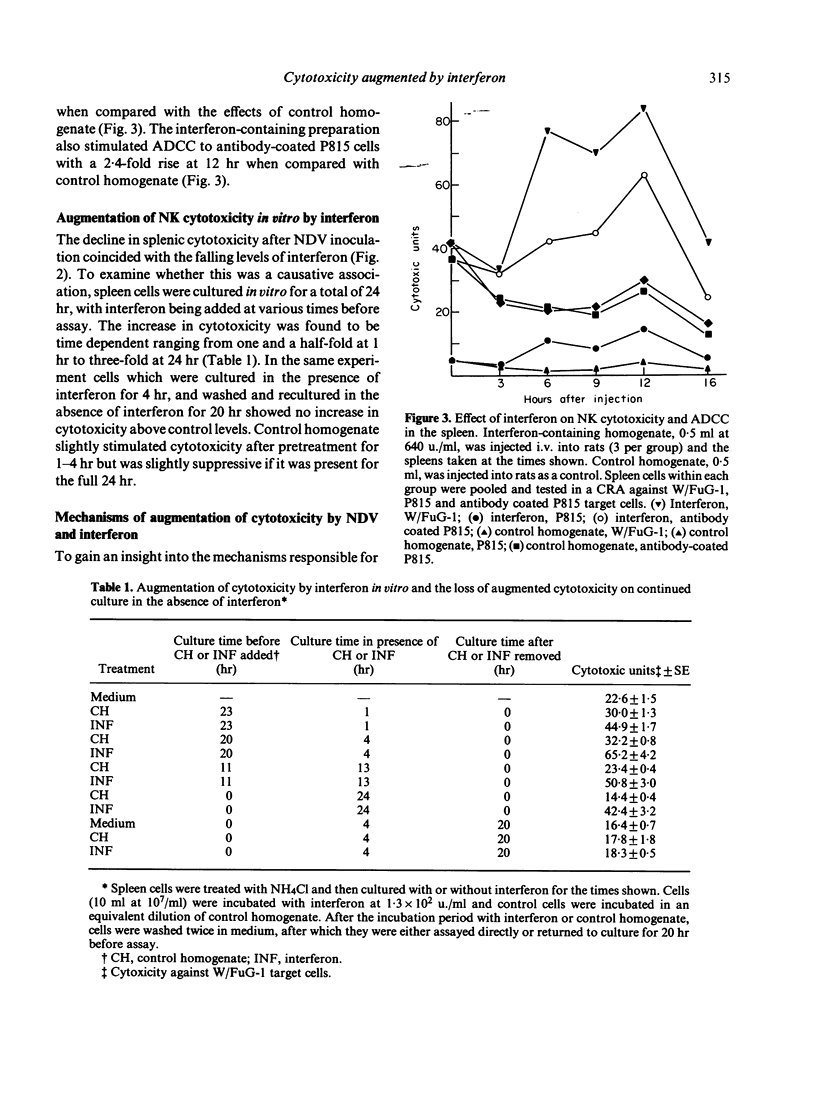
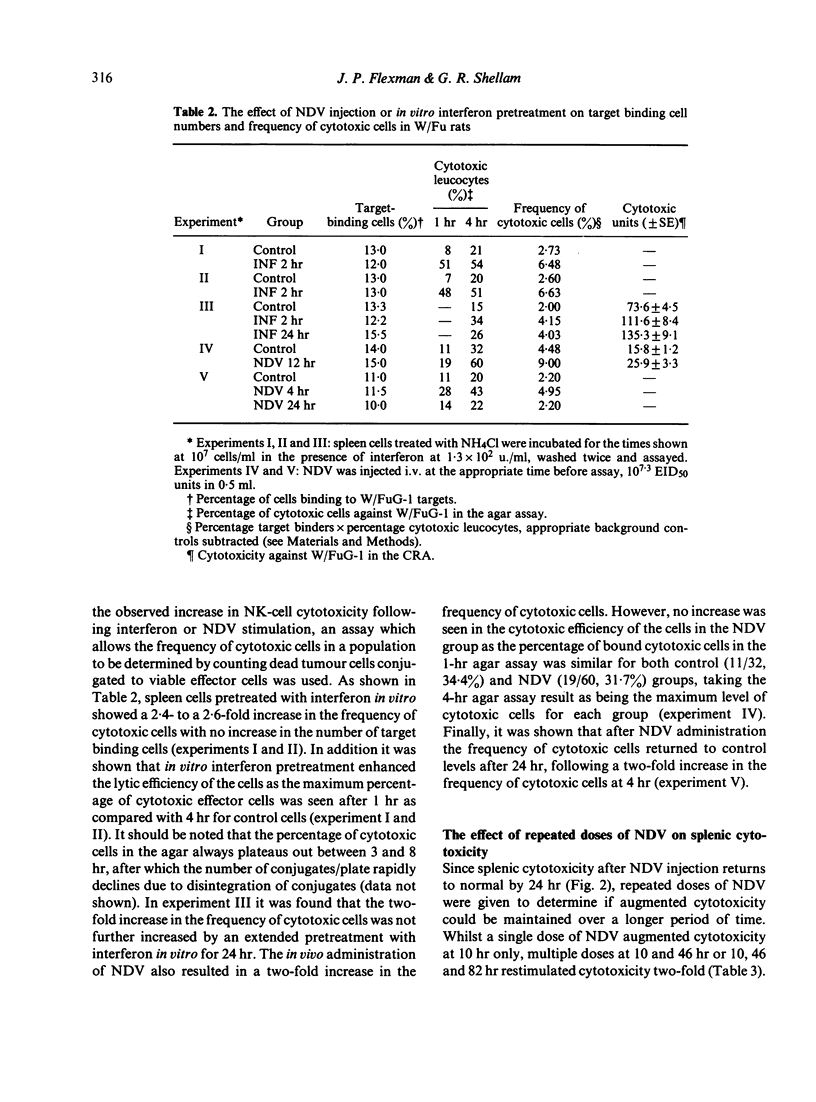
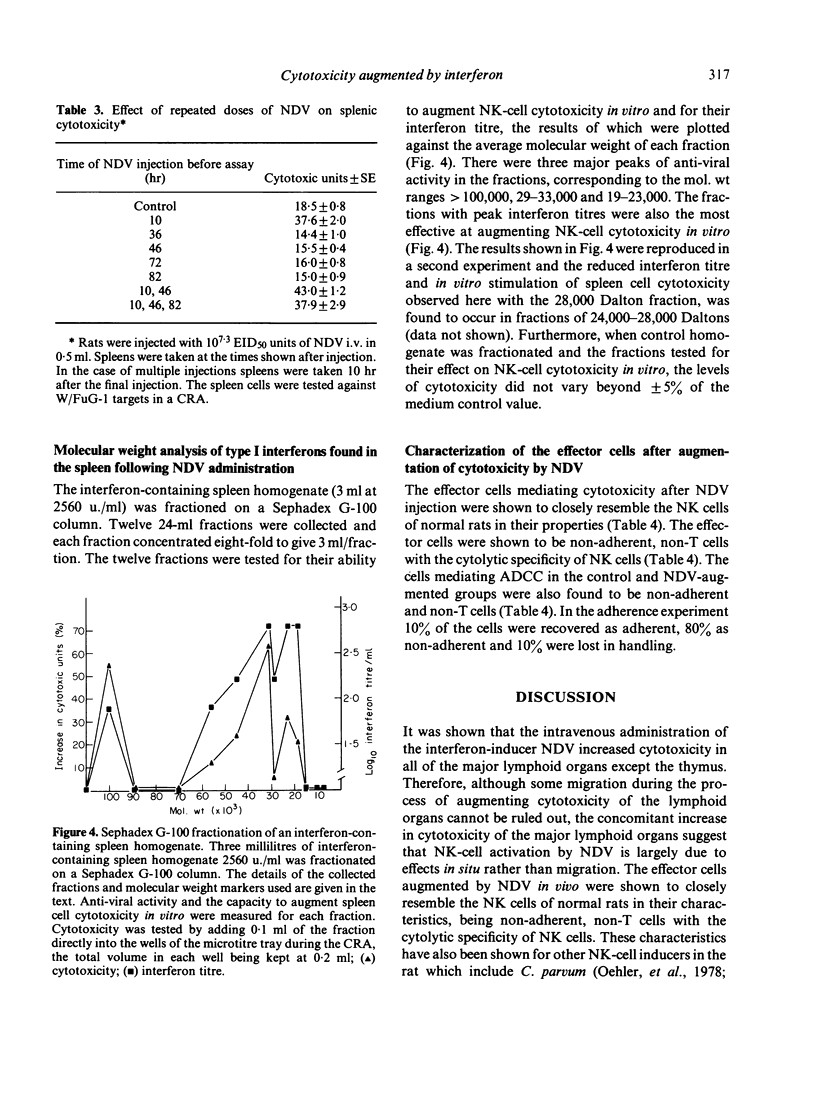
The interferon-induced Newcastle disease virus (NDV) was shown to augment cytotoxicity attributable to natural killer (NK) cells in all of the major lymphoid organs of W/Fu rats except the thymus. The levels of interferon isolated from the spleen following NDV inoculation correlated with the increase in splenic cytotoxicity from the same spleen. Spleen-derived interferon was shown to augment splenic cytotoxicity following intravenous inoculation, and to augment spleen cell cytotoxicity in vitro. Three major peaks of interferon type I were found in spleen homogenates corresponding to mol. wt of greater than 100,000, 29-33,000 and 19-23,000. All these fractions stimulated spleen cell cytotoxicity when tested in vitro. The rapid drop in splenic cytotoxicity 24 hr after NDV inoculation was associated with a rapid fall in interferon levels in vivo. The need for the continued presence of interferon for the stimulation of cytotoxicity was demonstrated when spleen cells pretreated with interferon for 4 hr in vitro lost their augmented cytotoxicity upon culturing for a further 20 hr in the absence of interferon. Although splenic cytotoxicity returned to control levels within 24 hr of a single 10(7.3) EID50 dose of NDV, repeated doses of NDV maintained augmented cytotoxicity over a longer period. Spleen cells either taken from rats injected with NDV or pretreated in vitro with interferon showed a two-fold increase in the number of cytotoxic cells bound to W/FuG-1 target cells, with no change in the target binding-cell numbers. However, only the cells pretreated with interferon showed an increase in lytic efficiency.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cudkowicz G., Hochman P. S. Do natural killer cells engage in regulated reactions against self to ensure homeostasis? Immunol Rev. 1979;44:13–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawkins H. J., Shellam G. R. Augmentation of cell-mediated cytotoxicity to a rat lymphoma. I. Stimulation of non-T-cell cytotoxicity in vivo by tumour cells. Int J Cancer. 1979 Aug;24(2):235–243. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910240216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djeu J. Y., Heinbaugh J. A., Holden H. T., Herberman R. B. Augmentation of mouse natural killer cell activity by interferon and interferon inducers. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):175–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djeu J. Y., Heinbaugh J. A., Holden H. T., Herberman R. B. Role of macrophages in the augementation of mouse natural killer cell activity by poly I:C and interferon. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):182–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djeu J. Y., Huang K. Y., Herberman R. B. Augmentation of mouse natural killer activity and induction of interferon by tumor cells in vivo. J Exp Med. 1980 Apr 1;151(4):781–789. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.4.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einhorn S., Blomgren H., Strander H. Interferon and spontaneous cytotoxicity in man. I. Enhancement of the spontaneous cytotoxicity of peripheral lymphocytes by human leukocyte interferon. Int J Cancer. 1978 Oct 15;22(4):405–412. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910220407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAZEKAS DE ST GROTH S., WHITE D. O. An improved assay for the infectivity of in influenza viruses. J Hyg (Lond) 1958 Mar;56(1):151–162. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400037621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidlund M., Orn A., Wigzell H., Senik A., Gresser I. Enhanced NK cell activity in mice injected with interferon and interferon inducers. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):759–761. doi: 10.1038/273759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Holden H. T. Natural cell-mediated immunity. Adv Cancer Res. 1978;27:305–377. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minato N., Reid L., Cantor H., Lengyel P., Bloom B. R. Mode of regulation of natural killer cell activity by interferon. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):124–137. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oehler J. R., Lindsay L. R., Nunn M. E., Holden H. T., Herberman R. B. Natural cell-mediated cytotoxicity in rats. II. In vivo augmentation of NK-cell activity. Int J Cancer. 1978 Feb 15;21(2):210–220. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910210213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojo E., Wigzell H. Natural killer cells may be the only cells in normal mouse lymphoid cell populations endowed with cytolytic ability for antibody-coated tumour target cells. Scand J Immunol. 1978 Apr;7(4):297–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela E., Timonen T., Cantell K. Human natural killer cell activity is augmented by interferon via recruitment of 'pre-NK' cells. Scand J Immunol. 1979;10(3):257–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb01348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoli D., Koprowski H. Mechanisms of activation of human natural killer cells against tumor and virus-infected cells. Immunol Rev. 1979;44:125–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00269.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senik A., Kolb J. P., Orn A., Gidlund M. Study of the mechanism for in vitro activation of mouse NK cells by interferon. Scand J Immunol. 1980;12(1):51–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shellam G. R. Gross-virus-induced lymphoma in the rat. V. Natural cytotoxic cells are non-T cells. Int J Cancer. 1977 Feb 15;19(2):225–235. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shellam G. R., Hogg N. Gross-virus-induced lymphoma in the rat. IV. Cytotoxic cells in normal rats. Int J Cancer. 1977 Feb 15;19(2):212–224. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shellam G. R., Winterbourn V., Dawkins H. J. Augmentation of cell-mediated cytotoxicity to a rat lymphoma. III. In vitro stimulation of natural killer cells by a soluble factor. Int J Cancer. 1980 Mar 15;25(3):331–339. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910250305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva A., Bonavida B., Targan S. Mode of action of interferon-mediated modulation of natural killer cytotoxic activity: recruitment of pre-NK cells and enhanced kinetics of lysis. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):479–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Targan S., Dorey F. Interferon activation of "pre-spontaneous killer" (pre-SK) cells and alteration in kinetics of lysis of both "pre-SK" and active SK cells. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2157–2161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey D. E. The requirement for macrophages in the augmentation of natural killer cell activity by BCG. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):840–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Santoli D. Anti-viral activity induced by culturing lymphocytes with tumor-derived or virus-transformed cells. Enhancement of human natural killer cell activity by interferon and antagonistic inhibition of susceptibility of target cells to lysis. J Exp Med. 1978 May 1;147(5):1314–1333. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.5.1314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Santoli D., Dee R. R., Knowles B. B. Anti-viral activity induced by culturing lymphocytes with tumor-derived or virus-transformed cells. Identification of the anti-viral activity as interferon and characterization of the human effector lymphocyte subpopulation. J Exp Med. 1978 May 1;147(5):1299–1313. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.5.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Jr Mouse natural killer cells: induction specificity, and function. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):1631–1635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


