Abstract
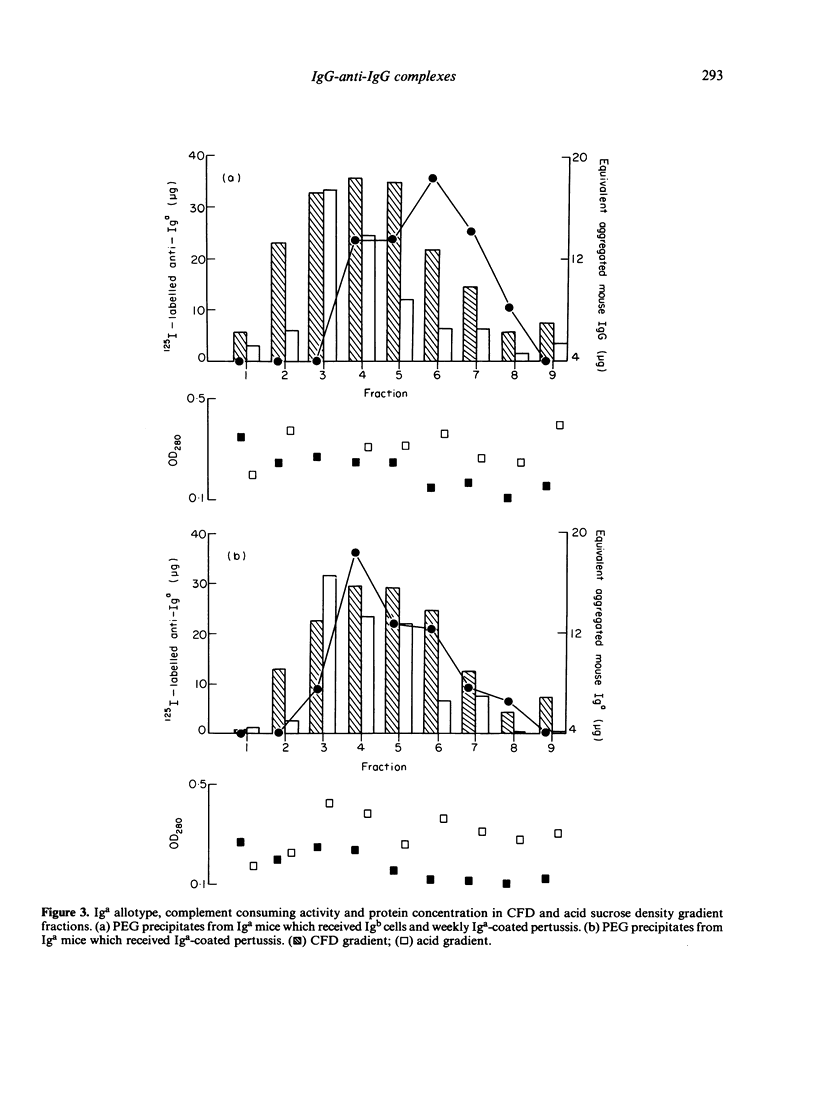
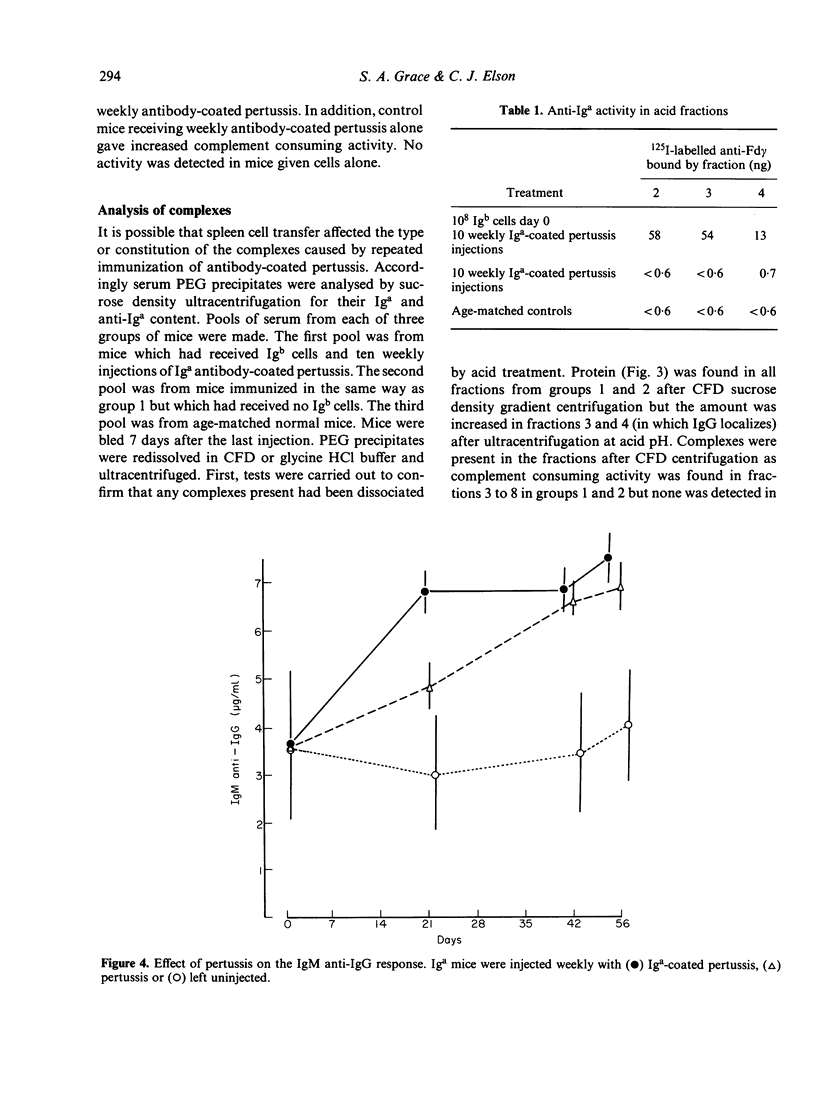
Weekly injection with antibody-coated pertussis led to the chronic production of serum complexes in mice. Mice bearing one allotype. Iga, received spleen cells from a congenic strain bearing another allotype, Igb, and weekly injections with Iga-coated pertussis. The serum complexes from these mice and from those receiving challenges alone were separated by ultracentrifugation at neutral and acid pH on sucrose density gradients and their fractions tested for their anti-Iga and Iga content. This revealed the presence of anti-host (Iga) allotype antibodies in fractions from mice that had received Igb cells but not from mice given Iga-coated pertussis alone. Iga allotype was detected in fractions from both groups. It is considered that anti-host allotype antibodies are continuously produced but that they cannot be detected in unfractionated serum because the antibody forms complexes with Iga. These findings are discussed in relation to rheumatoid disease in humans.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen C., Elson C. J., Scott D. G., Bacon P. A., Bucknall R. C. IgG antiglobulins in rheumatoid arthritis and other arthritides: relationship with clinical features and other parameters. Ann Rheum Dis. 1981 Apr;40(2):127–131. doi: 10.1136/ard.40.2.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dresser D. W. Most IgM-producing cells in the mouse secrete auto-antibodies (rheumatoid factor). Nature. 1978 Aug 3;274(5670):480–483. doi: 10.1038/274480a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dresser D. W., Popham A. M. Induction of an IgM anti-(bovine)-IgG response in mice by bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Nature. 1976 Dec 9;264(5586):552–554. doi: 10.1038/264552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. J., Jablonska K. F., Taylor R. B. Functional half-life of virgin and primed B lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Sep;6(9):634–638. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. J., Taylor R. B. The suppressive effect of carrier priming on the response to a hapten-carrier conjugate. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Oct;4(10):682–687. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830041009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grace S. A., Elson C. J., Coeshott C. M. Production of antibodies to host IgG after transfer of histocompatible cells primed to host allotype. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Feb;39(2):449–454. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harkiss G. D., Brown D. L. Detection of immune complexes by a new assay, the polyethylene glycol precipitation-complement consumption test (PEG-CC). Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Apr;36(1):117–129. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay F. C., Nineham L. J., Roitt I. M. Routine assay for detection of IgG and IgM antiglobulins in seronegative and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J. 1975 Jul 26;3(5977):203–204. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5977.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedberg H., Lundh B., Laurell A. B. Studies of the third component of complement in synovial fluid from arthritic patients. II. Conversion and its relation to total complement. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 May;6(5):707–712. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilter O. D., Turner M. W. Determination of IgG antiglobulins in rheumatoid disease using insolubilized human IgG. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Sep;15(1):93–101. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jablonska K. F. Autoagglutinin produced by organ fragment cultures of mouse spleen. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Nov;7(11):791–796. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830071109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNKEL H. G., MULLER-EBERHARD H. J., FUDENBERG H. H., TOMASI T. B. Gamma globulin complexes in rheumatoid arthritis and certain other conditions. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jan;40:117–129. doi: 10.1172/JCI104224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micklem H. S., Anderson N., Ure J., Jones H. P. Long-term immunoglobulin G production by transplanted thymus cells. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jun;6(6):425–429. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. G., Bacon P. A., Allen C., Elson C. J., Wallington T. IgG rheumatoid factor, complement and immune complexes in rheumatoid synovitis and vasculitis: comparative and serial studies during cytotoxic therapy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Jan;43(1):54–63. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg A. D., Huston D. P., Taurog J. D., Cowdery J. S., Ravecheé E. S. The cellular and genetic basis of murine lupus. Immunol Rev. 1981;55:121–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00341.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J. Etiopathogenesis of murine SLE. Immunol Rev. 1981;55:179–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrigiani G., Roitt I. M. Antiglobulin factors in sera from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and normal subjects. Quantitative estimation in different immunoglobulin classes. Ann Rheum Dis. 1967 Jul;26(4):334–340. doi: 10.1136/ard.26.4.334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Agnello V., Kunkel H. G. Gamma globulin complexes in synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Partial characterization and relationship to lowered complement levels. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 May;6(5):689–706. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


