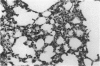
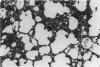
Abstract
The synthetic adjuvant, 6-0-mycoloyl-n-acetylmuramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine (mycol-MDP), is know to have a similar activity to the adjuvant moiety which resides in BCG cell walls (CW). Mycol-MDP plus a specific antigen, PPD, produced lung granulomata followed by anti-tuberculous protection in BCG CW high responder C57BL/6 (B6) mice, but not in low responder C3H/HeMs) (C3H) mice when a granuloma assay and an aerosol challenge with Mycobacterium bovis, Ravenel were carried out 4 weeks after the injection. However, when the granuloma assay and mycobacterial infection were performed 1 week after the injection, both B6 and C3H mice showed slight but definite lung granuloma formation accompanied by detectable protection. This suggested that the early development of granuloma was elicited by direct activation of macrophages with mycol-MDP. This possibility was confirmed since T-cell-deprived (B) mice produced lung granulomata 1 week after injection with mycol-MDP alone. However, contrary to our expectation, these B mice did not show anti-tuberculous protection. The role of T cells for anti-tuberculous immunity is discussed in relation to the adjuvant activity of mycol-MDP.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Audibert F., Heymer B., Gros C., Schleifer K. H., Seidl P. H., Chedid L. Absence of binding of MDP, a synthetic immunoadjuvant, to anti-peptidoglycan antibodies. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1219–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Congdon C. C., Morrison N. E. Growth of mycobacterium bovis (BCG) in T lymphocyte-depleted mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):57–64. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.57-64.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori K., Tanaka A. Granuloma formation by synthetic bacterial cell wall fragment: muramyl dipeptide. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):613–620. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.613-620.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Yamamoto K. I., Kakinuma M., Ishihara C., Azuma I. Suppression of BCG cell wall induced delayed-type hypersensitivity by BCG pre-treatment. I. Induction of adherent suppressor cells by live BCG injection and their characterization. Immunology. 1981 Feb;42(2):259–266. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore V. L., Mondloch V. M., Pedersen G. M., Schrier D. J., Allen E. M. Strain variation in BCG-induced chronic pulmonary inflammation in mice: control by a cyclophosphamide-sensitive thymus-derived suppressor cell. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):339–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. Importance of thymus-derived lymphocytes in cell-mediated immunity to infection. Cell Immunol. 1973 Apr;7(1):166–176. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher N. A., Chaparas S. D., Greenberg L. E., Merchant E. B., Vickers J. H. Response of congenitally athymic (nude) mice to infection with Mycobacterium bovis (strain BCG). J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Jun;54(6):1419–1426. doi: 10.1093/jnci/54.6.1419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya K., Nomoto K., Muraoka S., Shimotori S., Taniguchi T., Miyake T. Growth of two strains of Mycobacterium bovis (BCG) in athymic mice. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Jun;100(2):403–405. doi: 10.1099/00221287-100-2-403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., Yamazaki S., Someya S. Experimental mycobacterial infection in congenitally athymic "nude" mice. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1976 Feb;19(2):77–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Kakinuma M., Kato K., Okuyama H., Azuma I. Relationship of anti-tuberculous protection to lung granuloma produced by intravenous injection of synthetic 6-O-mycoloyl-N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine with or without specific antigens. Immunology. 1980 Aug;40(4):557–564. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Karinuma M. Genetic control of granuloma response to oil-associated BCG cell wall vaccine in mice. Microbiol Immunol. 1978;22(6):335–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1978.tb00378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]